Submitted:
14 February 2023
Posted:
17 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
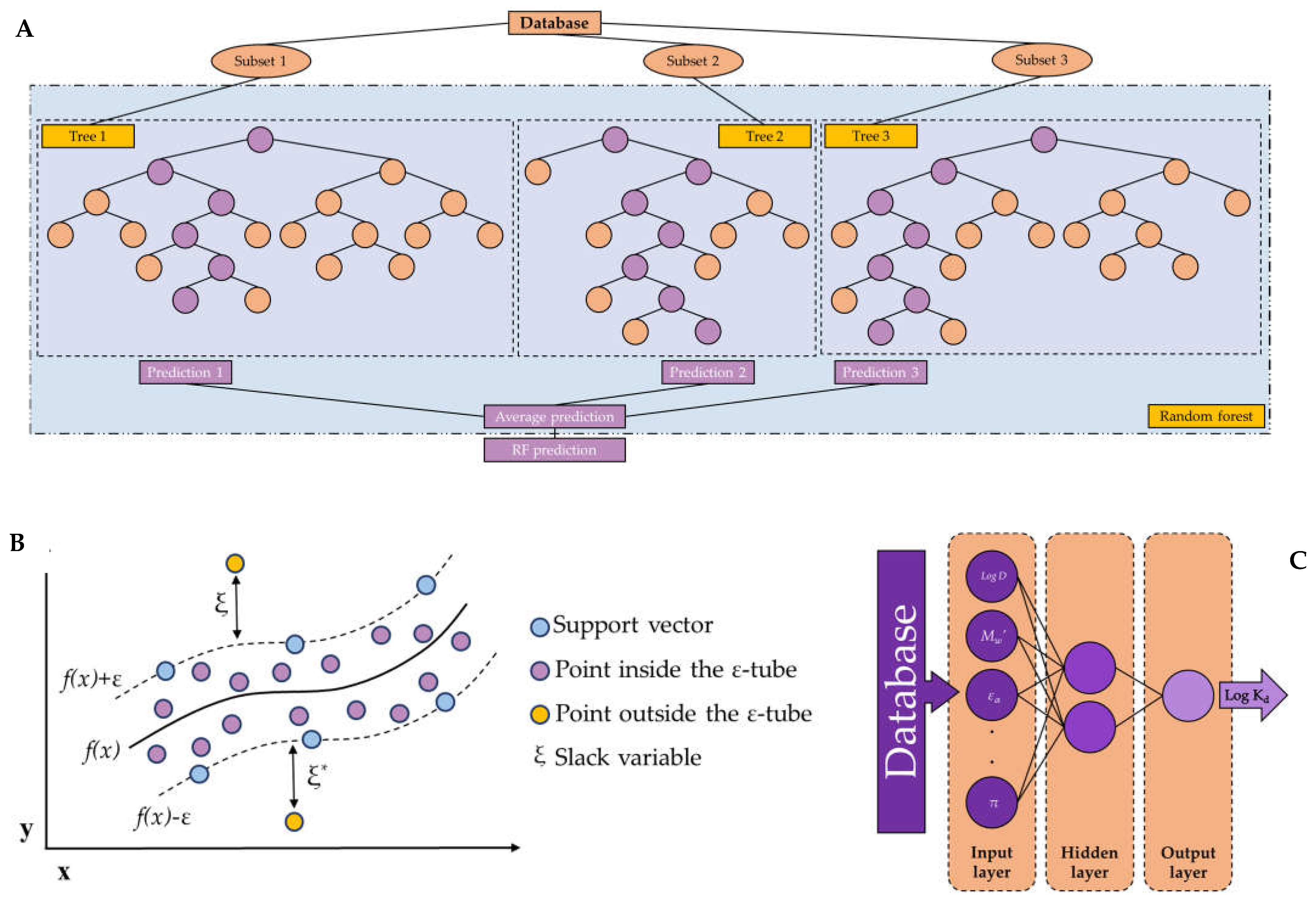
1.1. Random forest
1.2. Support vector machine
1.3. Artificial neural networks
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental data used
2.2. Models implemented
2.2.1. Random forest models
2.2.2. Support vector machine models
2.2.3. Artificial neural network models
2.2.4. Statistics used to analyze the models
2.2.5. Equipment and software used for the development of the models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ML models using input variables Type 1
| T | V | Z | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | RMSE | MAPE | r | RMSE | MAPE | r | RMSE | MAPE | r |
| PE/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.525 | 18.67 | 0.983 | 0.380 | 7.48 | 0.988 | 0.523 | 13.38 | 0.979 |
| SVM | 0.287 | 2.83 | 0.993 | 0.248 | 4.61 | 0.993 | 0.357 | 13.24 | 0.990 |
| ANN | 0.257 | 3.13 | 0.994 | 0.236 | 4.42 | 0.994 | 0.561 | 23.33 | 0.979 |
| PE/freshwater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.549 | 8.08 | 0.973 | 0.744 | 13.67 | 0.944 | 0.565 | 7.23 | 0.963 |
| SVM | 0.536 | 8.93 | 0.976 | 0.770 | 11.14 | 0.945 | 0.475 | 10.46 | 0.978 |
| ANN | 0.489 | 6.79 | 0.978 | 0.865 | 13.20 | 0.932 | 0.464 | 8.59 | 0.974 |
| PE/pure water - 1 | |||||||||
| RF | 0.471 | 11.28 | 0.968 | 0.176 | 3.31 | 0.992 | 0.531 | 9.48 | 0.929 |
| SVM | 0.356 | 5.93 | 0.974 | 0.132 | 2.06 | 0.993 | 0.411 | 6.90 | 0.958 |
| ANN | 0.309 | 4.92 | 0.981 | 0.225 | 3.92 | 0.982 | 0.729 | 12.21 | 0.937 |
| PE/pure water - 2 | |||||||||
| RF | 0.410 | 7.79 | 0.967 | 0.132 | 2.25 | 0.993 | 0.526 | 8.59 | 0.936 |
| SVM | 0.466 | 9.51 | 0.955 | 0.205 | 3.47 | 0.983 | 0.439 | 8.10 | 0.953 |
| ANN | 0.409 | 6.45 | 0.965 | 0.231 | 4.23 | 0.981 | 0.431 | 7.72 | 0.955 |
| PP/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.255 | 9.95 | 0.990 | 0.199 | 6.69 | 0.994 | 0.298 | 4.97 | 0.968 |
| SVM | 0.260 | 5.12 | 0.989 | 0.244 | 6.92 | 0.988 | 0.779 | 7.32 | 0.817 |
| ANN | 0.160 | 3.19 | 0.996 | 0.270 | 8.94 | 0.988 | 0.307 | 4.21 | 0.956 |
| PS/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.221 | 5.28 | 0.996 | 0.794 | 14.61 | 0.883 | 1.003 | 15.11 | 0.820 |
| SVM | 0.554 | 23.10 | 0.969 | 0.524 | 21.69 | 0.965 | 0.436 | 12.85 | 0.988 |
| ANN | 0.337 | 9.21 | 0.988 | 0.643 | 15.69 | 0.972 | 0.773 | 15.07 | 0.956 |
3.2. ML models using input variables Type 2
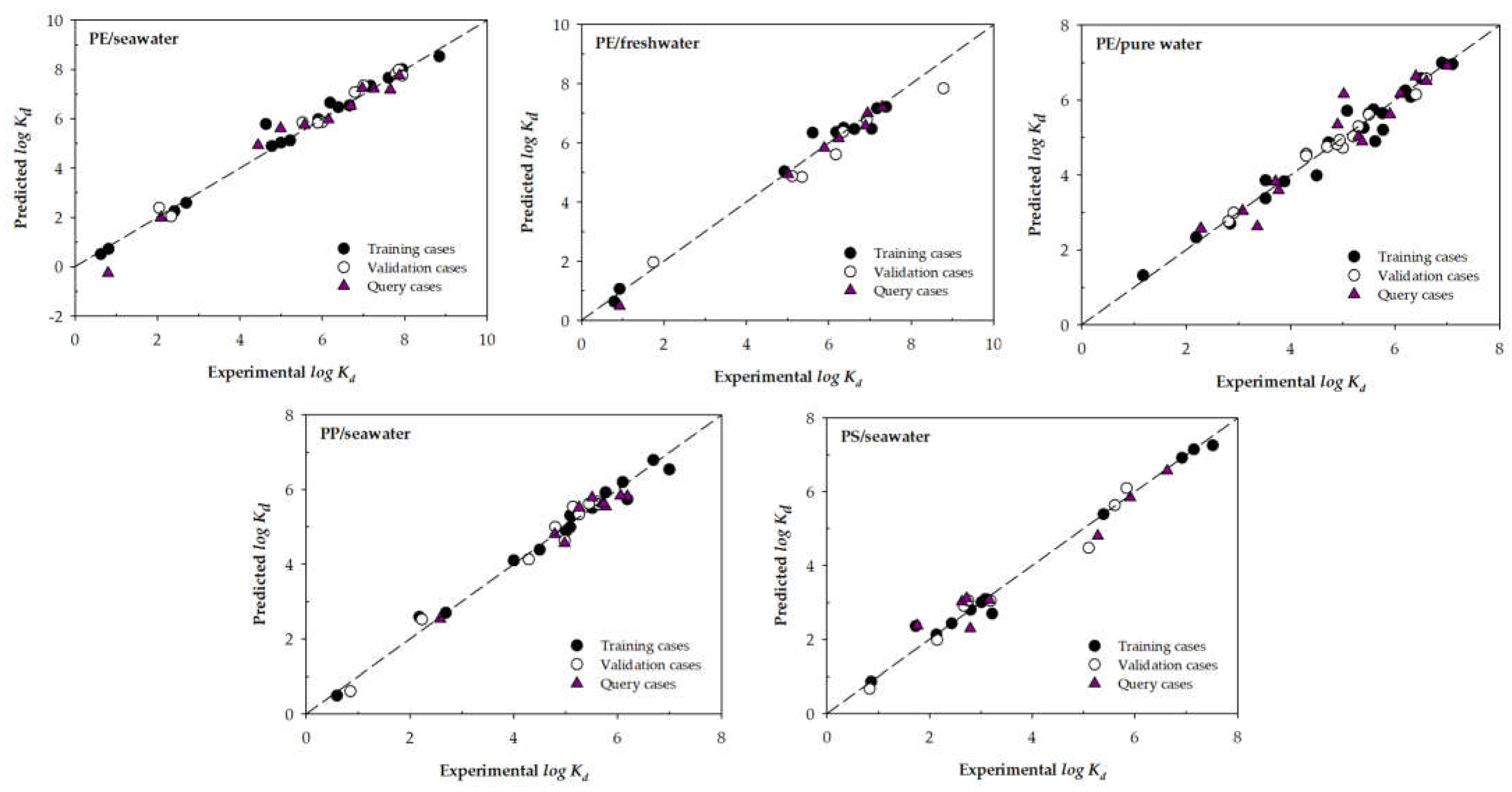
- Regardless of the input variables chosen, there is always some machine learning model that improves the adjustments of Li et al. (2020) (in terms of RMSE for the query phase).
- Including additional variables to develop the ML models does not always improve the variable selection carried out by Li et al. (2020). This is especially evident in the ML models destined to predict PE/seawater, where no model developed using the input variables selection Type 2 improves the models Type 1.
- To the best of the authors' knowledge, increasing the number of experimental cases for each microplastic/water group used to develop the models would be appropriate. Presumably, this increase would help the models present better adjustments.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Shim, J.E.; Park, I.H.; Choo, K.S.; Yeo, M.-K. Physical and Biomimetic Treatment Methods to Reduce Microplastic Waste Accumulation. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, K.K.; Dutta, S.; Banerjee, I.; Pohrmen, C.B.; Singh, R.K.; Das, H.T.; Dubey, S.; Kumar, V. Impact of Aquatic Microplastics and Nanoplastics Pollution on Ecological Systems and Sustainable Remediation Strategies of Biodegradation and Photodegradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar Naik, T.S.S.; Anil, A.G.; Dhiman, J.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Singh, J.; Ramamurthy, P.C. Micro (Nano) Plastics in Wastewater: A Critical Review on Toxicity Risk Assessment, Behaviour, Environmental Impact and Challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.-L.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Eldridge, S.M.; Johnston, P.; Hu, H.-W.; Geissen, V.; Chen, D. An Overview of Microplastic and Nanoplastic Pollution in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivekanand, A.C.; Mohapatra, S.; Tyagi, V.K. Microplastics in Aquatic Environment: Challenges and Perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, S.; Mai, L.; Jeong, C.-B.; Lee, J.-S.; Zeng, E.Y.; Xu, E.G. Key Mechanisms of Micro- and Nanoplastic (MNP) Toxicity across Taxonomic Groups. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 247, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.S.; Verones, F.; Jolliet, O.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Boulay, A.-M. A Framework for the Assessment of Marine Litter Impacts in Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peano, L.; Kounina, A.; Magaud, V.; Chalumeau, S.; Zgola, M.; Boucher, J. Plastic Leak Project, Methodological Guidelines; 2020.
- Ramachandraiah, K.; Ameer, K.; Jiang, G.; Hong, G.-P. Micro- and Nanoplastic Contamination in Livestock Production: Entry Pathways, Potential Effects and Analytical Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abihssira-García, I.S.; Kögel, T.; Gomiero, A.; Kristensen, T.; Krogstad, M.; Olsvik, P.A. Distinct Polymer-Dependent Sorption of Persistent Pollutants Associated with Atlantic Salmon Farming to Microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T. Addressing the Importance of Microplastic Particles as Vectors for Long-Range Transport of Chemical Contaminants: Perspective in Relation to Prioritizing Research and Regulatory Actions. Microplastics and Nanoplastics 2021, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Duan, Z.; Ruan, Y. Interaction of Microplastics and Nanoplastics with Natural Organic Matter (NOM) and the Impact of NOM on the Sorption Behavior of Anthropogenic Contaminants – A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumiti, A.; Losada-Carrillo, M.P.; Barros, M.; Cajaraville, M.P. Polystyrene Nanoplastics and Microplastics Can Act as Trojan Horse Carriers of Benzo(a)Pyrene to Mussel Hemocytes in Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Trojan Horse in the Intestine: A Review on the Biotoxicity of Microplastics Combined Environmental Contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, G.; Wei, X. QSPR Models for Predicting the Adsorption Capacity for Microplastics of Polyethylene, Polypropylene and Polystyrene. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathuria, C.; Mehrotra, D.; Misra, N.K. A Novel Random Forest Approach to Predict Phase Transition. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022, 13, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnek, A.; Baskin, I. Machine Learning Methods for Property Prediction in Chemoinformatics: Quo Vadis? J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1413–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduailij, M.; Khan, Q.W.; Tahir, M.; Sardaraz, M.; Alduailij, M.; Malik, F. Machine-Learning-Based DDoS Attack Detection Using Mutual Information and Random Forest Feature Importance Method. Symmetry (Basel). 2022, 14, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoufik, N.; Boumya, W.; Achak, M.; Chennouk, H.; Dewil, R.; Barka, N. The State of Art on the Prediction of Efficiency and Modeling of the Processes of Pollutants Removal Based on Machine Learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; He, X. Predictive Modeling of Groundwater Nitrate Pollution and Evaluating Its Main Impact Factors Using Random Forest. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, C.; Cetin, N. Prediction of Pistachio (Pistacia Vera L.) Mass Based on Shape and Size Attributes by Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Seok, C.; Lee, J. Prediction of Molecular Electronic Transitions Using Random Forests. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 5984–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random Forest: A Classification and Regression Tool for Compound Classification and QSAR Modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienefeld, C.; Kirchner, E.; Vogt, A.; Kacmar, M. On the Importance of Temporal Information for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings Using a Random Forest Regressor. Lubricants 2022, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.; Chang, M.W.L.; Chen, Y. Evaluation of Random Forests (RF) for Regional and Local-Scale Wheat Yield Prediction in Southeast Australia. Sensors 2022, 22, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geppert, H.; Vogt, M.; Bajorath, J. Current Trends in Ligand-Based Virtual Screening: Molecular Representations, Data Mining Methods, New Application Areas, and Performance Evaluation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Vogt, M.; Bajorath, J. Support Vector Machine Classification and Regression Prioritize Different Structural Features for Binary Compound Activity and Potency Value Prediction. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6371–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, H. Displacement Estimation of Six-Pole Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Using Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Support Vector Machine. Energies 2022, 15, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssein, E.H.; Hosney, M.E.; Oliva, D. A Hybrid Seagull Optimization Algorithm for Chemical Descriptors Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference (MIUCC); 2021; pp. 381–386.
- Sareminia, S. A Support Vector Based Hybrid Forecasting Model for Chaotic Time Series: Spare Part Consumption Prediction. Neural Process. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgeira-Crespo, P.; Míguez-Álvarez, C.; Cuevas-Alonso, M.; Doval-Ruiz, M.I. Decision Algorithm for the Automatic Determination of the Use of Non-Inclusive Terms in Academic Texts. Publications 2020, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Surges, C.J.C.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support Vector Regression Machines. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 1997; pp. 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A Tutorial on Support Vector Regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, T.H.; Shantha, M.; Pradeep, A.; Mohanan, P. Identification of Polar Liquids Using Support Vector Machine Based Classification Model. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2022, 11, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, K.; Huang, W. Self-Discharge Prediction Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Improved Support Vector Machine. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkorany, A.S.; Marey, M.; Almustafa, K.M.; Elsharkawy, Z.F. Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Support Vector Machines Optimized by Whale Optimization and Dragonfly Algorithms. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 69688–69699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazkar, H.R.; Niazkar, M. Application of Artificial Neural Networks to Predict the COVID-19 Outbreak. Glob. Heal. Res. Policy 2020, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Cheruku, S.; Reddy, N.S. The Role of Artificial Neural Networks in Prediction of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Composites—A Comprehensive Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3109–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Kaushik, A.C.; Ji, L.; Malik, S.I.; Ali, S.; Wei, D.-Q. Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction of Tuberculosis Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.E. Using the Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction and Validating Solar Radiation. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 2019, 27, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.; Pradhan, B.; Santosh, M. Artificial Neural Networks in Drought Prediction in the 21st Century–A Scientometric Analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 114, 108080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Baruah, R.D.; Singh, S.K.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Artificial Neural Networks in the Domain of Reservoir Characterization: A Review from Shallow to Deep Models. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 135, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer Feedforward Networks Are Universal Approximators. Neural Networks 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin-ike, K. A Two Phase Method for Determining the Number of Neurons in the Hidden Layer of a 3-Layer Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of SICE Annual Conference 2010; 2010; pp. 238–242.
- Ujong, J.A.; Mbadike, E.M.; Alaneme, G.U. Prediction of Cost and Duration of Building Construction Using Artificial Neural Network. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 23, 1117–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, K.; Zarafshan, P.; Khashehchi, M.; Pipelzadeh, E.; Chegini, G. Modeling and Predicting of Water Production by Capacitive Deionization Method Using Artificial Neural Networks. Desalination 2022, 540, 115992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.-F.; Yang, H.-T.; Chen, T.-T.; Guo, L.-P.; Leng, X.-Y.; Deng, P.-B.; Bi, J.; Pan, J.-G.; Wang, Y.-M. Artificial Neural Network-Genetic Algorithm-Based Optimization of Aerobic Composting Process Parameters of Ganoderma Lucidum Residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufnagl, B.; Steiner, D.; Renner, E.; Löder, M.G.J.; Laforsch, C.; Lohninger, H. A Methodology for the Fast Identification and Monitoring of Microplastics in Environmental Samples Using Random Decision Forest Classifiers. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagl, B.; Stibi, M.; Martirosyan, H.; Wilczek, U.; Möller, J.N.; Löder, M.G.J.; Laforsch, C.; Lohninger, H. Computer-Assisted Analysis of Microplastics in Environmental Samples Based on ΜFTIR Imaging in Combination with Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.-M.; Chang, D.-H.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.-D. Current Updates in Machine Learning in the Prediction of Therapeutic Outcome of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Should We Know? Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf Shirazi, A.; Frigaard, I. SlurryNet: Predicting Critical Velocities and Frictional Pressure Drops in Oilfield Suspension Flows. Energies 2021, 14, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldes, Ó.A.; Morales, J.; Cid, A.; Astray, G.; Montoya, I.A.; Mejuto, J.C. Electrical Percolation of AOT-Based Microemulsions with n-Alcohols. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cao, Z.; Murphy, A.; Qiao, Y. An Ensemble Machine Learning Method for Microplastics Identification with FTIR Spectrum. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifano, L.; Meiler, V.; Peter, R.; Fischerauer, G. Detection of Microplastics in Water Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy and Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the Sensors and Measuring Systems; 21th ITG/GMA-Symposium; 2022; pp. 356–359.
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM -- A Library for Support Vector Machines. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/ (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Hsu, C.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. A Practical Guide to Support Vector Classification. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Convolutional Neural Network for Soil Microplastic Contamination Screening Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. Projecting the Sorption Capacity of Heavy Metal Ions onto Microplastics in Global Aquatic Environments Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RapidMiner Documentation. Neural Net. Available online: https://docs.rapidminer.com/latest/studio/operators/modeling/predictive/neural_nets/neural_net.html (accessed on 17 October 2022).
| Model | Input variables | Model | Input variables | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log D | M'w | εα | εβ | qH+ | q- | V' | π | Log D | M'w | εα | εβ | qH+ | q- | V' | π | |||
| PE/seawater | PP/seawater | |||||||||||||||||
| Type 1 | Type 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Type 2 | Type 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| PE/freshwater | PS/seawater | |||||||||||||||||
| Type 1 | Type 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Type 2 | Type 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| PE/pure water | ||||||||||||||||||
| Type 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Type 1* | ||||||||||||||||||
| Type 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| T | V | Z | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | RMSE | MAPE | r | RMSE | MAPE | r | RMSE | MAPE | r |
| PE/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.824 | 38.89 | 0.954 | 0.373 | 7.69 | 0.988 | 0.693 | 26.80 | 0.970 |
| SVM | 0.336 | 5.52 | 0.991 | 0.243 | 5.22 | 0.994 | 0.443 | 16.38 | 0.984 |
| ANN | 0.040 | 0.56 | 1.000 | 0.306 | 5.46 | 0.989 | 0.762 | 15.28 | 0.946 |
| PE/freshwater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.424 | 16.78 | 0.991 | 0.697 | 8.78 | 0.962 | 0.392 | 11.86 | 0.986 |
| SVM | 0.320 | 6.87 | 0.991 | 0.473 | 7.05 | 0.990 | 0.210 | 8.18 | 0.999 |
| ANN | 0.289 | 4.94 | 0.992 | 0.446 | 7.10 | 0.991 | 0.272 | 10.40 | 0.997 |
| PE/pure water | |||||||||
| RF | 0.473 | 10.77 | 0.955 | 0.204 | 3.31 | 0.983 | 0.542 | 10.37 | 0.929 |
| SVM | 0.306 | 5.34 | 0.981 | 0.154 | 2.56 | 0.990 | 0.433 | 7.25 | 0.956 |
| ANN | 0.634 | 14.70 | 0.916 | 0.403 | 7.90 | 0.937 | 0.551 | 11.57 | 0.926 |
| PP/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.295 | 6.44 | 0.988 | 0.245 | 9.42 | 0.994 | 0.215 | 3.36 | 0.983 |
| SVM | 0.222 | 4.74 | 0.992 | 0.229 | 6.98 | 0.990 | 0.240 | 3.66 | 0.974 |
| ANN | 0.029 | 0.54 | 1.000 | 0.419 | 12.20 | 0.979 | 0.494 | 8.20 | 0.938 |
| PS/seawater | |||||||||
| RF | 0.486 | 11.07 | 0.980 | 0.475 | 15.16 | 0.970 | 0.873 | 23.01 | 0.882 |
| SVM | 0.248 | 4.72 | 0.994 | 0.290 | 8.50 | 0.986 | 0.385 | 12.05 | 0.976 |
| ANN | 0.309 | 7.01 | 0.990 | 0.445 | 9.74 | 0.984 | 0.407 | 12.43 | 0.973 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





