Introduction
Aging is a multifactorial and natural process that is associated with many physiological changes, functional disorders and behavioral capacity. Brain aging is considered an important aspect of the aging process because it plays a key role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease (1). Aging induces several physiological phenomena in the brain such as a reduction of the number of cerebral nerve cells, deterioration of tissue proteins, tissue atrophy, a slight decrease in the brain size, and reduction of cerebral blood flow (2). Several pathways cause brain aging, but the exact responsible molecular mechanisms are still unknown.
It has been wildly found that aging affects both angiogenesis and vascularization (3). Moreover, cerebral neurogenesis decreases with aging, causing a progressive cognitive decline (4). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) exerts both neurogenic and angiogenic functions (5). Studies indicate that VEGF-positive cells and microvessel density are decreased in the different brain regions of old rats, and exogenous VEGF may lead to an increase in vascular formation as well as a delay in the aging of the nervous system(6).
In addition to VEGF, which has a direct effect on the angiogenesis process, other factors such as transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) may indirectly mediate the angiogenesis process(7). TGF-β has different isoforms (TGF-β1, 2 and 3) that are inactively secreted from different tissues and organs. This multifunctional cytokine mediates various brain physiological and pathophysiological processes (8). TGF-β1 plays a crucial role in cell proliferation, differentiation, maturation and survival of various neuronal and non-neuronal cell types in the brain. Also, it regulates angiogenesis, neuroprotection, neuroimmune functions, neural regeneration and synaptic plasticity, which involve in cognitive functions (7). Increased TGF-β signaling in the brain with aging (9, 3) and many neurocognitive disorders (3) indicate that the pathology signaling pathway of TGF-β contributes to impaired neurogenesis in aging and dementia (7). TGF-β1 induces both pro and anti-inflammatory effects depending on the cell type, cytokine milieu and differentiation state of the responsible cells, and can exert positive and negative effects on adult neurogenesis (10). Due to the relationships between TGF-β1 signaling and aging, cellular senescence, and aging-associated disorders, it is important to find therapeutic approaches to better modulate this signaling for normal brain aging (7)
Oxidative stress is considered one of the main mechanisms of cellular aging. Due to the high concentration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and transition metals in brain tissue, it is very susceptible to oxidative damage (11). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are metabolic byproducts that levels of these oxidative stressors increase gradually whit aging, and can lead to irreversible damage to the cytoskeleton and the microtubular network, impairing mitochondrial function and damaging the central nervous system(12,13). Additionally, increasing cellular senescence and oxidative stress can cause inflammation, cell membrane damage and consequently neuronal death (14). The age-related oxidative brain impairment occurs due to lipid peroxidation products, protein oxidation, and oxidative alterations in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA (15).
During the aging process, apoptosis and susceptibility to apoptosis enhance in several types of intact cells (16). Apoptosis is programmed cell death that in two major regulatory intrinsic and extrinsic pathways induces neuronal death (14). The B cell leukemia/lymphoma 2(Bcl-2) family can regulate cell death in the central nervous system, and is related to apoptotic intrinsic pathway (17). The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and pro-apoptotic Bcl2 associated X protein (Bax) belong to Bcl-2 family, which have two distinct functional roles in cell death (14, 17). The loss of neuronal and glial cell populations is closely associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system (14) and motor neuron disability in neurodegenerative diseases (18). Apoptosis is traditionally considered an index of brain injury and contribute to various pathological conditions resulting in aging (1).
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is the most important neurotrophin in the brain that performs a neurotrophic function. BDNF exerts its biological actions through tyrosine receptor kinase B and plays a key role in regulating neuronal development, maintenance, survival and plasticity throughout life (1, 19). This neurotrophin influences the process of neurogenesis, and participates in both structural and functional neuroplasticity (14). Also, BDNF possesses other neuroprotective effects including anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidation, and suppression of autophagy (20). In the brain, BDNF is mainly synthesized in different types of cells and has a crucial role in learning and memory mechanisms (12). Studies have shown that BDNF decreased with normal brain aging and multiple brain disorders, indicating that a disorder of regulation of BDNF signaling is involved BDNF plays a crucial role in mental illness and neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (12, 21, and 22). Thus, drugs targeting BDNF signaling may be an effective neuroprotective agent for brain aging as well as neurodegenerative disorders.
It has already been demonstrated in the literature that curcumin, a lipophilic polyphenol compound derived from the rhizome of the plant Curcuma longa can enhance neuroprotection and is one of the most promising anti-aging natural compound (23, 24). In the previous study has shown that curcumin, exerts its neuroprotective and anti-aging effects in aged rat brain regions (25) and is able to can cross the blood–brain barrier (26). Curcumin has many pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-proliferative, and is nontoxic (24). Moreover, it has been shown that curcumin, may attenuate D galactose-induced brain aging via regulation of antioxidant enzymes and apoptosis (27). However, the ability of curcumin to improve normal brain aging by mediator factors in angiogenesis and neurogenesis has not been elucidated. In this study, we aimed to investigate the protective effect of curcumin on some factors involved in neurogenesis and angiogenesis in brain tissue of old rats.
Chemicals
Curcumin, all chemicals, and reagents for biochemical assays were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (USA). TBARS test kits were purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Brain BDNF, VEGF, TGF-β, BCl-2 and Bax were measured using a rat ELISA kit (Cusabio Biotech Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) from R & D Systems according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Animals and administration
Twenty-one healthy female Wistar rats that were 24 months old (body weight: 250–300 g) were purchased from the animal experiment center of Pasteur institute of Iran and were kept on a 12-hour light-dark cycle at a constant temperature (22 ± 2°C) and 50% humidity with food and water ad libitum. The animal experiment was carried out by the national Institutes of health's guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publications no. 80-23) revised in 1996 and approved by the Qaemshahar Branch, Islamic Azad University Animal Care (Approval No: 11768).
After one week of adaptation, the rats were randomly and equally assigned to three groups: 1) the control group received no treatment; 2) the sham group: rats underwent a sham operation and received an intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) of saline and 3) the Curcumin group: rats received curcumin (i.p., 30 mg/kg) for five days per week over eight weeks (28).
Preparation for brain samples
The rats were sacrificed after being anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine (60 mg/kg) and xylazine (5 mg/kg). The brains of the rats were carefully and quickly removed. Samples were homogenized in 0.05 M Tris-HCl buffer with protease inhibitors and then centrifuged at 4000g for 10 min. The supernatant was conserved at –80°C for subsequent experiments.
Biochemical analysis
The lipid peroxidation was measured using a thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) kit (Cayman Chemicals Co.). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed for BDNF, VEGF, TGF-β, BCl-2 and Bax (Cusabio Biotech Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Statistical analyses
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey test post hoc test for multiple comparisons among the groups. Data were analyzed using SPSS software v. 20.0. (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), and differences were taken to be statistically significant at P<0.05.
Lipid peroxidation and pro and anti-apoptosis factors findings
As shown in
Table 1, the curcumin-treated rats showed a significant attenuation in the lipid peroxidation as evidenced by the decreased level of TBARS compared with the control (19.16%, P<0.001) and saline (19.40%, P<0.001) groups. Furthermore, curcumin treatment up-regulated the level of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and reduced Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in the brains of aging rats, as compared to the control (22.59%, P=0.022; 34.69%, P<0.001, respectively) and saline (24.80%, P=0.012; 36.00%, P<0.001, respectively) groups, but had no significant effect on Bax protein.
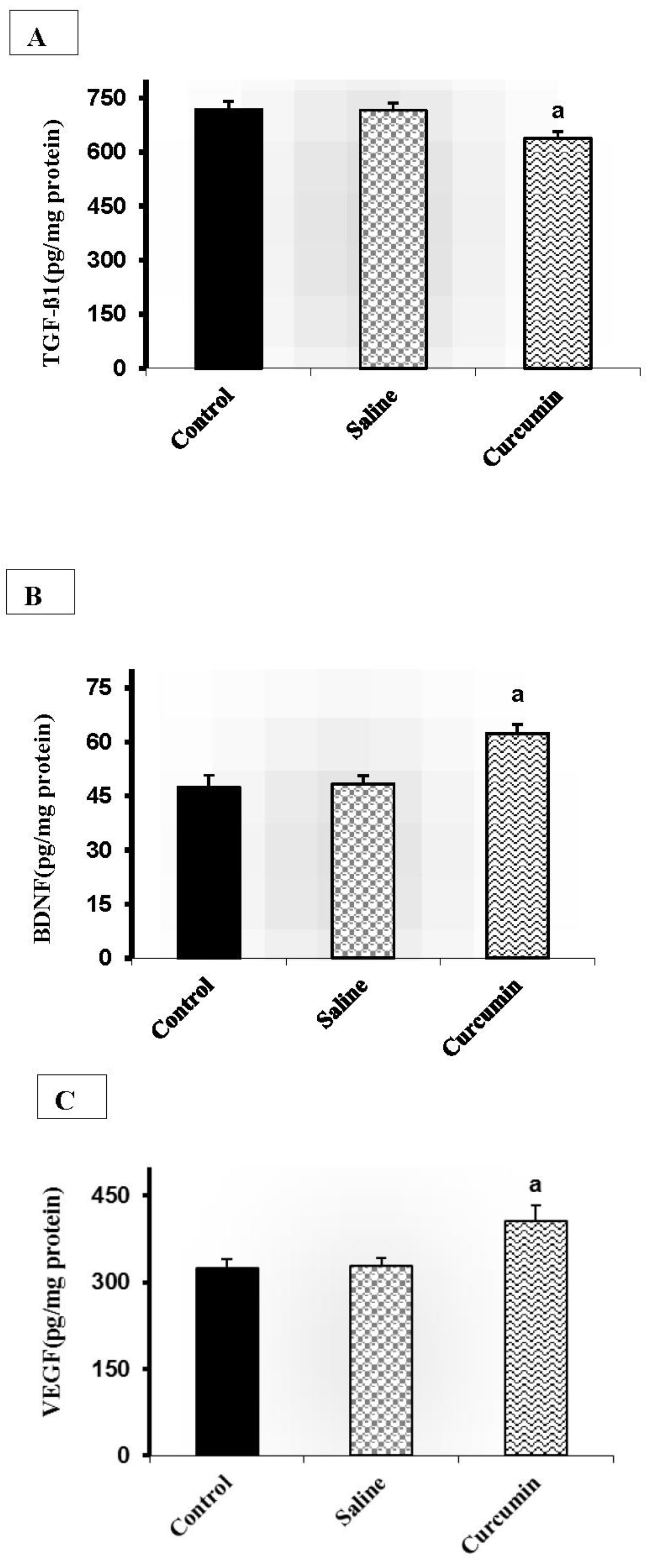
Findings of proteins involved in neurogenesis and angiogenesis
Figure 1 shows the effects of curcumin on the protein levels involved in neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the experimental groups. After curcumin treatment, the brain TGF-ß1 levels significantly decreased in the curcumin group when compared with the sham (11.25%, P<0.001) and control (10.92%, P<0.001) groups (
Figure 1A). Furthermore, eight weeks curcumin intervention significantly increased the levels of BDNF (
Figure 1B)and VEGF (
Figure 1C)proteins compared with the respective values in the control (31.70%, P<0.001; 25.13%, P<0.001, respectively), sham (29.22%, P<0.001; 12.34%, P<0.001, respectively) groups.
Discussion
The complex structural and molecular processes contribute to brain aging that led to a balance between protective and degenerative factors, and oxidative stress is known as one of the most important of these processes. Curcumin is a powerful antioxidant with anti-aging properties and neuroprotective effects via various molecular and cellular pathways. In the present study, we investigated the protective effects of curcumin on neurogenesis and angiogenesis pathways against the aging brain. The present findings demonstrated curcumin administration significantly decreased the lipid peroxidation and TGF-ß1 protein in brain tissue of old rats, suggesting that curcumin can alleviate oxidative damage in cellular senescence by enhancing the antioxidant capacity in the brains of aging rats (28, 29). Studies confirm the proinflammatory role of TGF-β in organ damage and diseases (30). TGF-β can regulate oxidative stress by inducing ROS production via the non-Smad pathway and suppressing antioxidant systems. Moreover, increased ROS and/or oxidative stress levels in turn may increment the bioavailability and activity of TGF-β. Thus oxidative stress as well as TGF- β can influence cellular senescence (31). As the brain ages, the production of neurotransmitters, ATP, cytokines, and ion changes in the local environment led to the switch of activation microglial cells to an activated phenotype, which could result in the increased brain TGF-β1 (32). TGF-β1 induced cerebrovascular dysfunction and neuroinflammation (33). It has been reported that the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin can improve spinal cord injury and suppress glial scar formation by inhibiting the generation of TGF-β1 and improving neural functionality by reducing in the expression of TGF-β1 (34, 35).
We found that chronic curcumin administration in old rats significantly increased the level of BCl-2 protein and decreased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in the brain, but was not accompanied by significant changes in the brain Bax protein level. These results suggest that curcumin can have a neuroprotective effect against neuronal apoptosis in old brain tissue by increasing the Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic protein, and failure to change protein Bax pro-apoptotic protein with curcumin treatment may be related to short treatment duration and/or dosage. Animal studies have demonstrated that pro- and anti-apoptosis factors were altered in the aged brain, with increased expression of BAX protein and a decrease in the Bcl-2 protein (1, 27, 29, 36). Moreover, the ratio of Bax to/ Bcl-2 is a crucial factor that determined the cellular response to death stimuli and the progress of cell apoptosis (1, 36) that decreased with the aging brain. It is well established that during aging, increased levels of mitochondrial ROS in higher animals and humans can activate apoptosis pathway, which is associated whit a decrease in the number of functioning cells (37). Similarly, recent studies have also reordered that administration of curcumin tended to regulate neuronal loss and suppress apoptosis in the cerebral cortex (27) and brain (38) by down-regulating Bax and increasing Bcl-2 expression through increasing antioxidant enzyme expression (27).
Moreover, our findings also demonstrated that curcumin administration caused an increase in BDNF and VEGF levels in the brain of old rats. These data provide further insights into the mechanisms underlying the improvement in brain health in normal aging. The up-regulation of VEGF and BDNF which are two key angiogenic and neurogenesis proteins may play a role in optimal brain aging. This is in line with an earlier report showing that oral treatment with curcumin (300 mg/, daily for 3 weeks), increased the levels of BDNF in the hippocampus of D-galactose-induced aged mice (39). Franco-Robles et al. (40) found that curcumin supplementation (50mg/kg, daily for 8 weeks) improved or restored BDNF levels to normal levels in diabetic db/db mice. Another study, has shown that treatment with curcumin significantly reversed the chronic unpredictable stress-induced decreased hippocampal BDNF levels in stressed rats (41). These observations confirm that the protective effect of curcumin on the aging brain occurs in part through enhancing the BDNF level, while the effect of curcumin on VEGF levels in the old brain remains unclear, and it can be considered one of the limitations of this study. Due to the involvement of the VEGF gene family in neuroprotection through multiple biological pathways, conflicting results have been reported for changes in VEGF during brain aging and brain disease. (42, 43). Accumulated evidence has indicated that the mRNA and protein expression of VEGF is reduced in the hippocampus and cortex of the amyloid beta-injected rats (44, 45), and increasing age is associated whit a decrease in VEGF levels in normal healthy brains (43, 46). Besides, studies reported treadmill exercise for 4 weeks increased the reduced mRNA expression level of VEGF in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease rats (45) and age-dependent loss of VEGF is reversed by physical exercise (46). Curcumin prevents amyloid-β aggregation, and after crossing the blood-brain barrier exerts its protective effect on neurons against toxic insults of aging and amyloid beta in humans (47). It seems that this curcumin's functional properties are in part related to up-regulation VEGF, which counteracts amyloid-β-induced morphological alteration synaptic dysfunction (48). It has been reported an age-related decline of VEGF in the brain and cerebral angiogenesis (49, 50) may lead to inhibition of apoptosis following brain injury (51). In addition, elevated cerebrospinal fluid VEGF can improve optimal brain aging (52). Both BDNF and VEGF exert angiogenic and neurotrophic effects via binding to their tyrosine kinase receptors (TrkB and Flk-1, respectively), BDNF can stimulate the formation of new vessels by releasing VEGF-mediated angiogenesis (53, 54). Furthermore, neurogenesis occurs in proximity to blood vessels with high VEGF expression, and the production and release of BDNF enhance the new vasculature (55).
Additionally, further studies are needed to explore the effect of curcumin on VEGF in brain aging and to determine the safe dose of curcumin and its optimal administration, especially during aging.
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that curcumin significantly alleviated brain aging in the old rats. The protective effects may be mediated, at least partly, through reducing the oxidative damage, enhancing the Bcl-2 protein, downregulating the levels of TGF-β1, and enhancing BDNF and VEGF proteins in brain aging. These results imply that curcumin could improve age-induced apoptosis, neurogenesis and angiogenesis changes, and suggested that curcumin had the potential to be used as a novel nutrient for preventing brain aging and age-related diseases.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu W, Wang X, Xiang Q, Meng X, Peng Y, Du N, Liu Z, Sun Q, Wang C, Liu X. Astaxanthin alleviates brain aging in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and increasing BDNF levels. Food Funct. 2014 Jan;5(1):158-66. [CrossRef]
- Park DC, Yeo SG. Aging. Korean J Audiol. 2013 Sep;17(2):39-44. [CrossRef]
- Pineda JR, Daynac M, Chicheportiche A, Cebrian-Silla A, Sii Felice K, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Boussin FD, Mouthon MA. Vascular-derived TGF-β increases in the stem cell niche and perturbs neurogenesis during aging and following irradiation in the adult mouse brain. EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Apr;5(4):548-62. [CrossRef]
- Gao P, Shen F, Gabriel RA, Law D, Yang EY, Yang GY, Young WL, Su H. Attenuation of brain response to vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis and neurogenesis in aged mice. Stroke. 2009 Nov;40(11):3596-600. [CrossRef]
- Greenberg DA, Jin K. From angiogenesis to neuropathology. Nature. 2005 Dec 15;438(7070):954-9. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Ren B, Li Z, Wu H, Zhang G, Yan P. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and microvessel density in different brain regions in aged rats]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2014 Jul;39(7):681-6. Chinese. [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy M, Anusuyadevi M, Aigner KM, Unger MS, Kniewallner KM, de Sousa DMB, Altendorfer B, Mrowetz H, Bogdahn U, Aigner L. TGF-β Signaling: A Therapeutic Target to Reinstate Regenerative Plasticity in Vascular Dementia? Aging Dis. 2020 Jul 23;11(4):828-850. [CrossRef]
- Aigner L, Bogdahn U. TGF-beta in neural stem cells and in tumors of the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 2008 Jan;331(1):225-41. [CrossRef]
- Doyle KP, Cekanaviciute E, Mamer LE, Buckwalter MS. TGFβ signaling in the brain increases with aging and signals to astrocytes and innate immune cells in the weeks after stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Oct 11;7:62. [CrossRef]
- Tominaga K, Suzuki HI. TGF-β Signaling in Cellular Senescence and Aging-Related Pathology. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 10;20(20):5002. [CrossRef]
- Ionescu-Tucker A, Cotman CW. Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Nov;107:86-95. [CrossRef]
- Molinari C, Morsanuto V, Ruga S, Notte F, Farghali M, Galla R, Uberti F. The Role of BDNF on Aging-Modulation Markers. Brain Sci. 2020 May 9;10(5):285. [CrossRef]
- Sechi S, Chiavolelli F, Spissu N, Di Cerbo A, Canello S, Guidetti G, Fiore F, Cocco R. An Antioxidant Dietary Supplement Improves Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Serum of Aged Dogs: Preliminary Results. J Vet Med. 2015;2015:412501. [CrossRef]
- Toricelli M, Pereira AAR, Souza Abrao G, Malerba HN, Maia J, Buck HS, Viel TA. Mechanisms of neuroplasticity and brain degeneration: strategies for protection during the aging process. Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jan;16(1):58-67. [CrossRef]
- Castelli V, Benedetti E, Antonosante A, Catanesi M, Pitari G, Ippoliti R, Cimini A, d'Angelo M. Neuronal Cells Rearrangement During Aging and Neurodegenerative Disease: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress and Organelles Dynamic. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 May 28;12:132. [CrossRef]
- Higami Y, Shimokawa I. Apoptosis in the aging process. Cell Tissue Res. 2000 Jul;301(1):125-32. [CrossRef]
- Andreotti DZ, Silva JDN, Matumoto AM, Orellana AM, de Mello PS, Kawamoto EM. Effects of Physical Exercise on Autophagy and Apoptosis in Aged Brain: Human and Animal Studies. Front Nutr. 2020 Jul 28;7:94. [CrossRef]
- Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006 Oct 19;443(7113):787-95. [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse EG, Xu B. New insights into the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009 Oct;42(2):81-9. [CrossRef]
- Chen SD, Wu CL, Hwang WC, Yang DI. More Insight into BDNF against Neurodegeneration: Anti-Apoptosis, Anti-Oxidation, and Suppression of Autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 3;18(3):545. [CrossRef]
- Hock C, Heese K, Hulette C, Rosenberg C, Otten U. Region-specific neurotrophin imbalances in Alzheimer disease: decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and increased levels of nerve growth factor in hippocampus and cortical areas. Arch Neurol. 2000 Jun;57(6):846-51. [CrossRef]
- Oh H, Lewis DA, Sibille E. The Role of BDNF in Age-Dependent Changes of Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Markers in the Human Prefrontal Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Dec;41(13):3080-3091. [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman A, Koliad A, Zayachkivska A, Lushchakc O. Curcumin: A therapeutic potential in ageing-related disorders. PharmaNutrition 2020,144; 100226. doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100226.
- Benameur T, Soleti R, Panaro MA, La Torre ME, Monda V, Messina G, Porro C. Curcumin as Prospective Anti-Aging Natural Compound: Focus on Brain. Molecules. 2021 Aug 7;26(16):4794. [CrossRef]
- Bala K, Tripathy BC, Sharma D. Neuroprotective and anti-ageing effects of curcumin in aged rat brain regions. Biogerontology. 2006 Apr;7(2):81-9. [CrossRef]
- Mythri RB, Bharath MM. Curcumin: a potential neuroprotective agent in Parkinson's disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(1):91-9. [CrossRef]
- Lee J, Kim YS, Kim E, Kim Y, Kim Y. Curcumin and hesperetin attenuate D-galactose-induced brain senescence in vitro and in vivo. Nutr Res Pract. 2020 Oct;14(5):438-452. [CrossRef]
- Habibian M, Moosavi, S, Farzanegi P. Regular Exercise Combined With Curcumin Supplementation: Protective Effects against Lead- Induced Cerebellar Oxidative Damage in an Animal Model. Neurophysiology 2016; 48 (1):17-22. [CrossRef]
- Banji OJ, Banji D, Ch K. Curcumin and hesperidin improve cognition by suppressing mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis induced by D-galactose in rat brain. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Dec;74:51-9. [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K, Zarrin V, Moghadam ER, Hashemi F, Makvandi P, Samarghandian S, Khan H, Hashemi F, Najafi M, Mirzaei H. Toward Regulatory Effects of Curcumin on Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Across Different Diseases: A Review. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 14;11:585413. [CrossRef]
- Krstić J, Trivanović D, Mojsilović S, Santibanez JF. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta and Oxidative Stress Interplay: Implications in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:654594. [CrossRef]
- Zia A, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S. Molecular and cellular pathways contributing to brain aging. Behav Brain Funct. 2021 Jun 12;17(1):6. [CrossRef]
- Ongali B, Nicolakakis N, Tong XK, Lecrux C, Imboden H, Hamel E. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces cerebrovascular dysfunction and astrogliosis through angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated signaling pathways. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 May;96(5):527-534. [CrossRef]
- Yuan J, Liu W, Zhu H, Chen Y, Zhang X, Li L, Chu W, Wen Z, Feng H, Lin J. Curcumin inhibits glial scar formation by suppressing astrocyte-induced inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res. 2017 Jan 15;1655:90-103. [CrossRef]
- Yuan J, Zou M, Xiang X, Zhu H, Chu W, Liu W, Chen F, Lin J. Curcumin improves neural function after spinal cord injury by the joint inhibition of the intracellular and extracellular components of glial scar. J Surg Res. 2015 May 1;195(1):235-45. [CrossRef]
- Mao Z, Zheng YL, Zhang YQ, et al. The anti-apoptosis effects of daidzein in the brain of D-galactose treated mice. Molecules. 2007;12(7):1455-1470. Published 2007 Jul 19. [CrossRef]
- Isaev N.K., Genrikhs E.E., Oborina M.V., Stelmashook E.V. Accelerated aging and aging process in the brain. Rev. Neurosci. 2018;29:233–240. [CrossRef]
- El-Far AH, Elewa YHA, Abdelfattah EA, Alsenosy AA, Atta MS, Abou-Zeid KM, Al Jaouni SK, Mousa SA, Noreldin AE. Thymoquinone and Curcumin Defeat Aging-Associated Oxidative Alterations Induced by D-Galactose in Rats' Brain and Heart. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6839. [CrossRef]
- Nam SM, Choi JH, Yoo DY, Kim W, Jung HY, Kim JW, Yoo M, Lee S, Kim CJ, Yoon YS, Hwang IK. Effects of curcumin (Curcuma longa) on learning and spatial memory as well as cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in adult and aged mice by upregulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor and CREB signaling. J Med Food. 2014 Jun;17(6):641-9. [CrossRef]
- Franco-Robles E, Campos-Cervantes A, Murillo-Ortiz BO, Segovia J, López-Briones S, Vergara P, Pérez-Vázquez V, Solís-Ortiz MS, Ramírez-Emiliano J. Effects of curcumin on brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and oxidative damage in obesity and diabetes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014 Feb;39(2):211-8. [CrossRef]
- Liu D, Wang Z, Gao Z, Xie K, Zhang Q, Jiang H, Pang Q. Effects of curcumin on learning and memory deficits, BDNF, and ERK protein expression in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress. Behav Brain Res. 2014 Sep 1;271:116-21. [CrossRef]
- Mahoney ER, Dumitrescu L, Moore AM, Cambronero FE, De Jager PL, Koran MEI, Petyuk VA, Robinson RAS, Goyal S, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Jefferson AL, Hohman TJ. Brain expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene family in cognitive aging and alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Mar;26(3):888-896. [CrossRef]
- Shim JW, Madsen JR. VEGF Signaling in Neurological Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 17;19(1):275. [CrossRef]
- Guo H, Xia D, Liao S, Niu B, Tang J, Hu H, Qian H, Cao B. Vascular endothelial growth factor improves the cognitive decline of Alzheimer's disease via concurrently inducing the expression of ADAM10 and reducing the expression of β-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 in Tg2576 mice. Neurosci Res. 2019 May;142:49-57. [CrossRef]
- Zarezadehmehrizi A, Hong J, Lee J, Rajabi H, Gharakhanlu R, Naghdi N, Azimi M, Park Y. Exercise training ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in amyloid beta-injected rat model: possible mechanisms of Angiostatin/VEGF signaling. Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Dec;36(8):2263-2271. [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda B, Sousa-Ribeiro D, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Aging and sedentarism decrease vascularization and VEGF levels in the rat substantia nigra. Implications for Parkinson's disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009 Feb;29(2):230-4. [CrossRef]
- Reddy PH, Manczak M, Yin X, Grady MC, Mitchell A, Tonk S, Kuruva CS, Bhatti JS, Kandimalla R, Vijayan M, Kumar S, Wang R, Pradeepkiran JA, Ogunmokun G, Thamarai K, Quesada K, Boles A, Reddy AP. Protective Effects of Indian Spice Curcumin Against Amyloid-β in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(3):843-866. [CrossRef]
- Martin L, Bouvet P, Chounlamountri N, Watrin C, Besançon R, Pinatel D, Meyronet D, Honnorat J, Buisson A, Salin PA, Meissirel C. VEGF counteracts amyloid-β-induced synaptic dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2021 May 11;35(6):109121. [CrossRef]
- Viboolvorakul S, Patumraj S. Exercise training could improve age-related changes in cerebral blood flow and capillary vascularity through the upregulation of VEGF and eNOS. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:230791. [CrossRef]
- Rivard A, Berthou-Soulie L, Principe N, Kearney M, Curry C, Branellec D, Semenza GL, Isner JM. Age-dependent defect in vascular endothelial growth factor expression is associated with reduced hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity. J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 22;275(38):29643-7. [CrossRef]
- Nag S, Manias J, Eubanks JH, Stewart DJ. Increased Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-D Following Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 30;20(7):1594. [CrossRef]
- Hohman TJ, Bell SP, Jefferson AL; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in neurodegeneration and cognitive decline: exploring interactions with biomarkers of Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015 May;72(5):520-9. [CrossRef]
- Deyama S, Bang E, Kato T, Li XY, Duman RS. Neurotrophic and Antidepressant Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Require Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jul 15;86(2):143-152. [CrossRef]
- Afarid M, Namvar E, Sanie-Jahromi F. Diabetic Retinopathy and BDNF: A Review on Its Molecular Basis and Clinical Applications. J Ophthalmol. 2020 May 18;2020:1602739. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Zhang C, Jiang H, Li Y, Zhang L, Robin A, Katakowski M, Lu M, Chopp M. Atorvastatin induction of VEGF and BDNF promotes brain plasticity after stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005 Feb;25(2):281-90. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).