Submitted:
13 February 2023
Posted:
14 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Aqueous solubility of berberine and oral bioavailability
2.1. Aqueous solubility of berberine
2.2. Oral bioavailability of berberine
3. Internalization of berberine into cells and molecular targets
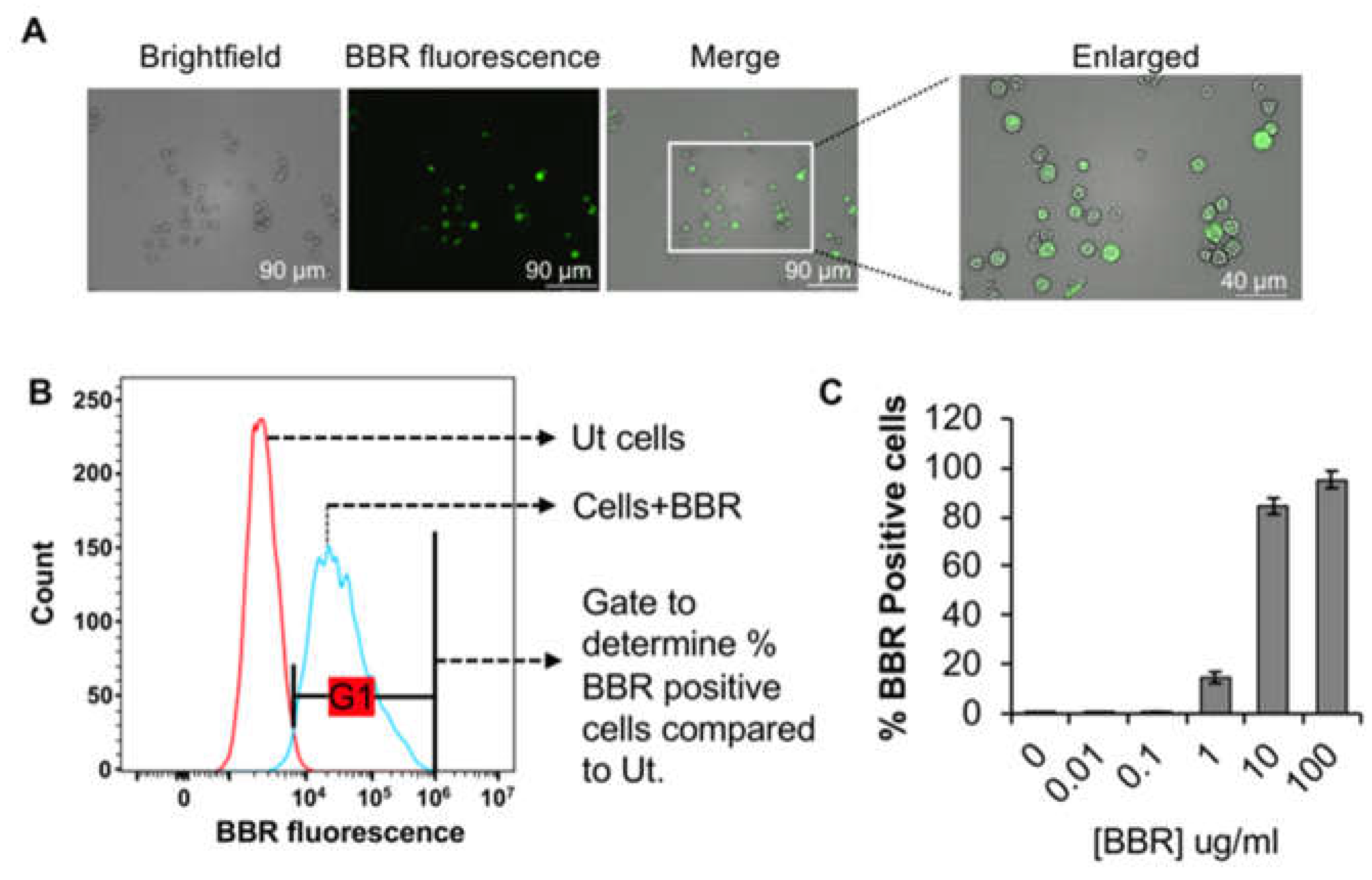
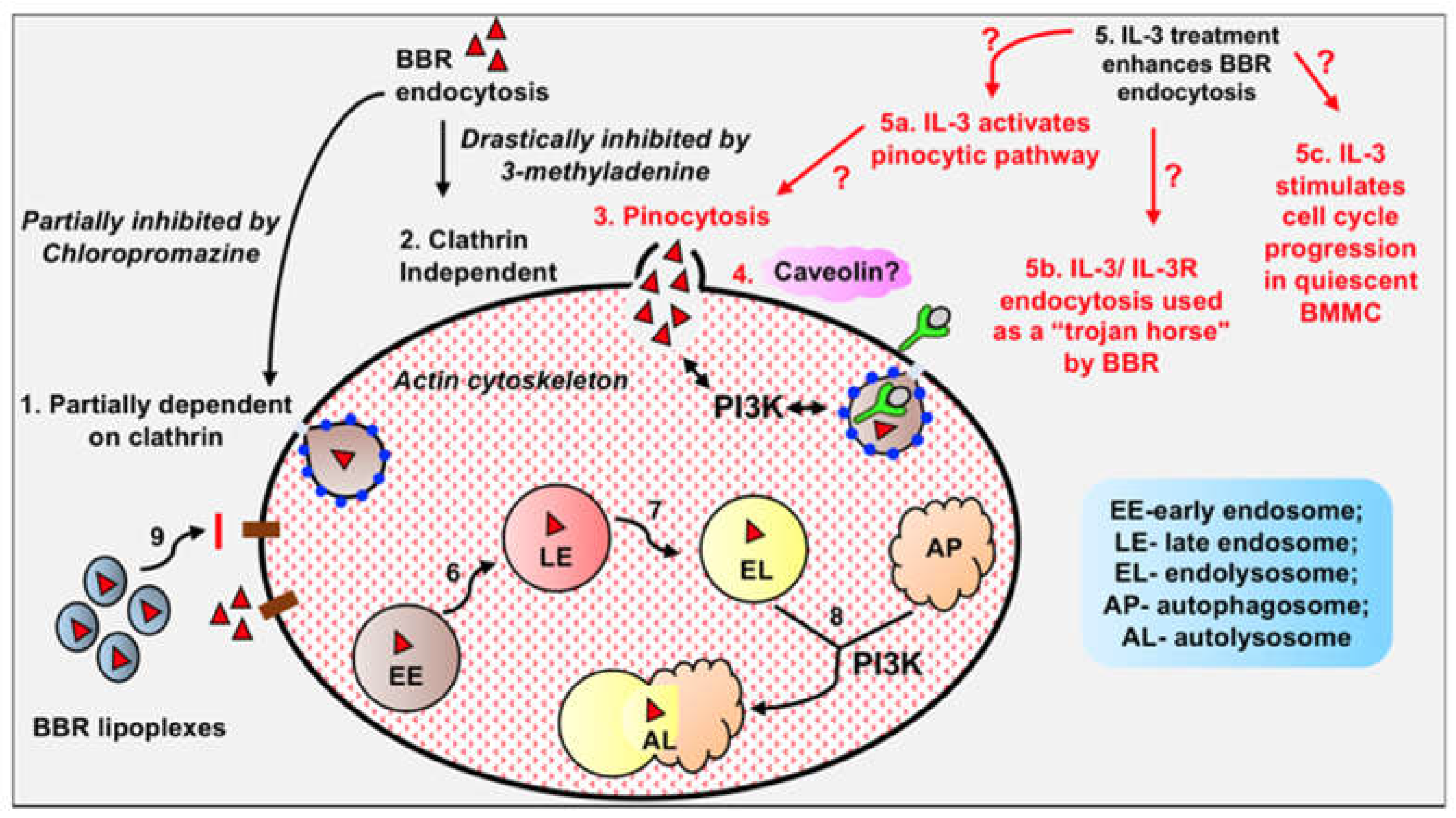
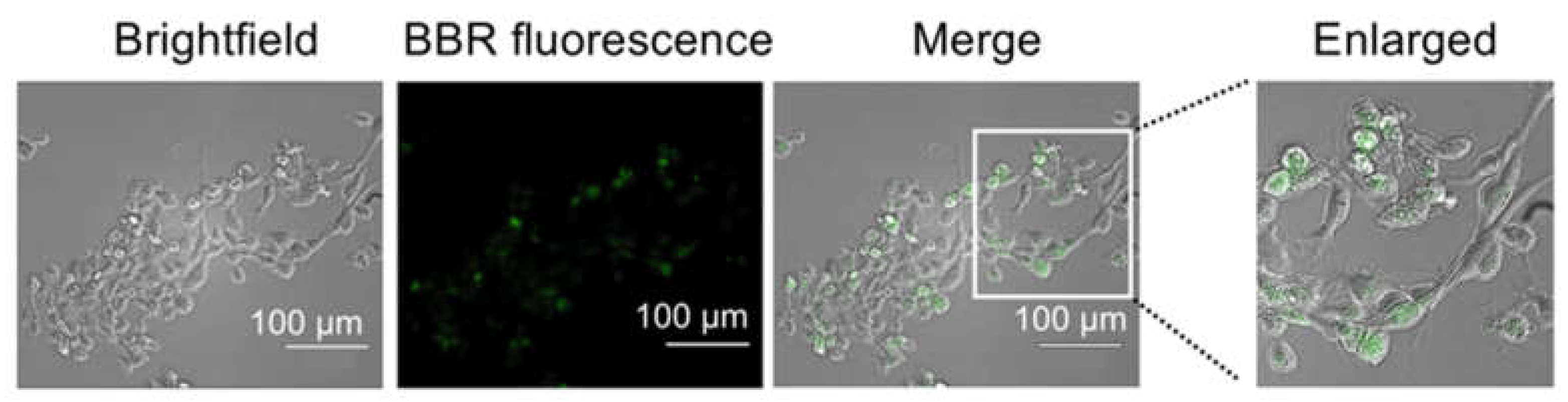
3.1. Internalization of berberine into cells
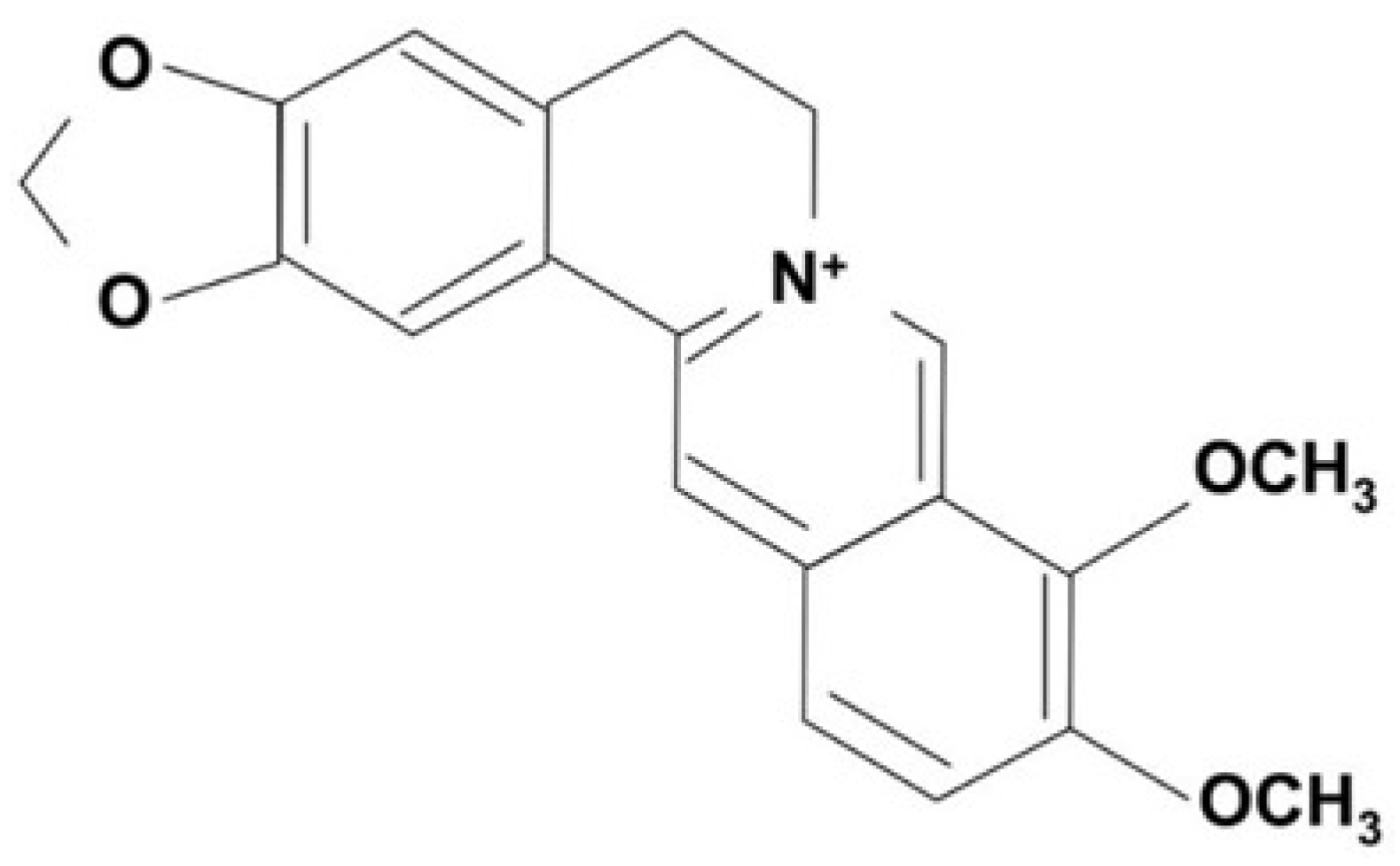
3.2. Molecular targets of berberine
4. Effects of berberine on metabolic pathways, apoptosis and necrosis of transformed cells
4.1. Effects of berberine on metabolic pathways of transformed cells
4.2. Effect of berberine on apoptosis and necrosis of transformed cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, J., et al., Berberine and Coptidis rhizoma as novel antineoplastic agents: a review of traditional use and biomedical investigations. J Ethnopharmacol, 2009, 126, 5–17. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X., et al., Hepatoprotective effects of Coptidis rhizoma aqueous extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver hepatotoxicity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 2009, 124, 130–136. [CrossRef]
- Q, Z., et al., - [Simultaneous determination of jatrorrhizine, palmatine, berberine, and obacunone in Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex by RP-HPLC]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2010, 35, 2061–2064.
- Germán-Acacio, J.M., D.E. Meza-Sánchez, and D. Morales-Morales, Chapter 3 - Therapeutically relevant natural products as AMPK activators in the treatment of diabetes, in Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, R. Atta ur, Editor. 2020, Elsevier. 57-90.
- Neag, M.A., et al., Berberine: Botanical Occurrence, Traditional Uses, Extraction Methods, and Relevance in Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Hepatic, and Renal Disorders. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9, 557. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberine, "Bureau CMMICoNMM" in Handbook of Effective Compositions in Plants. Vol. 1. 1991: Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. pp. 12-18.
- Gu, Y., et al., Effect of traditional Chinese medicine berberine on type 2 diabetes based on comprehensive metabonomics. Talanta, 2010, 81, 766–772. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.H., X.J. Zeng, and Y.Y. Li, Efficacy and safety of berberine for congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol, 2003, 92, 173–176. [CrossRef]
- Jagetia, G.C. and M.S. Baliga, Effect of Alstonia scholaris in enhancing the anticancer activity of berberine in the Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice. J Med Food, 2004, 7, 235–244. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q., et al., Preventive effect of Coptis chinensis and berberine on intestinal injury in rats challenged with lipopolysaccharides. Food Chem Toxicol, 2011, 49, 61–69. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P. and K.V. Sashidhara, Lipid lowering agents of natural origin: An account of some promising chemotypes. Eur J Med Chem, 2017, 140, 331–348. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A. and A.L. Catapano, Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 243, 449–461. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., et al., Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism, 2010, 59, 285–292. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., et al., Berberine hydrochloride IL-8 dependently inhibits invasion and IL-8-independently promotes cell apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncol Rep, 2014, 32, 2777–2788. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., et al., Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Berberine in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2014, 2014, 289264.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Berberine hydrochloride prevents postsurgery intestinal adhesion and inflammation in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2014, 349, 417–426. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., et al., Berberine inhibits free fatty acid and LPS-induced inflammation via modulating ER stress response in macrophages and hepatocytes. PLoS One, 2020, 15, e0232630.
- Habtemariam, S., Berberine and inflammatory bowel disease: A concise review. Pharmacol Res, 2016, 113 Pt A, 592–599. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q., et al., Effect of berberine on proinflammatory cytokine production by ARPE-19 cells following stimulation with tumor necrosis factor-α. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2012, 53, 2395–2402. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehteshamfar, S.-M., et al., Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory impacts of berberine on activation of autoreactive T cells in autoimmune inflammation. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2020, 24, 13573–13588. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z., et al., Anti-inflammatory activity of berberine in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via the Angptl2 pathway. BMC Immunology, 2020, 21, 28. [CrossRef]
- Battu, S.K., et al., Physicochemical Characterization of Berberine Chloride: A Perspective in the Development of a Solution Dosage Form for Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-C., et al., Solubility of Berberine Chloride in Various Solvents. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2006, 51, 642–644.
- Chen, W., et al., Bioavailability Study of Berberine and the Enhancing Effects of TPGS on Intestinal Absorption in Rats. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2011, 12, 705–711. [CrossRef]
- Feng, X., et al., Pharmacokinetics and Excretion of Berberine and Its Nine Metabolites in Rats. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Xue, M., et al., Characterization, pharmacokinetics, and hypoglycemic effect of berberine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine, 2013, 8, 4677–4687. [CrossRef]
- Hua, W., et al., Determination of berberine in human plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2007, 44, 931–937. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alolga, R., et al., Significant pharmacokinetic differences of berberine are attributable to variations in gut microbiota between Africans and Chinese. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6, 27671. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. and J.A. Zidichouski, Update on the Benefits and Mechanisms of Action of the Bioactive Vegetal Alkaloid Berberine on Lipid Metabolism and Homeostasis. Cholesterol, 2018, 2018, 7173920. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-T., et al., Extensive Intestinal First-Pass Elimination and Predominant Hepatic Distribution of Berberine Explain Its Low Plasma Levels in Rats. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S., et al., Research progress on berberine with a special focus on its oral bioavailability. Fitoterapia, 2016, 109, 274–282. [CrossRef]
- Battu, S.K., et al., Physicochemical Characterization of Berberine Chloride: A Perspective in the Development of a Solution Dosage Form for Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y., et al., CYP2D plays a major role in berberine metabolism in liver of mice and humans. Xenobiotica, 2011, 41, 996–1005. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., et al., Bioactivities of berberine metabolites after transformation through CYP450 isoenzymes. Journal of Translational Medicine, 2011, 9, 62. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F., et al., Isolation and identification of urinary metabolites of berberine in rats and humans. Drug Metab Dispos, 2008, 36, 2159–2165. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. and H.C. Chang, Determination of berberine in plasma, urine and bile by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl, 1995, 665, 117–123. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2008, 93, 2559–2565. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y., et al., Nanoemulsion improves hypoglycemic efficacy of berberine by overcoming its gastrointestinal challenge. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2019, 181, 927–934. [CrossRef]
- Gui, S., et al., Preparation and evaluation of a microemulsion for oral delivery of berberine. Die Pharmazie, 2008, 63, 516–519. [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.B. and M. Kulka, Internalization of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids by resting and activated bone marrow-derived mast cells utilizes energy-dependent mechanisms. Inflamm Res, 2022, 71, 343–356. [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, F., et al., The intracellular trafficking mechanism of Lipofectamine-based transfection reagents and its implication for gene delivery. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 25879. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C., et al., Organic anion-transporting polypeptides contribute to the hepatic uptake of berberine. Xenobiotica, 2015, 45, 1138–1146. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K., et al., Characterization of berberine transport into Coptis japonica cells and the involvement of ABC protein. J Exp Bot, 2002, 53, 1879–1886. [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.B. and M. Kulka, Is Clathrin Involved in Internalization of The Small Molecule Berberine by Primary Mouse Mast Cells?. Archives of Microbiology and Immunology, 2022, 6, 141–148. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W., et al., Interaction of herbal compounds with biological targets: a case study with berberine. Scientific World Journal, 2012, 2012, 708292. [CrossRef]
- Jeena, M.T., et al., Recent Progress in Mitochondria-Targeted Drug and Drug-Free Agents for Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 12. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., et al., Mitochondria-targeting fluorescent molecules for high efficiency cancer growth inhibition and imaging. Chem Sci, 2019, 10, 7946–7951. [CrossRef]
- Jean, S.R., et al., Peptide-Mediated Delivery of Chemical Probes and Therapeutics to Mitochondria. Acc Chem Res, 2016, 49, 1893–1902. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L., et al., Thermoresponsive drug delivery to mitochondria in vivo. Chem Commun (Camb), 2019, 55, 14645–14648. [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.C., et al., Mitochondrially targeted effects of berberine [Natural Yellow 18, 5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo(g)-1,3-benzodioxolo(5,6-a) quinolizinium] on K1735-M2 mouse melanoma cells: comparison with direct effects on isolated mitochondrial fractions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2007, 323, 636–649. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L., et al., Sustained antidiabetic effects of a berberine-containing Chinese herbal medicine through regulation of hepatic gene expression. Diabetes, 2012, 61, 933–943. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C., et al., Berberine induces apoptosis in human HSC-3 oral cancer cells via simultaneous activation of the death receptor-mediated and mitochondrial pathway. Anticancer Res, 2007, 27, 3371–3378.
- Peng, L, et al., Synergistic tumor-killing effect of radiation and berberine combined treatment in lung cancer: the contribution of autophagic cell death. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2008, 70, 529–542. [CrossRef]
- Turner, N., et al., Berberine and its more biologically available derivative, dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: a mechanism for the action of berberine to activate AMP-activated protein kinase and improve insulin action. Diabetes, 2008, 57, 1414–1418. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirhadi, E., M. Rezaee, and B. Malaekeh-Nikouei, Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of Berberis. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 104, 465–473. [PubMed]
- Ravera, S., et al., Berberine affects mitochondrial activity and cell growth of leukemic cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Sci Rep, 2020, 10, 16519. [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.J., et al., Mitochondria play an important role in the cell proliferation suppressing activity of berberine. Sci Rep, 2017, 7, 41712. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X., et al., Anticancer Effects of Honokiol via Mitochondrial Dysfunction Are Strongly Enhanced by the Mitochondria-Targeting Carrier Berberine. J Med Chem, 2020, 63, 11786–11800. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemani, R.G., et al., Comparison of SpO2 to PaO2 based markers of lung disease severity for children with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med, 2012, 40, 1309–1316. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.J., et al., Berberine inhibits human colon cancer cell migration via AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated downregulation of integrin beta1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 426, 461–467. [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T., et al., Berberine suppresses in vitro migration and invasion of human SCC-4 tongue squamous cancer cells through the inhibitions of FAK, IKK, NF-kappaB, u-PA and MMP-2 and -9. Cancer Lett, 2009, 279, 155–162. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., et al., Berberine inhibits the chemotherapy-induced repopulation by suppressing the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway and phosphorylation of FAK in ovarian cancer. Cell Prolif, 2017, 50. [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.L., Kirilov, and V.G. Roullin, Organogels, promising drug delivery systems: an update of state-of-the-art and recent applications. J Control Release, 2018, 271, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J., C. Saldias, and D. Diaz Diaz, Release of small bioactive molecules from physical gels. Chem Soc Rev, 2018, 47, 1484–1515. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y., et al., In vivo anti-apoptosis activity of novel berberine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles effectively ameliorates osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015, 28, 34–43. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L., et al., Cancer statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2022, 72, 7–33. [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.B., J. Kim, and G. K. Jayaprakasha, Berberine induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) through mitochondrial-dependent pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2010, 645, 70–78. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-D., et al., Berberine as a potential agent for breast cancer therapy. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, L., G. Kothandan, and R. Manoharan, Berberine and Emodin abrogates breast cancer growth and facilitates apoptosis through inactivation of SIK3-induced mTOR and Akt signaling pathway. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, 2020, 1866, 165897. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W., et al., Berberine inhibits the proliferation and migration of breast cancer ZR-75-30 cells by targeting Ephrin-B2. Phytomedicine, 2017, 25, 45–51. [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.-J., J. Li, and B. Yu, Annual review of LSD1/KDM1A inhibitors in 2020. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 214, 113254. [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, K. and G.S. Kumar, Therapeutic potential of nucleic acid-binding isoquinoline alkaloids: Binding aspects and implications for drug design. Medicinal Research Reviews, 2011, 31, 821–862. [CrossRef]
- Parra-Marín, O., et al., The highly diverse TATA box-binding proteins among protists: A review. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 2020, 239, 111312. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-Y., et al., TATA boxes in gene transcription and poly (A) tails in mRNA stability: New perspective on the effects of berberine. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5, 18326. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G., L.C. Cantley, and C.B. Thompson, Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science, 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [CrossRef]
- Kang, S., et al., SCTR regulates cell cycle-related genes toward anti-proliferation in normal breast cells while having pro-proliferation activity in breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol, 2015, 47, 1923–1931. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.C., et al., Effect miR-214-3p on proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells by targeting survivin protein. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 2019, 23, 7469–7474. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K., et al., Berberine Reverses Breast Cancer Multidrug Resistance Based on Fluorescence Pharmacokinetics In Vitro and In Vivo. ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 10645–10654. [CrossRef]
- Roy, L.-O., M.-B. Poirier, and D. Fortin, Chloroquine inhibits the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma partially by suppressing TGF-beta. Investigational New Drugs, 2015, 33, 1020–1031. [CrossRef]
- SORDILLO, L.A., P. SORDILLO, and L. HELSON, Curcumin for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Anticancer Research, 2015, 35, 6373–6378.
- Lin, T.-H., et al., Berberine enhances inhibition of glioma tumor cell migration and invasiveness mediated by arsenic trioxide. BMC Cancer, 2008, 8, 58. [CrossRef]
- Maiti, P., A. Plemmons, and G. Dunbar, Combination treatment of berberine and solid lipid curcumin particles increased cell death and inhibited PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway of human cultured glioblastoma cells more effectively than did individual treatments. PLOS ONE, 2019, 14, e0225660. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y., et al., Berberine Suppressed the Progression of Human Glioma Cells by Inhibiting the TGF-β1/SMAD2/3 Signaling Pathway. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 2022, 21, 15347354221130303. [CrossRef]
- Asemi, Z., et al., Therapeutic Potential of Berberine in the Treatment of Glioma: Insights into Its Regulatory Mechanisms. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 2021, 41, 1195–1201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L., et al., Treatment of Parkinson’s disease in Zebrafish model with a berberine derivative capable of crossing blood brain barrier, targeting mitochondria, and convenient for bioimaging experiments. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2021, 249, 109151. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L., et al., Overexpression of SMC4 activates TGFβ/Smad signaling and promotes aggressive phenotype in glioma cells. Oncogenesis, 2017, 6, e301–e301. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W., et al., Berberine Attenuates Cigarette Smoke Extract-induced Airway Inflammation in Mice: Involvement of TGF-β1/Smads Signaling Pathway. Current Medical Science, 2019, 39, 748–753. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, T.V., et al., Berberine induces apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme U87MG cells via oxidative stress and independent of AMPK activity. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47, 4393–4400. [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.S., et al., Berberine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Glioblastoma T98G Cells Is Mediated by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Accompanying Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2010, 33, 1644–1649. [CrossRef]
- Z, L., et al., - Berberine Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Interfering with Wild-Type and Mutant P53 in Human Glioma Cells. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13, 12151–12162. [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H. and C. Prives, Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell, 2009, 137, 413–431. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y., et al., Functional Diversity of p53 in Human and Wild Animals. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., et al., Berberine induces autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-pathway. Oncotarget, 2016, 7, 66944–66958. [CrossRef]
- Qu, H., et al., Berberine reduces temozolomide resistance by inducing autophagy via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell International, 2020, 20, 592. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y., et al., Berberine in combination with cisplatin suppresses breast cancer cell growth through induction of DNA breaks and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep, 2016, 36, 567–572. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q., et al., Berberine Radiosensitizes Human Esophageal Cancer Cells by Downregulating Homologous Recombination Repair Protein RAD51. PLOS ONE, 2011, 6, e23427. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q., et al., Post-translational modifications of proliferating cell nuclear antigen: A key signal integrator for DNA damage response (Review). Oncol Lett, 2014, 7, 1363–1369. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RG, X., et al., - Anticancer Effects and Mechanisms of Berberine from Medicinal Herbs: An Update Review. LID - 10.3390/molecules27144523 [doi] LID - 4523. Molecules, 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., et al., Berberine activates caspase-9/cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis to suppress triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2017, 95, 18–24. [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A. and W.S. El-Deiry, Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 2020, 17, 395–417. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khalki, L., et al., Berberine Impairs the Survival of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells: Cellular and Molecular Analyses. Molecules, 2020, 25, 506. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H. and M. Xu, DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Cell Research, 2000, 10, 205–211. [CrossRef]
- Hafner, A., et al., The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2019, 20, 199–210. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y., et al., Apoptosis Induction, a Sharp Edge of Berberine to Exert Anti-Cancer Effects, Focus on Breast, Lung, and Liver Cancer. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J., et al., Berberine-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial-related apoptotic pathway. Tumor Biology, 2015, 36, 1279–1288. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



