Submitted:
04 February 2023
Posted:
08 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
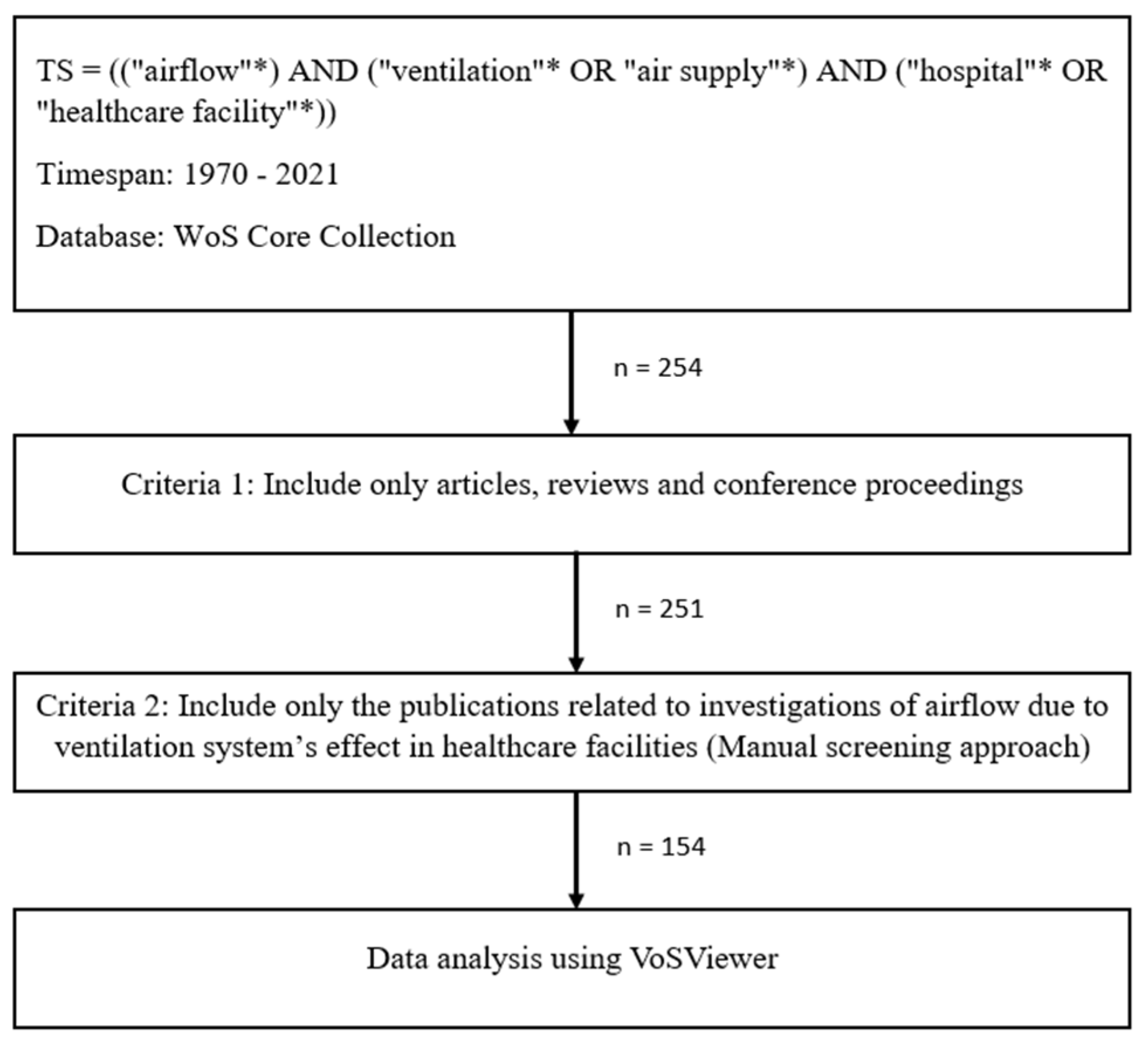
2.1. Retrieval of Publications
- (a)
- Publications with the term “ventilation” that were originally included in the keywords but were not relevant to airflow investigation, as there is also a medical term for ventilation that focused on human anatomy, rather than hospital or healthcare infrastructures (i.e., mechanical ventilation, invasive ventilation).
- (b)
- Publications that described the airflow analysis, but without ventilation system analysis, or vice versa.
2.2. Data Analysis
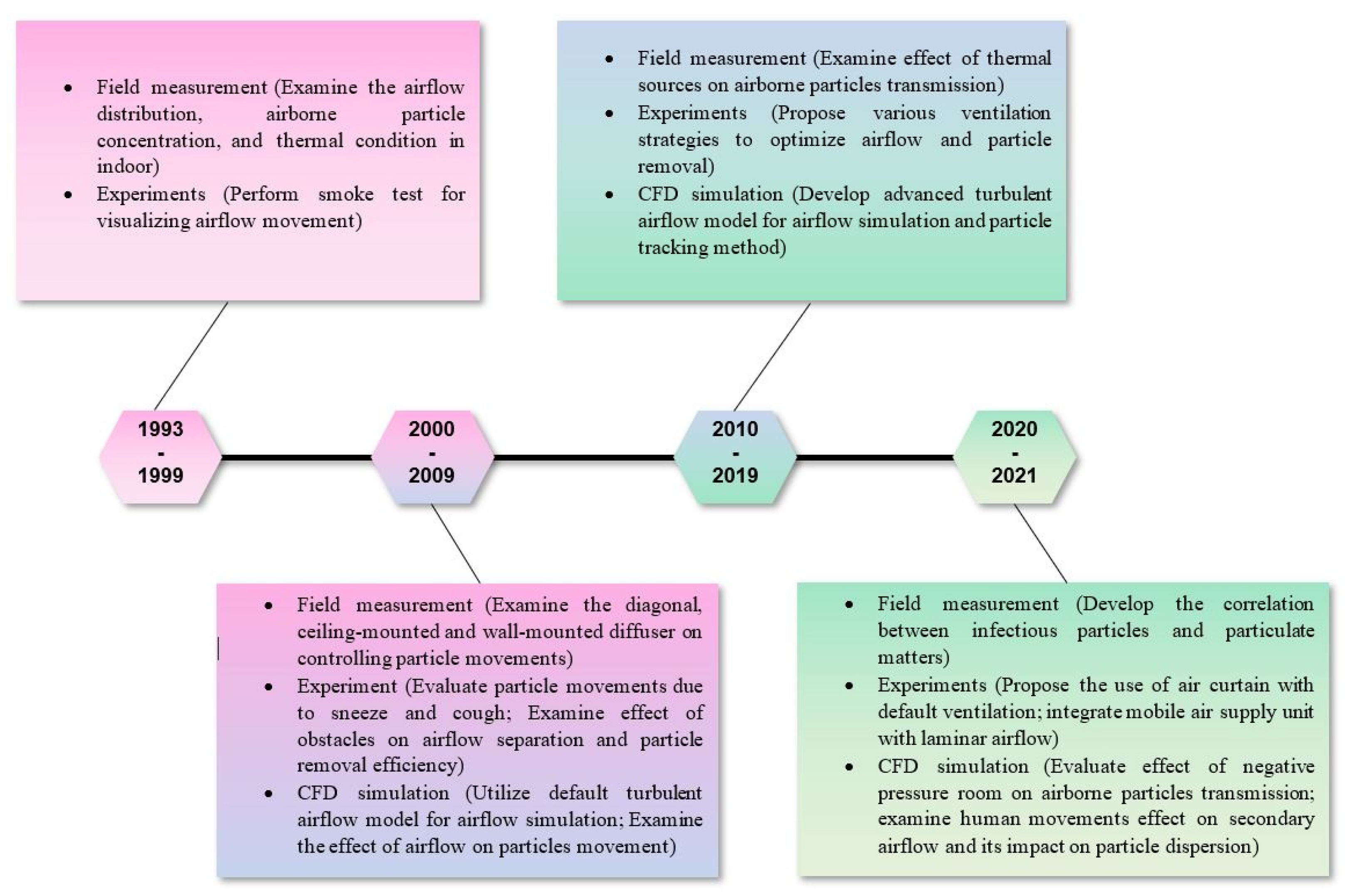
3. Results and Discussions
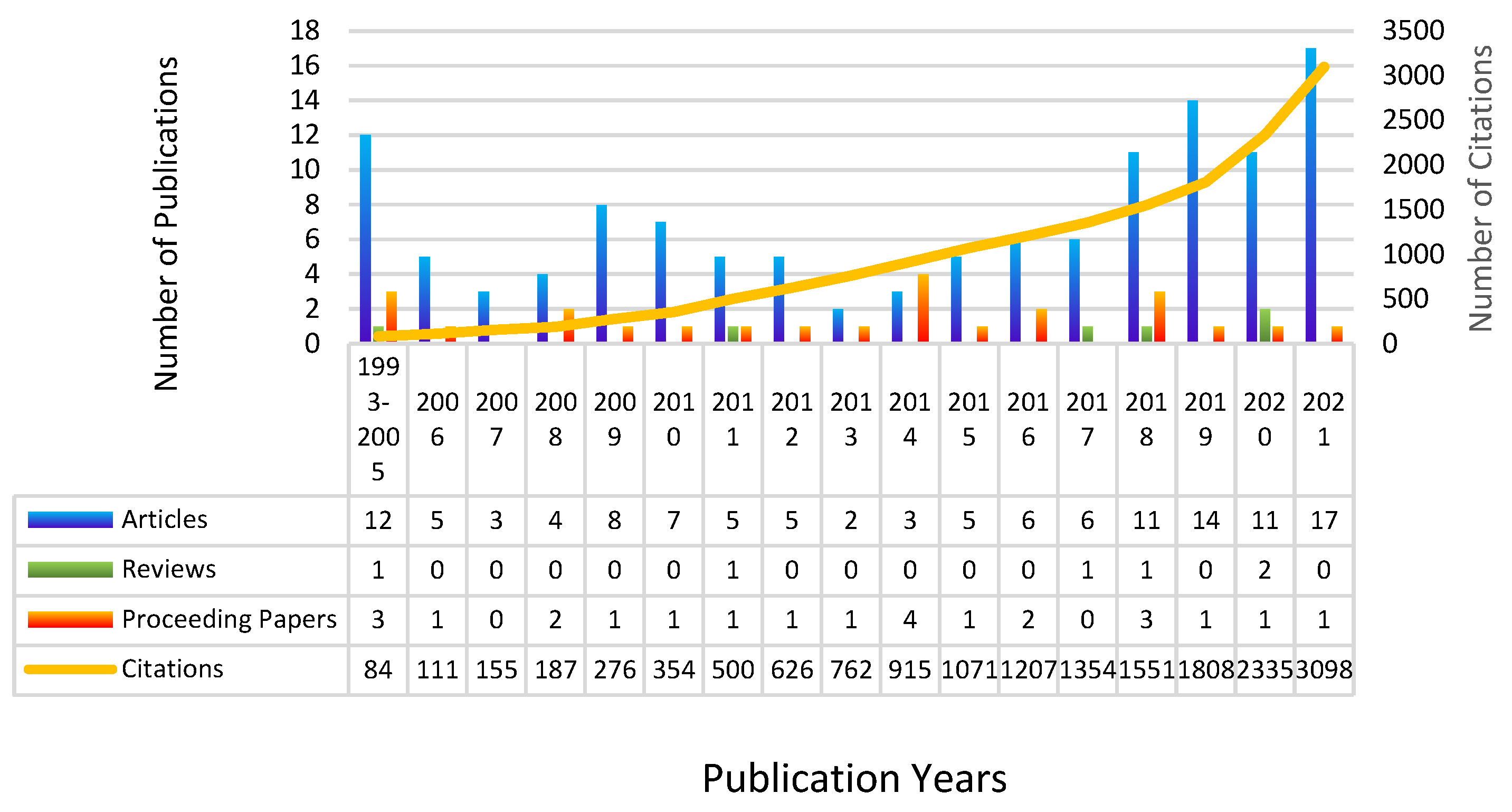
3.1. General Publications and Citation Trends
3.2. Journal Analysis
3.3. Top Cited Publications
3.4. Productivity and Collaboration Network
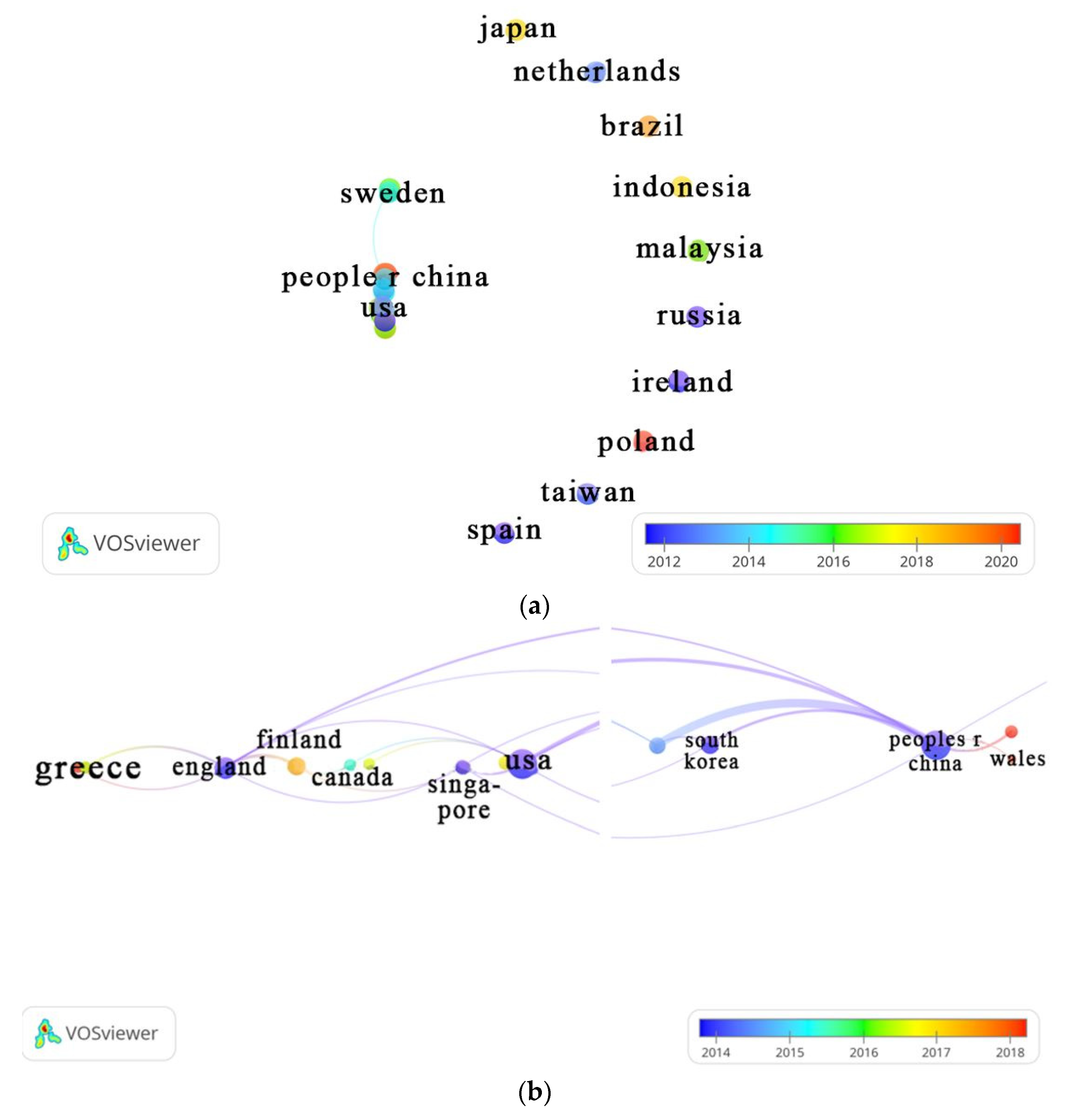
3.4.1. Country
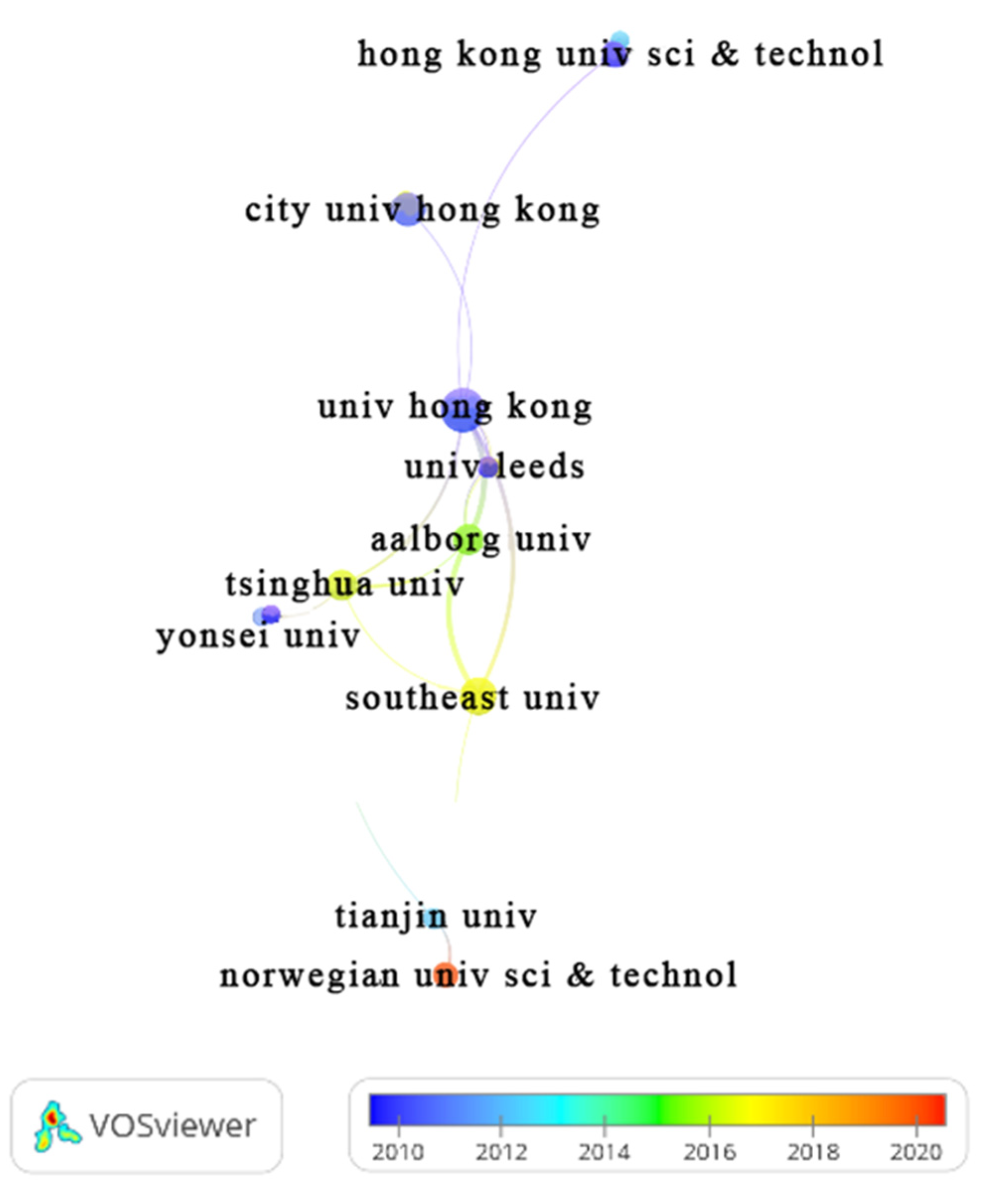
3.4.2. Organization/Affiliation
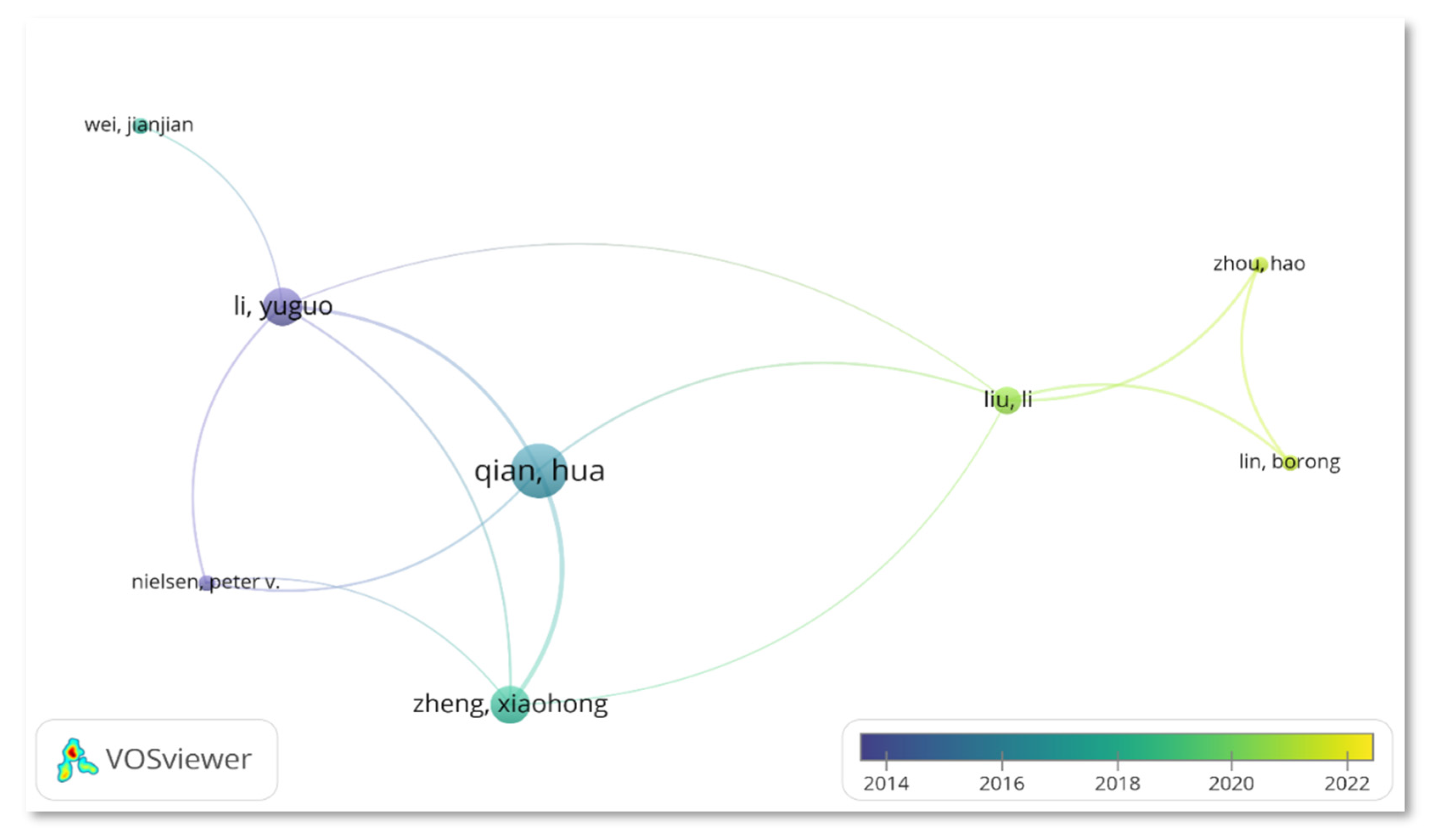
3.4.3. Author
3.5. Funding Agencies
| Funding Agency | Country, Region | TP | %TP | Year | TC | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970-2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||
| National Natural Science Foundation of China NSFC | China | 12 | 7.79 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 520 | 10 |
| Engineering Physical Sciences Research Council EPSRC | UK | 5 | 3.25 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 123 | 5 |
| Hong Kong Research Grants Council | China | 5 | 3.25 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 138 | 4 |
| UK Research Innovation UKRI | UK | 5 | 3.25 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 123 | 5 |
| Finnish Funding Agency for Technology Innovation Tekes | Finland | 4 | 2.60 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 4 |
| Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities | NA | 3 | 1.95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 35 | 3 |
| United States Department of Human Services | USA | 3 | 1.95 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 3 |
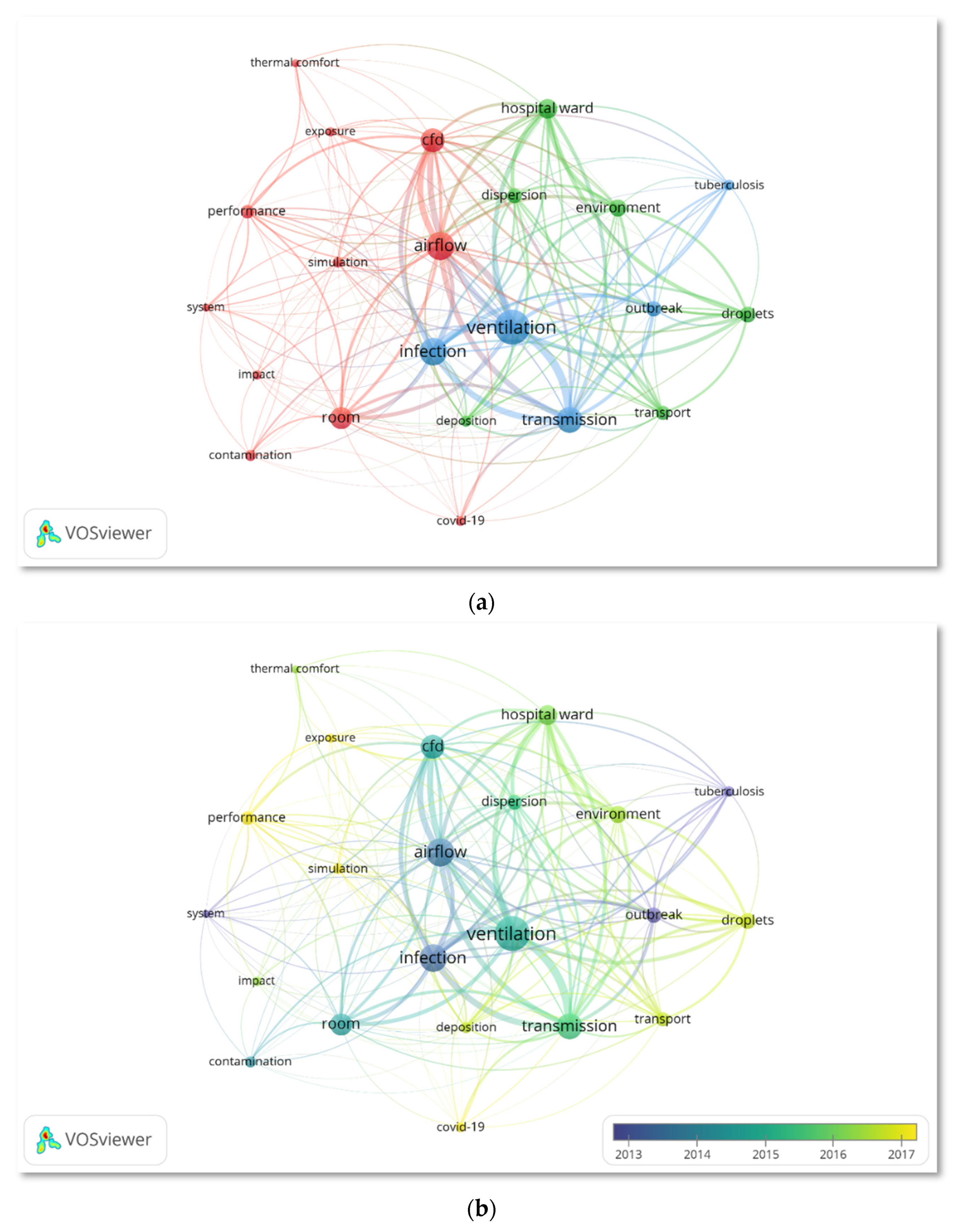
3.6. Keywords Co-Occurrence Analysis
3.7. Emerging Research Hotspots
3.7.1. Ventilation Strategies in Mitigating Airborne Infection
3.7.2. Application of CFD in Airborne Infection Control
3.7.3. Characteristics of Airborne Particles
3.8. Limitations of Bibliometric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Luo, X.; Huang, X.; Nielsen, P.V. Prediction and control of aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in ventilated context: from source to receptor. Sustainable Cities and Society 2022, 76, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.; Yi, H.; Park, J.H.; Park, H.W.; Park, K. A vertical laminar airflow system to prevent aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in building space: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and experimental approach. Indoor Built Environ. 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; Li, Y.G. Airborne spread of infectious agents in the indoor environment. Am. J. Infect. Control 2016, 44, S102–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.D.; Lester, D.; Rosengarten, G.; Aboltins, C.; Patel, M.; Cole, I. A spatiotemporally resolved infection risk model for airborne transmission of COVID-19 variants in indoor spaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, C. Presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in isolation ward environment 28 days after exposure. Int J Infect Dis 2020, 97, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, T.T.; Yang, X.Y. Ventilation performance in the operating theatre against airborne infection: numerical study on an ultra-clean system. Journal of Hospital Infection 2005, 59, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaussier, M.; Vanoli, E.; Zadegan, F.; Peray, H.; Bezian, E.; Jilesen, J.; Gandveau, G.; Gayraud, J.-M. Aerodynamic analysis of hospital ventilation according to seasonal variations. A simulation approach to prevent airborne viral transmission pathway during Covid-19 pandemic. Environment International 2022, 158, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.W.; Vincent, J.H.; Kuehn, T.H.; Brosseau, L.M. Studies of ventilation efficiency in a protective isolation room by the use of a scale model. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1996, 17, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, H.D.; Kosonen, R. Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook: Volume 1: Fundamentals; Academic Press: 2020.
- Qian, H.; Zheng, X. Ventilation control for airborne transmission of human exhaled bio-aerosols in buildings. Journal of thoracic disease 2018, 10, S2295–s2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.; Chan, A.H.S. Control and management of hospital indoor air quality. Med. Sci. Monitor 2006, 12, SR17–SR23. [Google Scholar]
- Aviv, D.; Chen, K.W.; Teitelbaum, E.; Sheppard, D.; Pantelic, J.; Rysanek, A.; Meggers, F. A fresh (air) look at ventilation for COVID-19: Estimating the global energy savings potential of coupling natural ventilation with novel radiant cooling strategies. Applied Energy 2021, 292, 116848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Tang, J.W.; Bahnfleth, W.; Bluyssen, P.M.; Boerstra, A.; Buonanno, G.; Cao, J.; Dancer, S.; Floto, A.; Franchimon, F.; et al. How can airborne transmission of COVID-19 indoors be minimised? Environment International 2020, 142, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargar, B.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Soltani, M.; Wright, K.E.; Ijaz, M.K.; Sattar, S.A. Mathematical modeling and simulation of bacterial distribution in an aerobiology chamber using computational fluid dynamics. Am. J. Infect. Control 2016, 44, S127–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Li, Y.; Seto, W.; Ching, P.; Ching, W.; Sun, H. Natural ventilation for reducing airborne infection in hospitals. Building and Environment 2010, 45, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, P.; Yang, R.-J. Virus diffusion in isolation rooms. Journal of Hospital Infection 2006, 62, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Kamar, H.M.; Chong, W.T.; Wong, S.L.; Kang, H.S. Systematic study on the relationship between particulate matter and microbial counts in hospital operating rooms. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2022, 29, 6710–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Lin, Z. Coughed droplet dispersion pattern in hospital ward under stratum ventilation. Building and Environment 2022, 208, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Li, Y.; Nielsen, P.V.; Hyldgaard, C.E. Dispersion of exhalation pollutants in a two-bed hospital ward with a downward ventilation system. Building and Environment 2008, 43, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, I.T.; Li, Y.; Wong, T.W.; Tam, W.; Chan, A.T.; Lee, J.H.; Leung, D.Y.; Ho, T. Evidence of airborne transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus. New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 350, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Dunn-Rankin, D. Transport of surgically produced aerosols in an operating room. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal 1998, 59, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, H. Positive-pressure isolation and the prevention of invasive aspergillosis. What is the evidence? Journal of Hospital Infection 2004, 56, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.T.; Yang, X.Y. Performance of ventilation system in a non-standard operating room. Building and Environment 2003, 38, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rui, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, J.; Tong, Y. Sources of atmospheric pollution: a bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2017, 112, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallison, S.P. What are Journals for? Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2015, 97, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakuma, B.B.; Wong, S.; Mong, G.R.; Utume, L.N.; Oladokun, O.; Wong, K.Y.; Ivase, T.J.; Abdullah, T.A.T. Bibliometric analysis of the research landscape on rice husks gasification (1995-2019). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 49467–49490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quantitative Science Studies 2020, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Wong, K.Y.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C.H. Microplastics and nanoplastics in global food webs: A bibliometric analysis (2009-2019). Mar Pollut Bull 2020, 158, 111432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Cui, Y. Bibliometric analysis of algal-bacterial symbiosis in wastewater treatment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019, 16, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, V.J.; Johnson, K.; Primack, J.; Jones, M.; Medoff, G.; Dunagan, W. Evaluation of rooms with negative pressure ventilation used for respiratory isolation in seven midwestern hospitals. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 1993, 14, 623–628. [Google Scholar]
- Cornet, M.; Levy, V.; Fleury, L.; Lortholary, J.; Barquins, S.; Coureul, M.-H.; Deliere, E.; Zittoun, R.; Brücker, G.; Bouvet, A. Efficacy of prevention by high-efficiency particulate air filtration or laminar airflow against Aspergillus airborne contamination during hospital renovation. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 1999, 20, 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Kamar, H.M.; Kamsah, N.; Wong, K.Y.; Musa, M.N.; Deris, M.S. Field measurement of airborne particulate matters concentration in a hospital’s operating room. Jurnal Teknologi (Science & Engineering) 2015, 77, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, P.M.; Nicas, M.; Harrison, R.J. Tuberculosis isolation comparison of written procedures and actual practices in three California hospitals. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2000, 21, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, N.; Kliasova, G. Possible sources of aspergilla infection in a hematological hospital. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv 2005, 77, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadrizadeh, S.; Holmberg, S.; Tammelin, A. A numerical investigation of vertical and horizontal laminar airflow ventilation in an operating room. Building and Environment 2014, 82, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, J.; Jo, S.; Bae, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Cha, H.H.; Lim, Y.-J.; Kwak, S.H.; Hong, M.J.; Kim, E.O. Nosocomial outbreak of COVID-19 in a hematologic ward. Infection & Chemotherapy 2021, 53, 332. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.L.; Mong, G.R.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Ngadi, N.; Wong, K.Y.; Hernández, M.M.; Armenise, S.; Chong, C.T. Upcycling of plastic waste to carbon nanomaterials: a bibliometric analysis (2000–2019). Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Some questions on dispersion of human exhaled droplets in ventilation room: answers from numerical investigation. Indoor Air 2010, 20, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.T.; Yang, X.Y. Ventilation performance in operating theatres against airborne infection: review of research activities and practical guidance. Journal of Hospital Infection 2004, 56, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.; Hott, U.; Sohr, D.; Daschner, F.; Gastmeier, P.; Rüden, H. Operating room ventilation with laminar airflow shows no protective effect on the surgical site infection rate in orthopedic and abdominal surgery. Annals of surgery 2008, 248, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, M.; Levy, V.; Fleury, L.; Lortholary, J.; Barquins, S.; Coureul, M.H.; Deliere, E.; Zittoun, R.; Brucker, G.; Bouvet, A. Efficacy of prevention by high-efficiency particulate air filtration or laminar airflow against Aspergillus airborne contamination during hospital renovation. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.P.; Sze To, G.N.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Fang, L.; Melikov, A. Modeling the fate of expiratory aerosols and the associated infection risk in an aircraft cabin environment. Aerosol Science and Technology 2009, 43, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Educational Policy Development in China for the 21st Century: Rationality and Challenges in a Globalizing Age. Chinese Education & Society 2017, 50, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The U.S. Department of Education. Laws and Guidance. n.a.
- Prehn, F.; Timmermann, E.; Kettlitz, M.; Schaufler, K.; Gunther, S.; Hahn, V. Inactivation of airborne bacteria by plasma treatment and ionic wind for indoor air cleaning. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarella, C.; Agodi, A.; Auxilia, F.; Lytsy, B.; Mura, I.; Parneix, P.; Popp, W.; Brusaferro, S. Air quality in the operating theatre: a perspective. Aerobiologia 2020, 36, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, W.; Alefelder, C.; Bauer, S.; Daeschlein, G.; Geistberger, P.; Gleich, S.; Herr, C.; Hubner, N.O.; Jatzwauk, L.; Kohnen, W.; et al. Air quality in the operating room: Surgical site infections, HVAC systems and discipline - position paper of the German Society of Hospital Hygiene (DGKH). GMD Hyg. Infect. Control 2019, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.S. The SARS epidemic in Hong Kong: what lessons have we learned? J R Soc Med 2003, 96, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Youtie, J.; Porter, A.L.; Wang, X. How does national scientific funding support emerging interdisciplinary research: A comparison study of big data research in the US and China. PloS one 2016, 11, e0154509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Educational policy development in China for the 21st century: Rationality and challenges in a globalizing age. 2017, 50, 133-141.
- Thompson, K. Education Policies - A Summary. 2017, 2022.
- Tang, J.W.; Noakes, C.J.; Nielsen, P.V.; Eames, I.; Nicolle, A.; Li, Y.; Settles, G.S. Observing and quantifying airflows in the infection control of aerosol- and airborne-transmitted diseases: an overview of approaches. Journal of Hospital Infection 2011, 77, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Nordin, A.H.; Lee, C.T.; Ngadi, N.; Wong, K.Y.; Oladokun, O. Uncovering the dynamics in global carbon dioxide utilization research: a bibliometric analysis (1995-2019). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 13842–13860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASHRAE. Standard 170, Ventilation of Health Care Facilities. 2017.
- NHS. Scottish Health Technical Memorandum 03-01 - Specialised ventilation in healthcare premises. part A: The concept, design, specification, installation and acceptance testing of healthcare ventilation system 2022.
- Chartier, Y.; Pessoa-Silva, C. Natural ventilation for infection control in health-care settings. 2009.
- Kong, X.; Guo, C.; Lin, Z.; Duan, S.; He, J.; Ren, Y.; Ren, J. Experimental study on the control effect of different ventilation systems on fine particles in a simulated hospital ward. Sustain Cities Soc 2021, 73, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolashikov, Z.D.; Melikov, A.K.; Kierat, W.; Popiołek, Z.; Brand, M. Exposure of health care workers and occupants to coughed airborne pathogens in a double-bed hospital patient room with overhead mixing ventilation. HVAC&R Research 2012, 18, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Haslinda, M.K.; Nazri, K.; Alia, S.N. Effects of surgical staff turning motion on airflow distribution inside a hospital operating room. Evergreen 2019, 6, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadrizadeh, S.; Aganovic, A.; Bogdan, A.; Wang, C.; Afshari, A.; Hartmann, A.; Croitoru, C.; Khan, A.; Kriegel, M.; Lind, M.; et al. A systematic review of operating room ventilation. Journal of Building Engineering 2021, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Lee, C.T.; Wong, S.L.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Wahab, R.A.; Lee, K.Q.; Chiong, M.C.; Ho, W.S.; Othman, M.H.D.; et al. Numerical assessment of ceiling-mounted air curtain on the particle distribution in surgical zone. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Osborne, A.L. Simulation-based feasibility study of improved air conditioning systems for hospital operating room. Frontiers of Architectural Research 2013, 2, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Kek, H.Y.; Tey, W.Y.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Mong, G.R.; Kuan, G.; Ho, W.S.; Kang, H.S.; et al. Controlling infectious airborne particle dispersion during surgical procedures: Why mobile air supply units matter? Building and Environment 2022, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, B.; Lindgren, M.; Karlsson, C.; Bergstrom, A.; Friberg, S. Mobile zoned/exponential LAF screen: a new concept in ultra-clean air technology for additional operating room ventilation. J Hosp Infect 2002, 50, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrizadeh, S.; Holmberg, S.; Nielsen, P.V. Three distinct surgical clothing systems in a turbulent mixing operating room equipped with mobile ultraclean laminar airflow screen: A numerical evaluation. Science and Technology for the Built Environment 2016, 22, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Vogelsang, A.C.; Förander, P.; Arvidsson, M.; Löwenhielm, P. Effect of mobile laminar airflow units on airborne bacterial contamination during neurosurgical procedures. J Hosp Infect 2018, 99, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yin, H.; Rong, R.; Cao, G.; Deng, Q. Prevention of surgical site infection under different ventilation systems in operating room environment. Front Environ Sci Eng 2021, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, Y.H.; Chandrasegaran, D.; Badarudin, A. The ventilation of multiple-bed hospital wards in the tropics: A review. Build Environ 2011, 46, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Nielsen, P.V.; Jensen, R.L.; Heiselberg, P.; Liu, L.; Heikkinen, J. Protected zone ventilation and reduced personal exposure to airborne cross-infection. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, X. Effectiveness of personalized air curtain in reducing exposure to airborne cough droplets. Building and Environment 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Oladokun, M.; Lin, Z. Reducing the exposure risk in hospital wards by applying stratum ventilation system. Building and Environment 2020, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, Z. Coughed droplet dispersion pattern in hospital ward under stratum ventilation. Building and Environment 2022, 208, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, E.S.; Nafchi, A.M.; DesJardins, J.D.; LeMatty, A.S.; Falconer, R.J.; Ashley, N.D.; Roth, B.S.; Moschella, P. Design and in-vitro testing of a portable patient isolation chamber for bedside aerosol containment and filtration. Building and Environment 2022, 207, 108467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeidat, B.; Alrebei, O.F.; Abdallah, I.A.; Darwish, E.F.; Amhamed, A. CFD Analyses: The Effect of pressure suction and airflow velocity on coronavirus dispersal. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Ghahramani, A.; Mousavi, E. The effect of door opening on air-mixing in a positively pressurized room: Implications for operating room air management during the COVID outbreak. Journal of Building Engineering 2021, 44, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.R.; Li, Y.F.; Zhou, H.; Lin, J.L.; Zheng, Z.Z.; Xu, H.J.; Lin, B.R.; Lin, M.G.; Liu, L. Affordable measures to monitor and alarm nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 infection due to poor ventilation. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dai, X.; Wei, J.; Ai, Z.; Fan, Y.; Tang, L.; Jin, T.; Ge, J. Numerical comparison of the efficiency of mixing ventilation and impinging jet ventilation for exhaled particle removal in a model intensive care unit. Building and Environment 2021, 200, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Kong, M.; Dong, B.; Birnkrant, M.J.; Zhang, J. A systematic approach to estimating the effectiveness of multi-scale IAQ strategies for reducing the risk of airborne infection of SARS-CoV-2. Building and environment 2021, 200, 107926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Cao, G.; Pedersen, C.; Lu, S.; Stenstad, L.-I.; Skogås, J.G. Suitability evaluation on laminar airflow and mixing airflow distribution strategies in operating rooms: A case study at St. Olavs Hospital. Building and Environment 2021, 194, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, H.; Zhou, R.; Zheng, X. A novel circulated air curtain system to confine the transmission of exhaled contaminants: A numerical and experimental investigation. In Proceedings of the Building Simulation; 2020; pp. 1425–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, E.S.; Grosskopf, K.R. Renovation in hospitals: A case study of source control ventilation in work zones. Advances in Building Energy Research 2020, 14, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Holmberg, S.; Sadrizadeh, S. Impact of door opening on the risk of surgical site infections in an operating room with mixing ventilation. Indoor Built Environ. 2021, 30, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Yamanaka, T.; Sagara, K.; Momoi, Y.; Suzuki, T. Displacement ventilation with radiant panel for hospital wards: Measurement and prediction of the temperature and contaminant concentration profiles. Building and environment 2019, 160, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Qian, H.; Liu, L. Numerical investigation of airborne infection in naturally ventilated hospital wards with central-corridor type. Indoor Built Environ. 2018, 27, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, J. Numerical study of airborne droplets propagation inside a hospital consulting room. Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2021, 189-200.
- Pei, G.; Taylor, M.I. Effects of indoor airflow and ventilation strategy on the airborne virus transmission. ASHRAE Transactions 2021, 127, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, N.; Yamanaka, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Ihama, T.; Wakasa, M. Influence of vertical airflow along walls on temperature and contaminant concentration distributions in a displacement-ventilated four-bed hospital ward. Building and Environment 2020, 183, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Oladokun, M.; Lin, Z. Reducing the exposure risk in hospital wards by applying stratum ventilation system. Building and Environment 2020, 183, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, S.; Indyka, P.; Sojka, Z.; Kotarba, A. Development of structured Co3O4-based catalyst for N2O removal from hospital ventilation systems. Catalysis Today 2020, 348, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesan, M.K.; Mui, K.W.; Wong, L.T. A numerical study of ventilation strategies for infection risk mitigation in general inpatient wards. In Proceedings of the Building simulation; 2020; pp. 887–896. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Hanifan, A.H. Study on ventilation performance in operating room with variation ventilation design. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; 2020; p. 012040. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Z.; Huang, T.; Melikov, A. Airborne transmission of exhaled droplet nuclei between occupants in a room with horizontal air distribution. Building and Environment 2019, 163, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aganovic, A.; Steffensen, M.; Cao, G. CFD study of the air distribution and occupant draught sensation in a patient ward equipped with protected zone ventilation. Building and Environment 2019, 162, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Othman, M.H.D.; Kek, H.Y.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Wahab, R.A.; Sheng, D.D.C.V.; Wahab, N.H.A.; et al. Why do ventilation strategies matter in controlling infectious airborne particles? A comprehensive numerical analysis in isolation ward. Building and Environment 2023, 231, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Othman, M.H.D.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Vui Sheng, D.D.C.; Kek, H.Y.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Chiong, M.C.; Zubir, M.A.; et al. Does human movement-induced airflow elevate infection risk in burn patient’s isolation ward? A validated dynamics numerical simulation approach. Energy and Buildings 2023, 283, 112810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.V. Fifty years of CFD for room air distribution. Building and Environment 2015, 91, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.; Vanoli, E.; Decorde, B.; Lancelot, M.; Duprat, C.; Josserand, C.; Jilesen, J.; Bouadma, L.; Timsit, J.F. Modeling of aerosol transmission of airborne pathogens in ICU rooms of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory failure. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadi, F.; Fazeli, A. A Review on Applications of CFD Modeling in COVID-19 Pandemic. Arch Comput Methods Eng 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, X.; Ho, W.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Hassim, M.H.; Hashim, H.; Muis, Z.A.; Yunus, N.A.; Teck Ling, G.H. Study of fresh air supply vent on indoor airflow and energy consumption in an enclosed space. Chemical Engineering Transactions 2021, 83, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhai, Z. The efficacy of social distance and ventilation effectiveness in preventing COVID-19 transmission. Sustain Cities Soc 2020, 62, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dbouk, T.; Drikakis, D. On respiratory droplets and face masks. Phys Fluids (1994) 2020, 32, 063303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaie, M.; Lakzian, E.; Khan, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Mahian, O.; Ahmadi, G. COVID-19 spread in a classroom equipped with partition - A CFD approach. J Hazard Mater 2021, 420, 126587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtius, J.; Granzin, M.; Schrod, J. Testing mobile air purifiers in a school classroom: Reducing the airborne transmission risk for SARS-CoV-2. Aerosol Science and Technology 2021, 55, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, L.; Popovici, C.-G.; Stătescu, C.; Sascău, R.; Verdeș, M.; Ciocan, V.; Șerban, I.-L.; Mărănducă, M.A.; Hudișteanu, S.-V.; Țurcanu, F.-E. Impact of HVAC-systems on the dispersion of infectious aerosols in a cardiac intensive care unit. International journal of environmental research and public health 2020, 17, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q. Optimization of multi-V filter design for airliner environmental control system using an empirical model. Separation and Purification Technology 2021, 257, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, D.; Buonanno, M.; Grilj, V.; Shuryak, I.; Crickmore, C.; Bigelow, A.W.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Johnson, G.W.; Brenner, D.J. Far-UVC light: A new tool to control the spread of airborne-mediated microbial diseases. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tysiac-Mista, M.; Dubiel, A.; Brzoza, K.; Burek, M.; Palkiewicz, K. Air disinfection procedures in the dental office during the COVID-19 pandemic. Med Pr 2021, 72, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Zhao, X.; Manay, A.; Chen, Q. Effective ventilation and air disinfection system for reducing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection risk in office buildings. Sustain Cities Soc 2021, 75, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, H.M.; Wong, K.Y.; Kamsah, N. The effects of medical staff turning movements on airflow distribution and particle concentration in an operating room. Journal of Building Performance Simulation 2020, 13, 684–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Kamar, H.; Kamsah, N. Medical staff’s posture on airflow distribution and particle concentration in an operating room. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2020; p. 012103. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Kamar, H.; Kamsah, N. Enhancement of airborne particles removal in a hospital operating room. International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering 2019, 16, 7447–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Othman, M.H.D.; Kek, H.Y.; Wahab, R.A.; Ern, G.K.P.; Chong, W.T.; Lee, K.Q. Current and potential approaches on assessing airflow and particle dispersion in healthcare facilities: a systematic review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothamer, D.A.; Sanders, S.; Reindl, D.; Bertram, T.H. Strategies to minimize SARS-CoV-2 transmission in classroom settings: combined impacts of ventilation and mask effective filtration efficiency. Science and Technology for the Built Environment 2021, 27, 1181–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Grantham, M.; Pantelic, J.; Bueno de Mesquita, P.J.; Albert, B.; Liu, F.; Ehrman, S.; Milton, D.K.; null, n.; Adamson, W.; et al. Infectious virus in exhaled breath of symptomatic seasonal influenza cases from a college community. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dbouk, T.; Drikakis, D. On coughing and airborne droplet transmission to humans. Physics of Fluids 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, R.; Li, J. Coughs and sneezes: their role in transmission of respiratory viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2020, 202, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Ooka, R.; Kikumoto, H.; Oh, W.; Bu, Y.; Hu, S. Measurements of exhaled airflow velocity through human coughs using particle image velocimetry. Building and Environment 2021, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudalski, N.; Mohamed, A.; Mubareka, S.; Bi, R.; Zhang, C.; Savory, E. Experimental investigation of far-field human cough airflows from healthy and influenza-infected subjects. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Ooka, R.; Kikumoto, H.; Oh, W. Recent research on expiratory particles in respiratory viral infection and control strategies: A review. Sustain Cities Soc 2021, 73, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, G.; Bi, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, G. Distribution of droplet aerosols generated by mouth coughing and nose breathing in an air-conditioned room. Sustainable Cities and Society 2019, 51, 101721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Y. Enhanced spread of expiratory droplets by turbulence in a cough jet. Building and Environment 2015, 93, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, L.H.; Leo, B.F.; Nor, N.S.M.; Yip, C.W.; Ibrahim, N.; Hamid, H.H.A.; Latif, M.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Nadzir, M.S.M. Modeling aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from human-exhaled particles in a hospital ward. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 53478–53492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaweera, M.; Perera, H.; Gunawardana, B.; Manatunge, J. Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: A critical review on the unresolved dichotomy. Environ Res 2020, 188, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
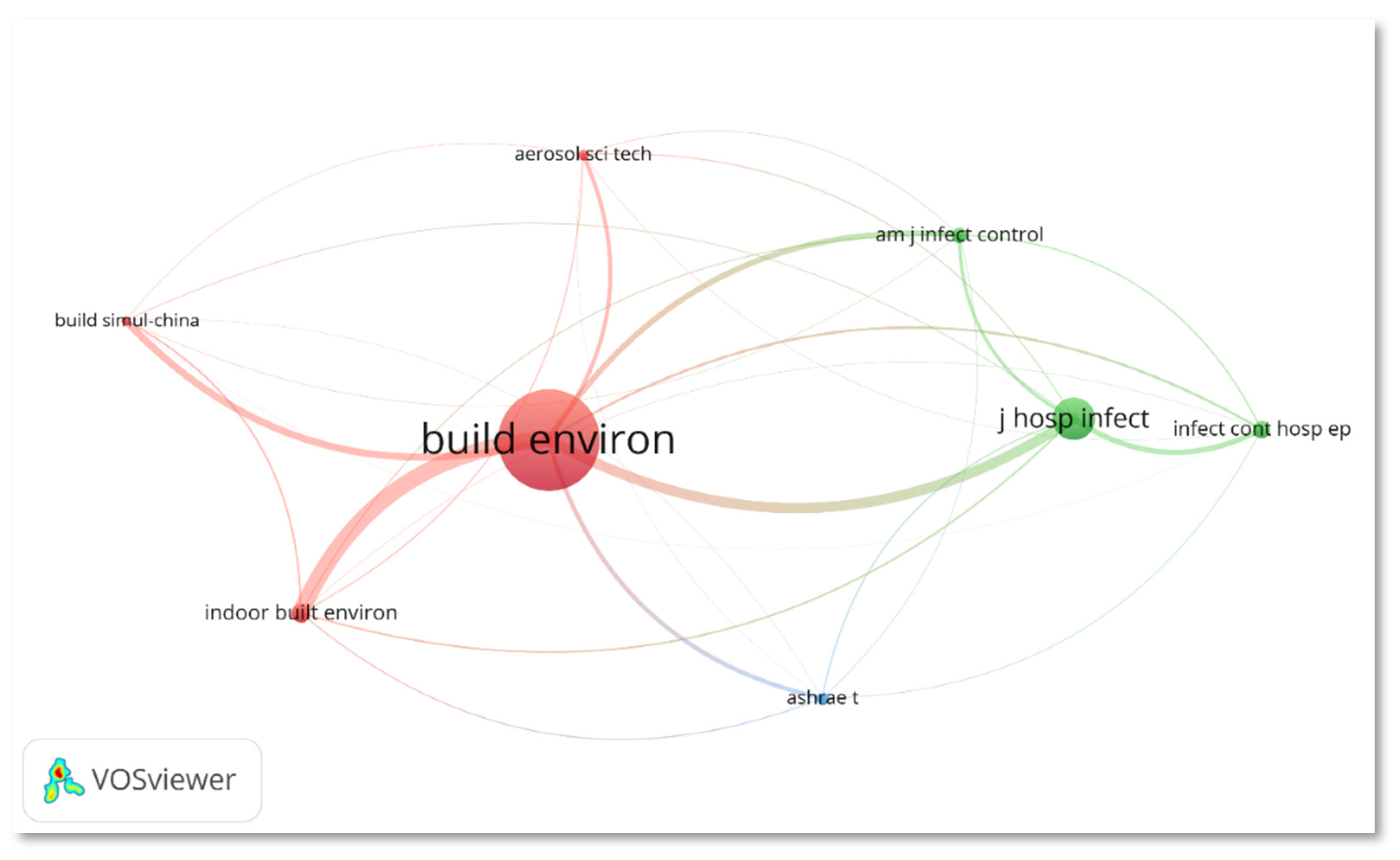
| Journal | Category (Q, Rank) (2020) | I.F. (2020) | TP | %TP | Cumulative Percentage | TC | TC/TP |
| Building and Environment | Construction & Building Technology (Q1/6/67) Engineering, Civil (Q1/6/137) Engineering, Environmental (Q1/12/54) |
6.456 | 29 | 18.71 | 18.71 | 680 | 23.45 |
| Indoor and Built Environment | Construction & Building Technology (Q2/29/67) Engineering, Environmental (Q3/36/54) Public, Environmental & Occupational Health (Q2/86/203) |
3.015 | 9 | 6.45 | 25.16 | 168 | 16.80 |
| Journal of Hospital Infection | Infectious Diseases (Q2/36/93) Public, Environmental & Occupational Health (Q2/56/203) |
3.926 | 8 | 5.16 | 30.32 | 325 | 40.63 |
| Building Simulation | Construction & Building Technology (Q2/20/67) Thermodynamics (Q1/14/60) |
3.751 | 7 | 4.52 | 34.84 | 67 | 9.57 |
| ASHRAE Transactions | Engineering, Building and Construction (NA) Engineering, Mechanical (NA) |
(NA) | 6 | 3.87 | 38.71 | 9 | 1.50 |
| Aerosol Science and Technology | Engineering, Chemical (Q3/72/143) Engineering, Mechanical (Q2/51/133) Environmental Sciences (Q3/145/274) Meteorology & Atmosphere Sciences (Q3/51/94) |
2.908 | 5 | 3.23 | 41.94 | 265 | 53.00 |
| American Journal of Infection Control | Infectious Diseases (Q3/59/93) Public, Environmental & Occupational Health (Q2/92/203) |
2.918 | 5 | 3.23 | 45.17 | 268 | 53.60 |
| Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology | Infectious Diseases (Q3/53/93) Public, Environmental & Occupational Health (Q2/76/203) |
3.254 | 5 | 3.23 | 48.40 | 219 | 43.80 |
| Title of Publication | References | Citations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 - 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Average per year | Total | ||
| Airborne spread of infectious agents in the indoor environment | [3] | 1 | 3 | 8 | 11 | 65 | 101 | 32.14 | 189 |
| Operating room ventilation with laminar airflow shows no protective effect on the surgical site infection rate in orthopaedic and abdominal surgery | [42] | 81 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 18 | 9 | 10.47 | 154 |
| Some questions on the dispersion of human exhaled droplets in ventilation room: answers from the numerical investigation | [40] | 44 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 23 | 35 | 10.46 | 116 |
| Efficacy of prevention by high-efficiency particulate air filtration or laminar airflow against Aspergillus airborne contamination during hospital renovation | [43] | 90 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 4.04 | 97 |
| Dispersion of exhalation pollutants in a two-bed hospital ward with a downward ventilation system | [19] | 40 | 13 | 7 | 11 | 7 | 15 | 6.40 | 93 |
| Control and management of hospital indoor air quality | [11] | 29 | 4 | 5 | 16 | 16 | 12 | 5.06 | 82 |
| Ventilation control for airborne transmission of human-exhaled bioaerosols in buildings | [10] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 23 | 36 | 16.80 | 62 |
| Ventilation performance in the operating theatre against airborne infection: a numerical study on an ultra-clean system | [6] | 43 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 12 | 10 | 4.56 | 79 |
| Natural ventilation for reducing airborne infection in hospitals | [15] | 25 | 0 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 19 | 5.85 | 66 |
| Modelling the Fate of Expiratory Aerosols and the Associated Infection Risk in an Aircraft Cabin Environment | [44] | 29 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 14 | 5.36 | 61 |
| Countries / Regions | TP | %TP | Year | TC | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 - 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||
| China | 51 | 32.90 | 27 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 1785 | 24 |
| USA | 32 | 20.65 | 21 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 469 | 15 |
| England | 13 | 8.39 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 295 | 10 |
| South Korea | 11 | 7.14 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 261 | 7 |
| Denmark | 10 | 6.45 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 402 | 8 |
| Finland | 7 | 4.52 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 6 |
| Sweden | 7 | 4.52 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 216 | 6 |
| Germany | 5 | 3.23 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 177 | 4 |
| Italy | 5 | 3.23 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 78 | 4 |
| Japan | 5 | 3.23 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 25 | 3 |
| Norway | 5 | 3.23 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 72 | 4 |
| Organization (country, region). | TP | %TP | Year | TC | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 - 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||
| University of Hong Kong (China) | 13 | 8.44 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 754 | 10 |
| Southeast University China (China) | 10 | 6.49 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 313 | 9 |
| City University of Hong Kong (China) | 8 | 5.20 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 330 | 7 |
| Aalborg University (Denmark) | 7 | 4.55 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 238 | 6 |
| Tsinghua University (China | 7 | 4.56 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 197 | 4 |
| University of Nebraska Lincoln (USA) | 6 | 3.90 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 59 | 5 |
| University of Nebraska System (USA) | 6 | 3.90 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 59 | 5 |
| Hong Kong University of Science Technology (China) | 5 | 3.25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 5 |
| Norwegian University of Science Technology NTNU (Norway) | 5 | 3.25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 72 | 4 |
| Authors | Country | TP | %TP | Year | TC | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970-2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||
| Qian, Hua | China | 12 | 7.79 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 378 | 9 |
| Li, Yuguo | China | 8 | 5.20 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 447 | 6 |
| Nielsen, Peter V. | Denmark | 8 | 5.20 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 227 | 6 |
| Mousavi Ehsan S. | USA | 7 | 4.55 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 52 | 4 |
| Zheng, Xiaohong | China | 7 | 4.55 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 194 | 6 |
| Grosskopf, Kevin R. | USA | 6 | 3.90 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 59 | 5 |
| Kalliomaki, Petri | Finland | 5 | 3.25 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 68 | 5 |
| Koskela, Hannu | Finland | 5 | 3.25 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 68 | 5 |
| Liu, Li | China | 5 | 3.25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 29 | 3 |
| Tang, Julian W. | England | 5 | 3.25 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 140 | 5 |
| Indoor Environment / Ventilation Strategies |
Type of Disease/ Contaminant Involved |
Boundary Conditions | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Indoor environment: General four-bed patient rooms / standard hospital patient rooms in South Korea - dimension: 6.1m × 4.7m × 2.7m Ventilation strategy: Mechanical ventilation system, vertical laminar airflow (VLAF) - the influence of the VLAF environment was tested on the room with a mechanical ventilation setting - supply air velocity: 0.5 m/s - exit pressure: 0 Pa - constant air temperature range:23 - 25°C - constant humidity range: 45-55% - Air change rate per hour: 15 – 16 ACH |
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) |
Aerosol particles: - density: 1000kg/ - diameter: 5 µm Exit vent: - pressure: 0 Pa Human nose: - nostril radius: 2.5 - respiration direction: 150° downwards - respiration velocity: 3.93m/s - respiration cycle: 3.43s Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): - incompressible physics model - Re-normalization Group (RNG) turbulence model with 20% intensity |
CFD results showed that the best option to provide uniform unidirectional airflow was 500mm-spaced ceiling nozzles (20mm-diameter) The appropriate value of air–terminal velocity identified was 0.3 m/s From the design of the VLAF environment field particle detection tests, a single person’s expiratory aerosols were removable within a short period (~20s) |
[2] |
|
Indoor environment: Hospital ward - dimension: 5.5m × 3.3m × 2.4m Ventilation strategy: Stratum ventilation (SV) - the centre height of the supply air grilles was 1.5m from the floor - exhaust diffusers were at the wall opposite the supply air grilles, 0.3m from the floor Displacement (DV) - Supply air diffuser was on the wall opposite the bed - exhausts diffusers were at the ceiling Mixing ventilation (MV) - three four-way diffusers on the ceiling - exhaust diffusers setting was the same as SV - minimum supply airflow rate of the ward: 6 ACH |
Airborne infectious disease | Wall/floor: - wall; heat flux: 0; discrete phase model; trap Lamp: - wall; heat flux: 150W/; discrete phase model; trap Patient/healthcare worker: - wall; heat flux: 45 W/; discrete phase model; trap Infector mouth: - velocity – inlet; temperature: 32°C; discrete phase model; trap Supply air terminal: - velocity – inlet; airflow rate: 12 ACH; discrete phase model; escape Exhaust air terminal: - outflow; discrete phase model; escape |
Under SV, exposure risk was at the minimum due to strong deposition at the initial dispersion stage, thus decreasing the concentration of the droplets Results showed that SV has better control over the 50 µm diameter droplet compared with DV and MV |
[74] |
|
Indoor environment: Hospital patient room equipped with whole room negative pressure (WRNP) system - dimension: 31.3 area × 3.0m height Ventilation strategy: Covering for Operations during the Viral Emergency Response (COVER) system COVER: - low – cost, portable isolation chamber that fits over the torso of a supine patient on a hospital bed - frame dimension: 45.7cm superior – inferiorly, 63.5cm medial – laterally, 63.5cm anterior – posteriorly - complete with 2 high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters (25cm × 25cm) |
SARS-CoV-2 | WRNP system: - low mode: clean room at 2208/h - high mode: clean room at 3400/h - 15 minutes test - 15s intervals |
Noise and temperature measurements: - over 50 hours of continuous use, no significant decrease in a performance recorded COVER efficiency: - the environmental particulate spread was reduced through the COVER device, compared to no containment device |
[75] |
|
Indoor environment: General hospital isolation wards Ventilation strategy: Natural ventilation - fresh air volume of 160L/s Mechanical ventilation: MV, DV, personalized ventilation (PV), downward ventilation (DWV), protected zone ventilation (PZV), SV |
SARS-CoV-2 | NA (no investigation was performed) *This paper investigated different ventilation strategies to offer a better understanding and insights into effective ventilation design |
Among mechanical ventilation strategies, MV and PV have high use priority during the epidemic. DWV, PZW and SV have medium priority while DV is not recommended to be used in healthcare facilities during the pandemic. | [1] |
|
Indoor environment: King Abdullah University Hospital (KAUH)’s emergency department (ED) - divided into several functional spaces, including a patient waiting area, triage, recovery area, minor procedure room, a major operating room (OR), medical services and consultation rooms, and monitoring units Ventilation strategy: Mechanical ventilation - heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system - inlet and outlet grilles positioned 2.7m and 2.4m from the floor, respectively - 100% fresh air supply - total airflow rates: 11,500/h - temperature range: 24 – 26°C - relative humidity level: 30-60% |
SARS-CoV-2 | CFD: Mesh properties: - element maximum size: 100mm - number of elements: 16 × - growth rate: 1.2 - defeature size: 0.5mm - curvature minimum size: 1mm - curvature normal angle: 18° - skewness: 0.8 - inflation transition ratio: 0.75 - inflation number of layers: 5 k-Epsilon model Analysis type: steady state Inlet: - velocity inlets; turbulence intensity: 5% |
Results suggested that high–risk areas be isolated by doors. Inlets and outlets were suggested to be repositioned. Results showed that three critical ED areas, which were the overnight patient bed, surgical rooms and resuscitation rooms had much higher air velocity, dispersion and mixing levels. |
[76] |
|
Indoor environment: Operating room (OR) - dimension: 5.48m × 5.44m × 2.5m - swing door at one corner; dimension: 1.98m × 0.98m Ventilation strategy: Mechanical ventilation - OR was equipped to supply air at different flowrate through an overhead diffuser, wall-mounted grilles or several floor-mounted baffles - diffuser was mounted on the wall, 0.3m from the ceiling; dimension: 0.3m × 0.3m |
SARS-CoV-2 | Inlet airflow flow regime: - Still air - 70% air; positive pressure differential of 10Pa between the room and outside - 100% air; 190cfm (90L/s) air inlet; steady state Door opening exercise: - once - twice Average door operation time: - range of 5 – 13s Data logging duration: 60s Number of repetitions: 60 |
The points closest to the door tip responded to the changes quicker than those located further, thus indicating that the transient change in velocity field from the door opening and closing was location specific At 100% air inlet airflow condition, 7.5 of air can leave every time the swing door is operated, thus indicating that almost 2 ACH of air escapes during a typical surgical procedure. |
[77] |
|
Indoor environment: Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital (Changgung Hospital)’s fever clinic (FC) and ED that was located in the outpatient building Ventilation strategy: FC: natural ventilation ED: Mechanical ventilation |
SARS-CoV-2 | Quantitative assessment of nosocomial infection risk: - direct measurement method - surrogate method |
Real-time concentration can be used as an indicator for evaluating ventilation conditions. |
[78] |
|
Indoor environment: Indoor hematologic ward. Divided into 16 rooms. Ventilation strategy: Eight rooms were classified as positive pressure, with HEPA filters. The remaining eight rooms were designed with ambient air |
SARS-CoV-2 | Whole–genome sequencing: - viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) was extracted to determine viral genomic sequences - human ribosomal RNA was depleted to isolate pure SARS-CoV-2 only Airflow simulation: - carried out using the conventional CFD program STAR-CCM+ ver 2020 - realizable k – epsilon model used for turbulence model |
Based on the airflow simulation, even though the patient from room 1, which was located adjacent to the bathroom did not use the shared bathroom, the air was spread from the bathroom to room 1. Due to the unintended negative pressure of the adjacent room, airflow was associated with poor ventilation in the shared bathroom Thus, the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 could happen quickly in the multi-patient room such as the hematologic ward |
[38] |
|
Indoor environment: Four–bed intensive care unit (ICU) - dimension: 7m × 6.3m × 2.5m - area per patient: 11 - two beds were placed along both the left – and right–hand sides of the room (2.67m distance between the beds) Ventilation strategy: Two forms of MV - MV – ceiling air ventilation - side air ventilation Impinging jet ventilation (IJV) - supplies high–momentum air downwards from an air inlet near the ground level - moves fresh air from an indoor floor to the ceiling Ventilation strategies consist of: - two IJV air supply inlets and two IJV return air outlets - two MV return air inlets and outlets each - two MV side air inlets and two MV outlets |
Airborne infectious disease / nosocomial infections | Air supply ventilation rate: 6 – 12 ACH (8 ACH was selected for the study) Air supply velocity: - IJV: 1.47M/S - ceiling air ventilation: 0.57m/s - side air ventilation: 0.44m/s The temperature of supplied air: 17°C The relative humidity effect was neglected Heat flux density: 35 W/ Patient’s mouth area / expiratory area: 1.3 Exhalation speed and flowrate: 3.85m/s and 30L/min, respectively Exhaled flow temperature: 35°C Boundary effects on particles at walls and exhaust outlets were set as “trap” and “escape”, respectively |
Results showed that IJV exhibited the “plug flow” characteristic that removes fine particles efficiently and reduced the infection, thereby reducing cross–infection Compared to ceiling air ventilation, side air ventilation increased infections. |
[79] |
|
Indoor environment: Comprised of different scales: - whole building - room - personal space - breathing zone Ventilation strategy: Indoor air quality (IAQ) control strategies: - source control - ventilation - air cleaning |
Respiratory diseases: SARS-CoV-2, influenza, tuberculosis, middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and measles |
Outdoor air rate: - baseline supply air with different cases of 50%, 75%, and 100% outdoor air, respectively Total supply airflow rate: - 50% more supply air, 25% outdoor air - double supply air, 25% outdoor air Air distribution: - MV baseline with DV - MV baseline with partitions (semi-open space) - MV baseline with DV + partitions |
Effectiveness of multi-scale control strategies: - average risk reduction of 27% was achieved when using 100% outdoor air - reduction of 37% in average-risk was achieved after doubling the total sir supply - DV reduced 26% average infection risk, while partitions achieved a 46% reduction in infection risk - integrating both DV and partitions achieved 96% infection risk reduction |
[80] |
|
Indoor environment: Two Hospital OR - OR1 area: 53 - OR2 area: 51.84 Ventilation strategy: MV system – the supply air was quickly and evenly mixed with air in the indoor environment Laminar airflow (LAF) system – unidirectional, low-turbulence downward airflow that was delivered by a large surface over the operating area Ventilation rate: - OR1: 3700/h - OR2: 12, 850/h |
Nosocomial infectious disease | Bacteria concentration: ~0.1/min Particle concentration range: 0.3 – 10.0µm Air temperature rate: 20 - 60°C; ±0.2°C accuracy Relative humidity: 0 – 90%; ±1.1% accuracy |
OR with MV system was deemed “unsuitable” due to unsatisfactory performance in thermal comfort indexes and energy consumption OR with LAF was identified as “suitable”. This is due to the guaranteed clean and safe operation environment |
[81] |
|
Indoor environment: A room - dimension: 9m × 9m × 4m - a manikin (1.75m tall) as infector, placed at the centre of the room Ventilation strategy: MV - circulated curtain system formed by four air pillars (2m–height, each) that surrounded the manikin in a quadrilateral shape - inlet’s outlet’s widths were 20mm and 40mm, respectively - the distance between the human and air pillar was 1.5m |
SARS-CoV-2 | CFD: - Jet velocity from the air pillar: 3.5m/s - SIMPLE algorithm, second–order upwind scheme (FLUENT 17.0) - RNG k – Epsilon turbulence model - non – slip boundary conditions were applied to all walls - discrete phase model (DPM) |
Airflow patterns with air curtain - velocity gradually decreased from inlet to outlet - strong turbulence was observed for air curtains with fewer air pillars Dispersion of exhaled contaminants -airflow rotated clockwise, influenced by the action of the air curtain - air curtain effectively prevented contaminants from spreading outwards Results proved that air curtain has great potential in reducing cross–infection risk. This was due to air pillars generating exhaled flow with vortex–like clockwise rotation. |
[82] |
|
Indoor environment: The actual hospital, evacuated for renovation - hospital zones and construction zones were separated by two swing door - to control dust migration, the doors were sealed with no vestibule - no pressure differentials between the two zones Ventilation strategy: - supply diffusers (9) and exhaust grilles (1) were placed according to the mechanical plan |
Airborne particulates (not specified) | Exhaust grilles: - size: 0.2m × 0.2m - flowrate at boundaries (negative mode): 0.098/s - flowrate at boundaries (neutral mode): 0.098/s Supply diffusers 1 – 4: - size: 0.3m × 0.3m - flowrate at boundaries (negative mode): 0.030/s - flowrate at boundaries (neutral mode): 0.060/s Supply diffusers 5: - size: 0.6m × 0.6m - flowrate at boundaries (negative mode): 0.060/s - flowrate at boundaries (neutral mode): 0.120/s Supply diffusers 6 – 9: - size: 0.3m × 0.3m - flowrate at boundaries (negative mode): 0.030/s - flowrate at boundaries (neutral mode): 0.060/s |
The concentration of the contaminant was larger under the negative airflow model, due to the overall upward motion of air An additional increase of 26% in particulate removal can be achieved according to the supply and exhaust air location |
[83] |
|
OR in New Karolina Solna University Hospital - separated from the adjacent corridor by a partition wall (0.2m-thickness) - dimension: 8.6m × 7.5m × 3.2m - corridor dimension: 7.5m × 2.8m × 3.2m - a doorway was created by opening the partition wall; dimension: 1.5m × 2.1m (L × H) Ventilation strategy: MV - air supplied through 24 diffusers in the ceiling; total airflow rate: 2.0 /s; dimension: 0.6m × 0.6m with 9 × 9 nozzles - corridor was ventilated at an airflow rate of 0.12/s, with air discharged through two ceiling-mounted diffusers (0.6m × 0.6m) and extracted through four exhaust vents (0.35m × 0.35m) near the corner of the ceiling - OR was kept under a positive pressure of 5Pa - supply air to the OR was kept at a constant 20°C |
Airborne infectious disease / surgical site infectious disease | Numerical model: Two – equation Realizable k – Epsilon model was adopted The staggered scheme PRESTO! was applied Pressure – based segregated solver was used in ANSYS FLUENT 18.2, with a SIMPLE algorithm |
Under a temperature difference of 3°C, the overall OR contamination increased by 2.1 colony-forming units per cubic meter (CFU/) by a single-door opening A 20 – 30% reduction in the OR exhaust flow decreased airborne bacteria–carrying particles (BCP)’s contamination to a sufficiently low level |
[84] |
|
Indoor environment: A closed chamber - dimension: 3m × 3m ×2.69m - all envelopes (four walls, ceiling, and floor) were insulated with a 50mm-thick polystyrene layer - two people simulators (manikins) were used Ventilation strategy: DV with a vertical radiant panel - chamber was kept at 23 – 26°C (except the underfloor) - fresh air was supplied from a semi-circular wall-mounted diffuser (0.4m × 0.26m × 0.75) that was located on the floor in the middle of the wall - exhaust grill (with 200φ holes) was mounted on the ceiling near the wall where the inlet was placed. |
NA |
the flow rate was controlled at 0.5L/min Inhaled air was maintained at 14.4L/min |
When a vertical radiant panel was utilized for heating, it generated a stronger plume that diffused contaminated air As the supply airflow rate increased, the height of the interface layer and stagnation went up Personal exposure of a standing person was less contaminated than their surrounding at the breathing zone height |
[85] |
|
Indoor environment: A hospital ward located in Nanjing, China. - there was a corridor in the centre of the ward, and three cubicles on both sides (8.0m × 2.7m × 5.5m) - cubicle’s door (2.1m × 1.4m) linked to the corridor and windows (1.0m × 1.6m) were located on the wall opposite the door Ventilation strategy: Natural ventilation |
Airborne infectious disease | Validation: particle distribution in a ventilated chamber - ventilated chamber - one inlet and one outlet (same rectangular shape) on opposite walls - room air and particles were mixed and supplied through the inlet Case description: - heat flux: ~25W/ - wind speed range: 0.5 – 4 m/s - exposure duration for each patient: 4h - pulmonary ventilation: 0.36/h - inhalation and exhalation were in a steady state at a speed of 0.77m/s - exhalation air temperature: 34°C |
Due to the index patient being located in the corridor and the opposite upstream cubicle, results from the simulation showed that the predicted infection risks of the downstream cubicle were up to 10.48% and 11.58%, respectively |
[86] |
|
Indoor environment: Hospital consulting room - dimension: 6.53m × 3.07m × 2.80m - table and cabinet were placed against the inner wall. Ventilation strategy: - air inlet and outlet were rectangular settings at the top of the room. - two arrangements of the examination bed, one was located in the corner, and the other was located in the middle of the room, named Position A and Position B, respectively. |
SARS-CoV-2 | Simulation cases: - inlet and outlet boundary conditions for the particles were set as “escape” - boundary conditions on the walls for the particles were set as “trap” - cough was used as the injection mode of the droplet aerosols; time of occurrence: 0s; lasted for 2s; velocity: 10.8m/s - droplets’ diameters and density were 3µm and 1000kg/, respectively - airflow temperature for coughing: 308K - initial droplet aerosols were assumed to consist of 98.2% water and 1.8% solid in volume |
Droplet aerosols were discharged earlier by the existing ventilation system when the bed was arranged in the centre of the room, under the same conditions As the air velocity increased, the purification capacity of the ventilation system increased in both arrangements. However, the ventilation strategy involving Positive B performed better at a low air velocity |
[87] |
|
Indoor environment: Room; personal space; breathing zone Ventilation strategy: MV, DV |
SARS-CoV-2 | Emission mode: - breathing - talking Personal physical distance |
Compared to MV, an exhalation jet from the infector under DV can penetrate the breathing zone of an exposed person. This resulted in higher human exposure to viral aerosols Due to a dilution effect and a more pronounced air stratification, human exposure can be effectively reduced by increasing the ventilation rate |
[88] |
|
Indoor environment: Four–bed hospital ward - dimension: 5m × 5.55m × 2.77m - 12.5mm plasterboard was installed and assumed to be adjacent to the outdoor air - Outer chamber (OC): a space between two walls, simulated the outdoors Ventilation strategy: DV - air inside the OC was fully mixed by circulators - clean air was supplied through five supply inlets (0.32m × 0.62m).; HEPA) filters were installed in each supply inlet. - supply air temperature was controlled at 15°C and 20°C - exhaust opening (φ = 0.13m) was in the ceiling - extract airflow rate: 391/h - exhaust air temperature range: 15 – 22°C |
NA | Simulation: - four person simulators were placed on each bed to simulate a person lying down (φ = 0.3m; H = 1.5m each, respectively) - heat generated by each person was maintained at 40W - total heat generation in the experimental room was 400W - flow rate was maintained at 0.5L/min for each emission (2.0L/min total) |
The contaminated air in the upper zone was transported back to the occupied zone as there was a downward convective airflow along the vertical surface in a room with DV The contaminant stagnated before reaching the ceiling due to the upward convection airflow along the wall was stronger than the contaminated plume |
[89] |
|
Indoor environment: Two–bed hospital ward - dimension: 5.5m × 3.0m × 2.4m - heat sources were two patients, one healthcare worker and three ceiling lamps Ventilation strategy: SV - four air supply grilles are mounted on the wall opposite to the headboards and the centre height was 1.5 from the floor MV - three air supply four–way diffusers on the ceiling DWV - three air supply grilles on the ceiling For all three ventilation strategies above - two exhaust louvres were 1,5m above the floor on the wall near the bedhead - air supply grilles size: 0.2m × 0.2m DV - air supply diffuser was 0.15m above the floor (1.0m × 0.6m) - exhaust louvres were on the ceiling above patient |
Airborne infectious disease | Two scenarios: - Scenario 1: both patients lying in bed - Scenario 2: Patient 1 was sitting, and Patient 2 was lying in bed concentration from patient’s mouth: 4000 ppm The velocity of breathing and coughing flow was 0.89m/s and 20m/s, respectively Mouth size: 0.02 × 0.02 Supply air flow rate: 12 ACH |
Contaminant concentration in the breathing zone was comparably lower under SV. The breathing zone ranged from around 1.3m to 1.7m |
[90] |
|
Indoor environment: Hospital environment, specifically in the chemical-related department such as drugs rooms Ventilation system: 0 – 2%, 40 – 60% humidity, airflow, temperature window 400 – 600°C |
Diseases caused by emission |
decomposition tests: - the flow of model feed: 5%, 30L/min - a mixture of gases typical for hospital ventilation system: 0.5%, 2 vol. % , 2 vol. % , 30L/min - total gas hourly space velocity for powdered catalyst: 7000 estimated |
Results showed that even the addition of a minor amount of Pb enhanced the catalytic activity of cobalt spinel |
[91] |
|
Indoor environment: Typical semi-closed six-bedded general inpatient ward cubicle - dimension: 7.5m × 6m × 2.7m - 1m between–bed spacing Ventilation strategy: Mechanical ventilation - positive pressure towards the corridor - accommodated six supine patient - supply air was delivered to the cubicle through four ceiling-mounted diffusers - supply air and ward air exhausted to the corridor was set to be equal for all ACH - for exhausting 10% and 50% of the supply air, local exhaust grilles (0.5m × 0.2m) were installed |
MERS-CoV | CFD simulation: Computational domain - 7.5m × 6m × 2.7m; RNG k–Epsilon turbulence model with enhanced wall treatment Total supply airflow rate - 0.1240 kg/s for ACH = 3; 0.2480kg/s for ACH = 6; 0.3720kg/s for ACH = 9; 0.5374kg/s for ACH = 12; air temperature: 285K Inlet (0.6m × 0.6m) airflow rate - 0.031kg/s for ACH = 3; 0.062kg/s for ACH = 6; 0.093kg/s for ACH = 9; 0.1343kg/s for ACH = 12; air temperature: 285K Diffuser (0.6m × 0.6m) - four supply diffusers; 4 – way spread patterns; air supplied at an angle of 15°C from ceiling; adiabatic Exhaust grille (0.5m × 0.2m) - outflow with flowrate weighting; 295K (backflow temperature); adiabatic; escape boundary condition; exhaust air: 0% / 10% / 50% of total supply air |
Within a mechanical ventilated space, both air change and exhaust airflow rates have significant effects on the particle distribution | [92] |
|
Indoor environment: OR Ventilation strategy: VLAF, horizontal laminar flow system (HLAF) system, slot fan system |
Airborne infectious disease | Case 1 (VLAF) - pressure setup: +15Pa - temperature setup: 20°C - inlet (3.1m × 2.6m) position: in the upper operating table (ceiling) - outlet (0.58m × 2.6m) position: behind interlayer - velocity inlet: 0.33m/s - method: simulation and experimental Case 2 (HLAF) - pressure setup: +15Pa - temperature setup: 20°C - inlet (2.35m × 1.76m) position: on the wall in front of interlayer - outlet (0.58m × 2.6m) position: behind interlayer - velocity inlet: 0.33m/s - method: simulation and experimental Case 3 (slot fan) - pressure setup: +15Pa - temperature setup: 20°C - inlet (0.025cm × 1.2m) position: in the upper operating table (ceiling) - outlet (0.58m × 2.6m) position: behind interlayer - velocity inlet: 0.33m/s - method: simulation |
Case 2 was determined as the best case in ventilation and removal efficiency. | [93] |
|
Indoor environment: The test room is located in a laboratory hall - dimension: 4.4m × 4.7m × 2.6m Ventilation strategy: SV - 100% outdoor air was supplied horizontally into the test room from one sidewall through a perforated diffuser - while room air was exhausted through a perforated diffuser mounted on the opposite wall - room air temperature was maintained constant at 22, 24 or 28°C - supply air temperature varied by approximately 0.3°C - two types of supply diffusers were performed: four circular diffusers and one large rectangular diffuser. |
Airborne infectious disease | Experimental condition - steady-state condition - room air temperature was stabilized at ±0.1°C - 18 cases - ACH range: 2 – 6 ACH |
The mixing between the exhaled air and the room air was intensified by the air supplied horizontally to the breathing zone. This reduced the exposure risk of a person near and flattened the risk-distance curves. |
[94] |
|
Indoor environment: Small single–bed patient ward - dimension: 3.5m × 2.5m × 2.65m Ventilation strategy: Protected occupied zone ventilation (POV) - POV was designed to shield occupants from cross-contamination by dividing an indoor space into two zones with different levels of contaminant concentrations using a downward plane jet - a slot diffuser was installed in the middle of the room, 2.2m above the floor - room temperature was maintained at 23.1 ± 0.3°C - two circular exhaust openings with opening areas of 0.0256 were located in the sidewalls |
Airborne infectious disease | CFD simulation: Turbulence model - RNG - Realizable - SST k – ω |
SST k – ω models predicted the velocity and temperature profiles agreeably according to the experimental findings, compared to the other two turbulent models | [95] |
|
Indoor environment: Isolation ward Dimension: 4.0 m × 2.5 m × 2.65 m Ventilation strategy: Ceiling-mounted supply air diffuser (unidirectional airflow) with air curtain Inlet air velocity: 19°C |
Airborne infectious disease | CFD simulation: Turbulence model -RNG k-ε Particle tracking: -Discrete phase model |
Utilising the combination of ceiling-mounted air diffuser and air curtain jet results in zero particle settlement on both patient’s and the patient’s bed. | [96] |
|
Indoor environment: Isolation ward 6.0 m × 4.2 m × 3.0 m Ventilation strategy: Ceiling-mounted supply air diffuser (Unidirectional airflow) Inlet air velocity: 16.55°C Turbulent intensity: 10% Velocity: 0.77 m/s |
Airborne infectious disease | CFD simulation: Turbulence model -RNG k-ε Particle tracking: -Discrete phase model |
A higher walking speed of 1.0 m/s reduces the number of particles settled on the burn patient, therefore potentially reducing the associated nosocomial infection risk. | [97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





