Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
03 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
0.1. Review objectives and research strategy
0.2. Content of the article
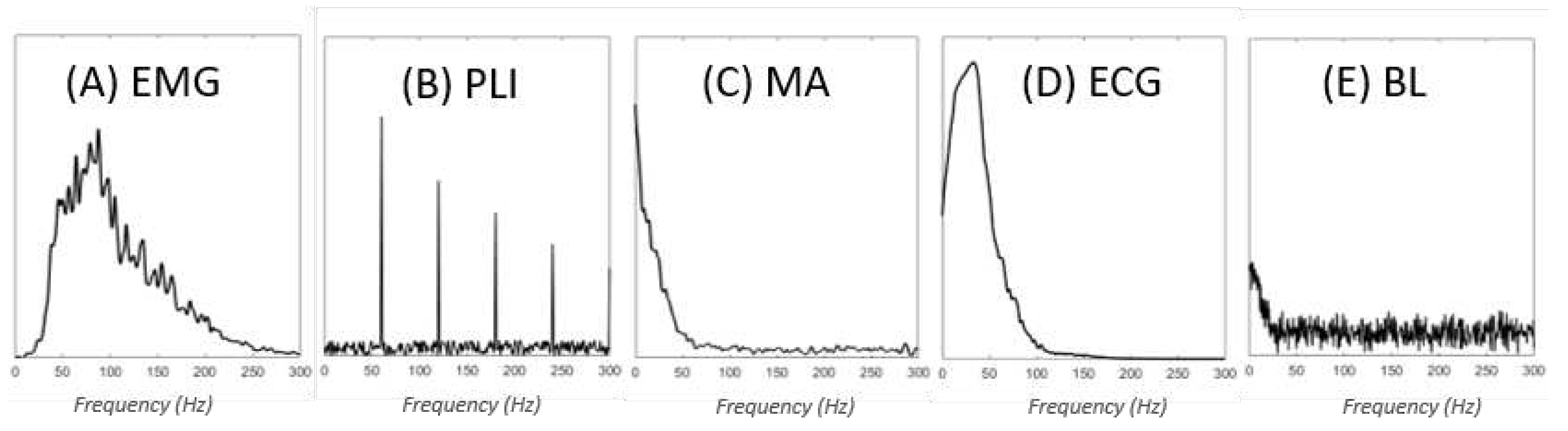
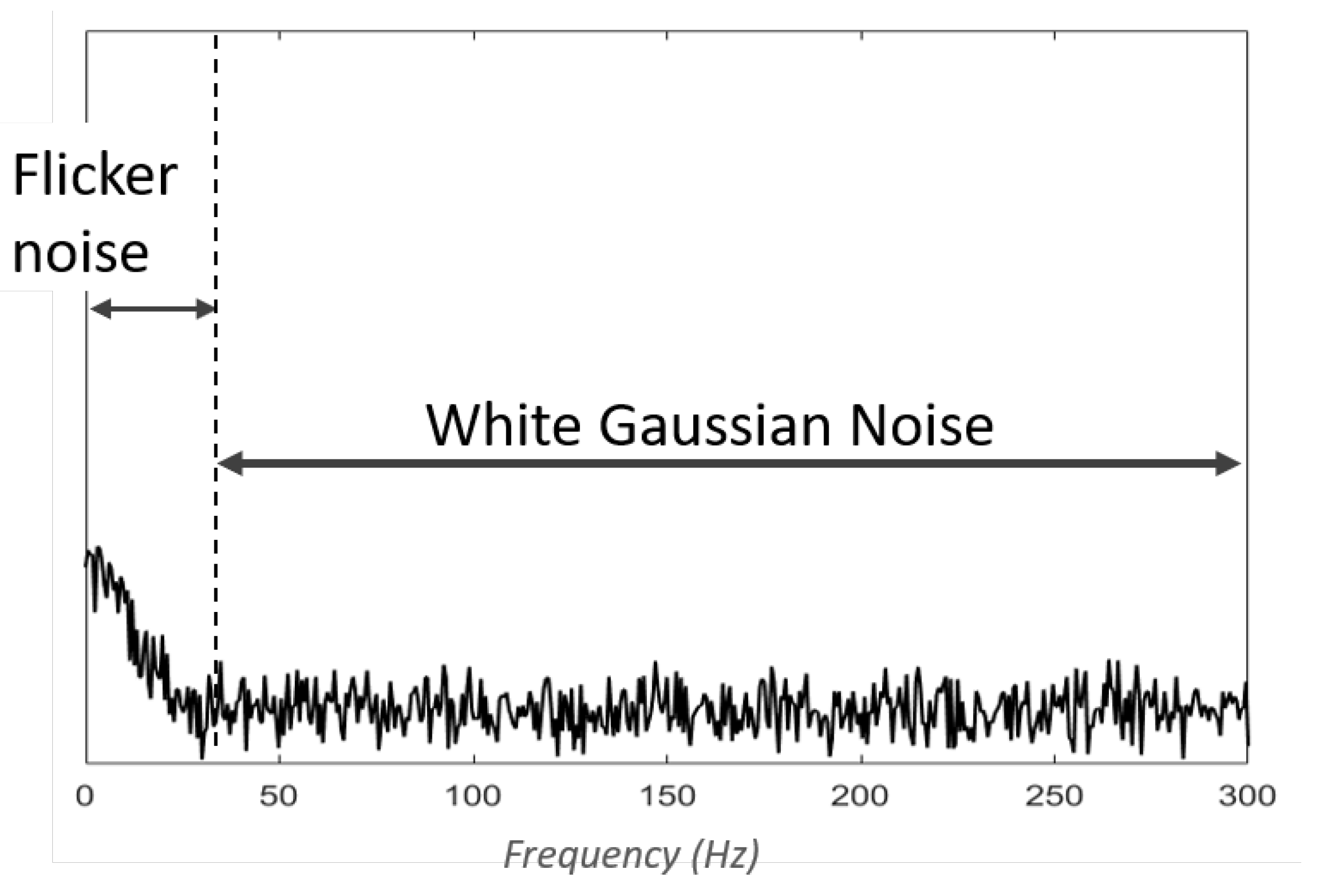
1. Contaminant types
1.1. Other terminology considerations
2. Contaminant Reduction methods
2.1. Conventional digital filters
2.2. Gating and clipping methods
2.3. Subtraction methods in the time domain
2.3.1. Estimation of PLI using the regression method on a reference signal:
2.3.2. Estimation of PLI using spectral analysis on a reference signal:
2.3.3. Estimation of PLI using the least squares algorithm on the signal itself
2.3.4. Template estimation of the ECG interference signal
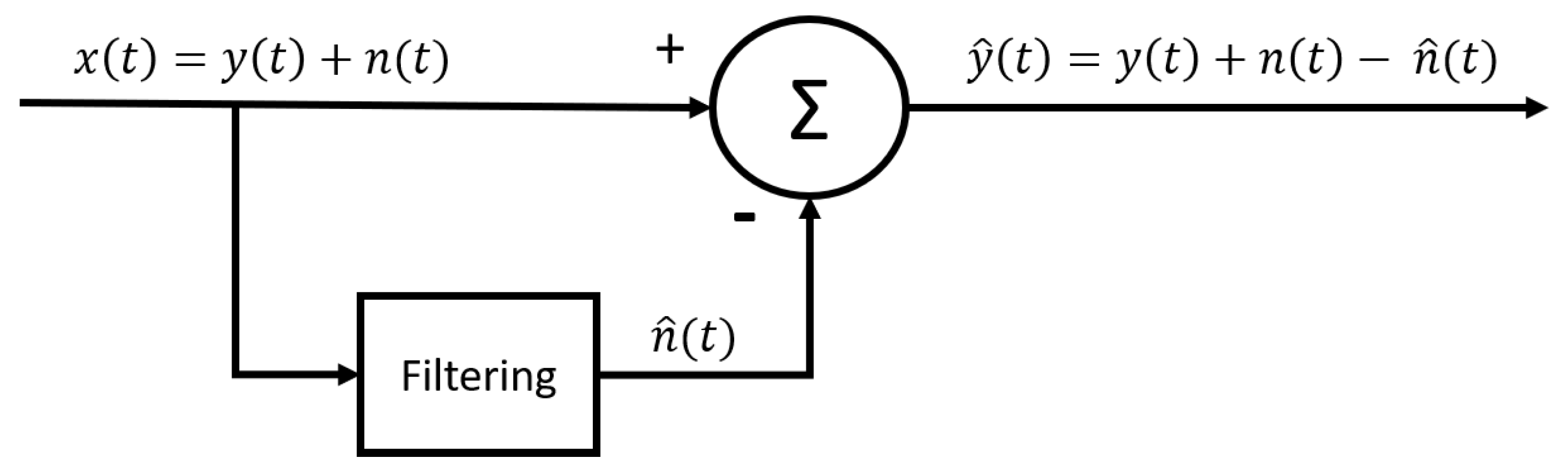
2.3.5. Adaptive estimation of the interference signal by means of filtering the raw signal
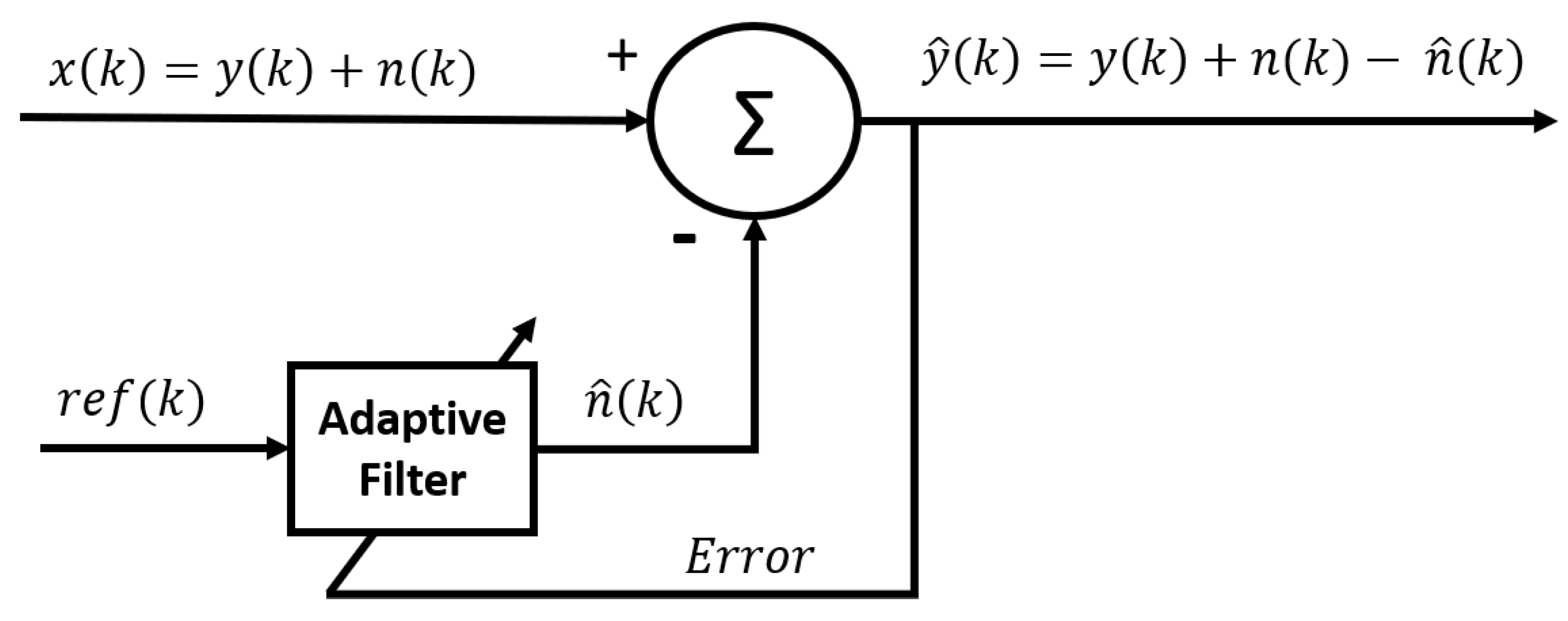
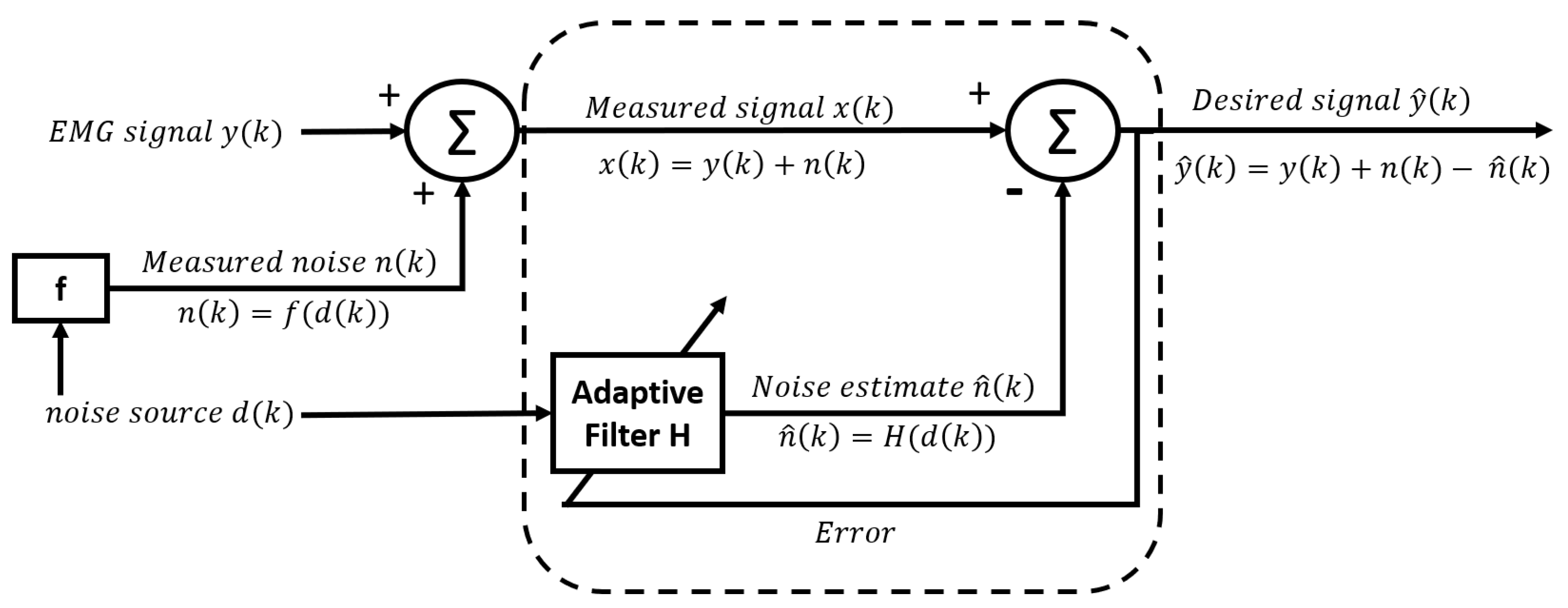
2.3.6. Adaptive noise canceller (ANC)
2.3.7. Nonlinear ANC
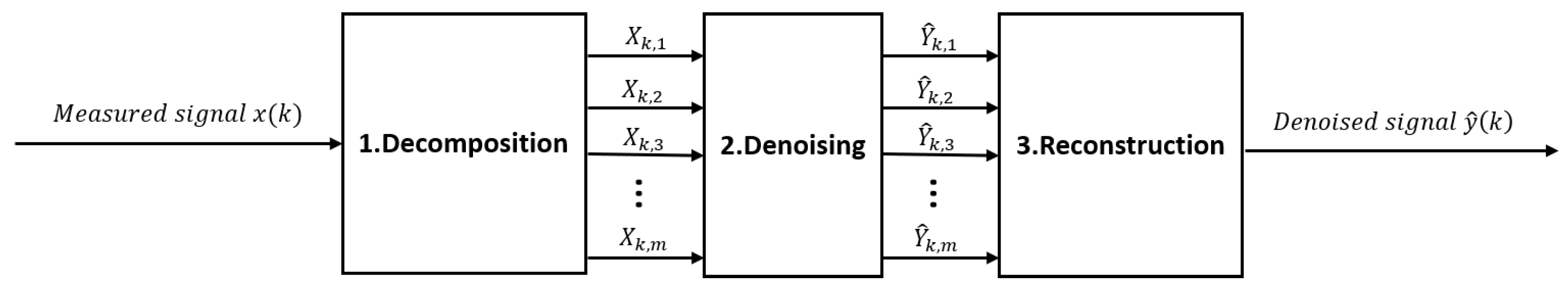
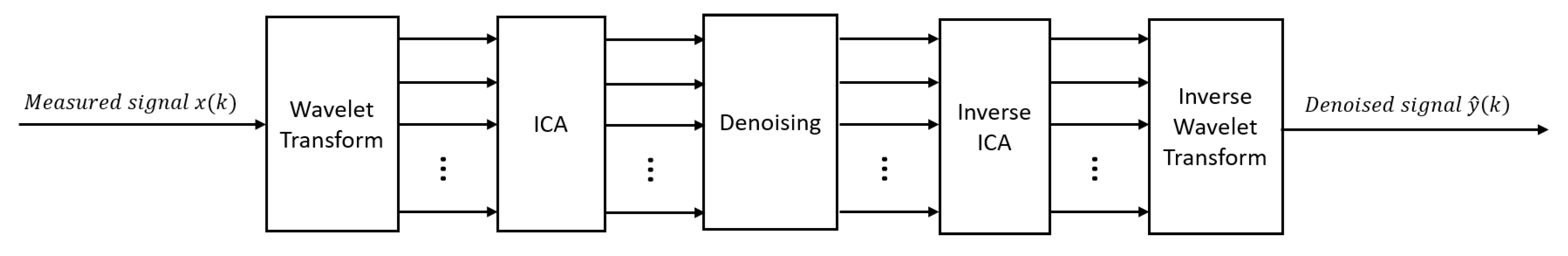
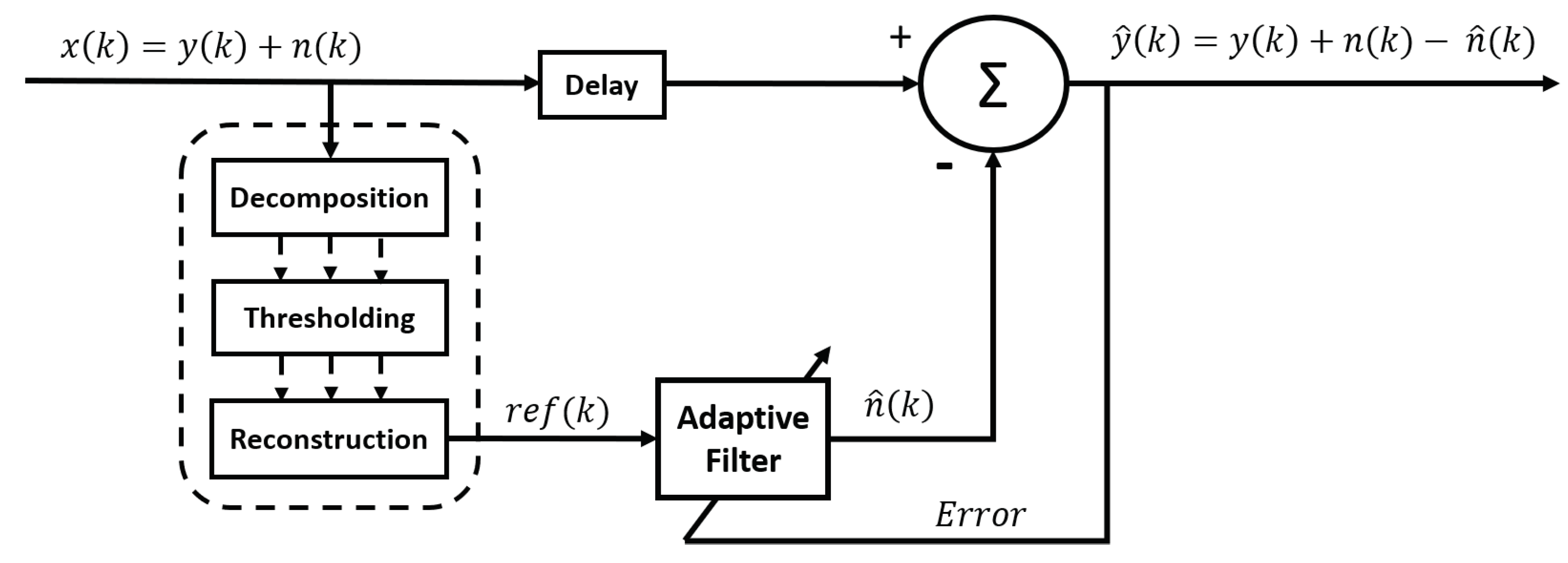
2.4. Denoising methods after signal decomposition
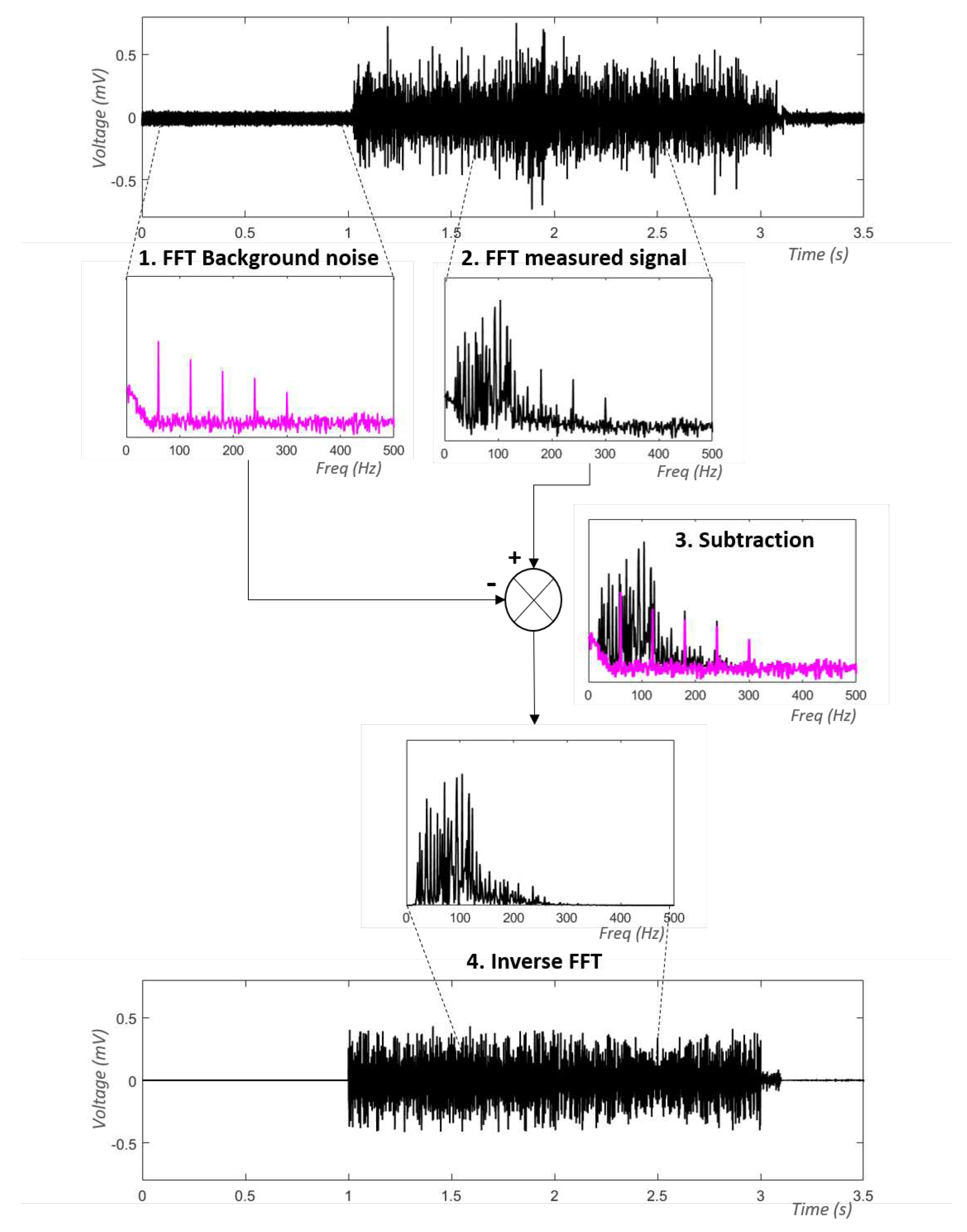
2.4.1. Decomposition methods after Fourier decomposition
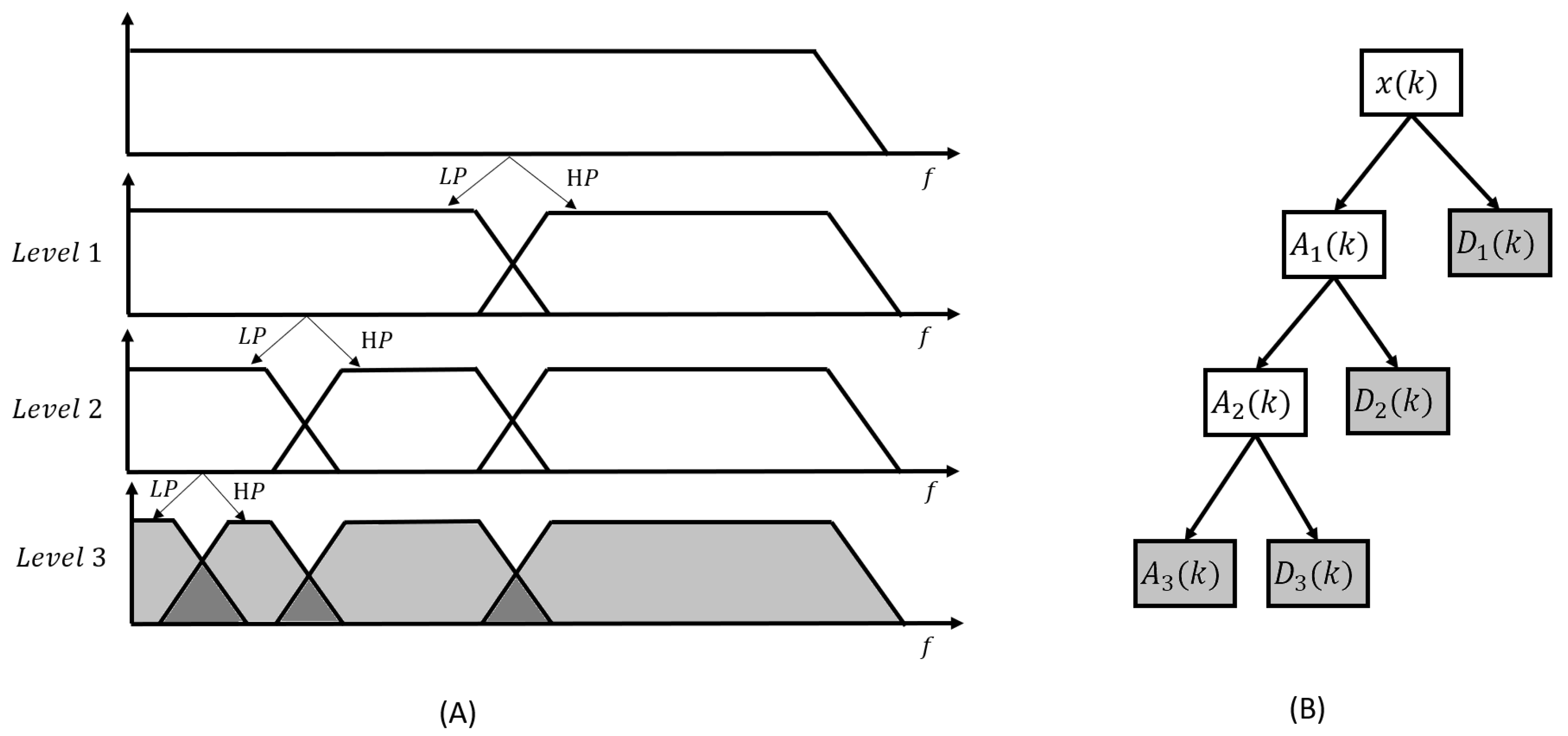
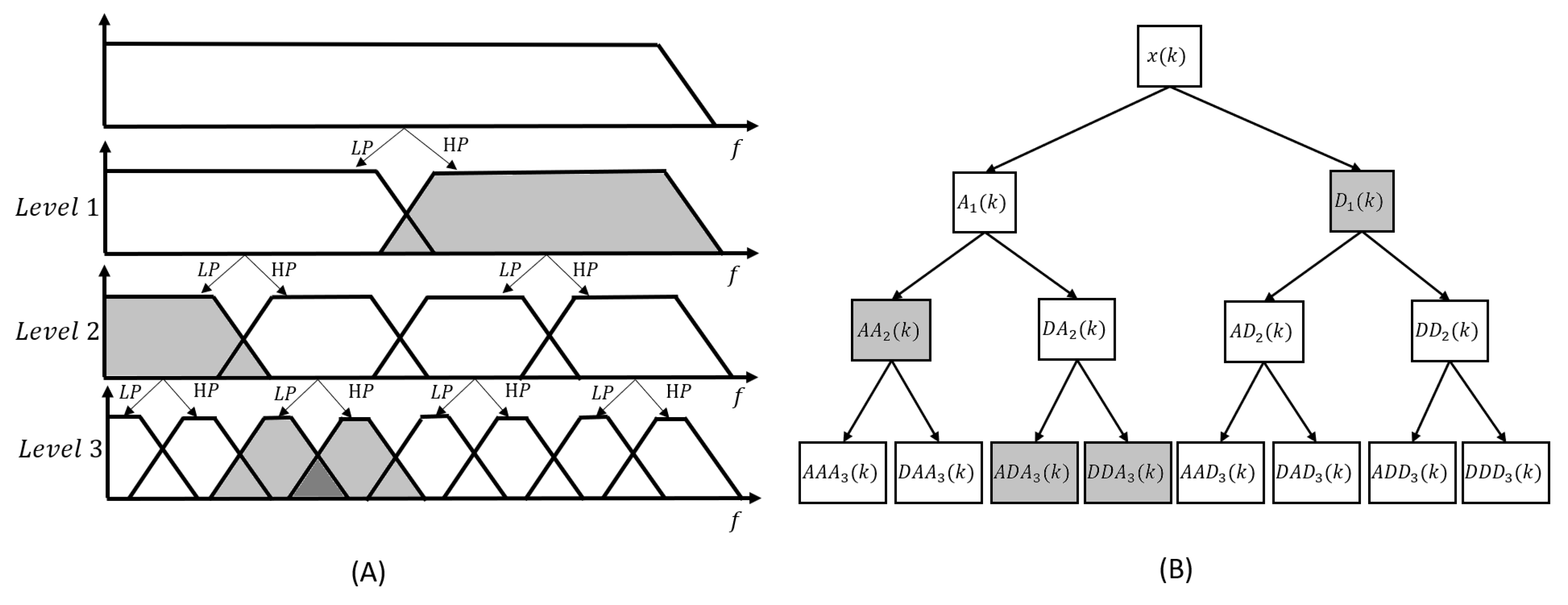
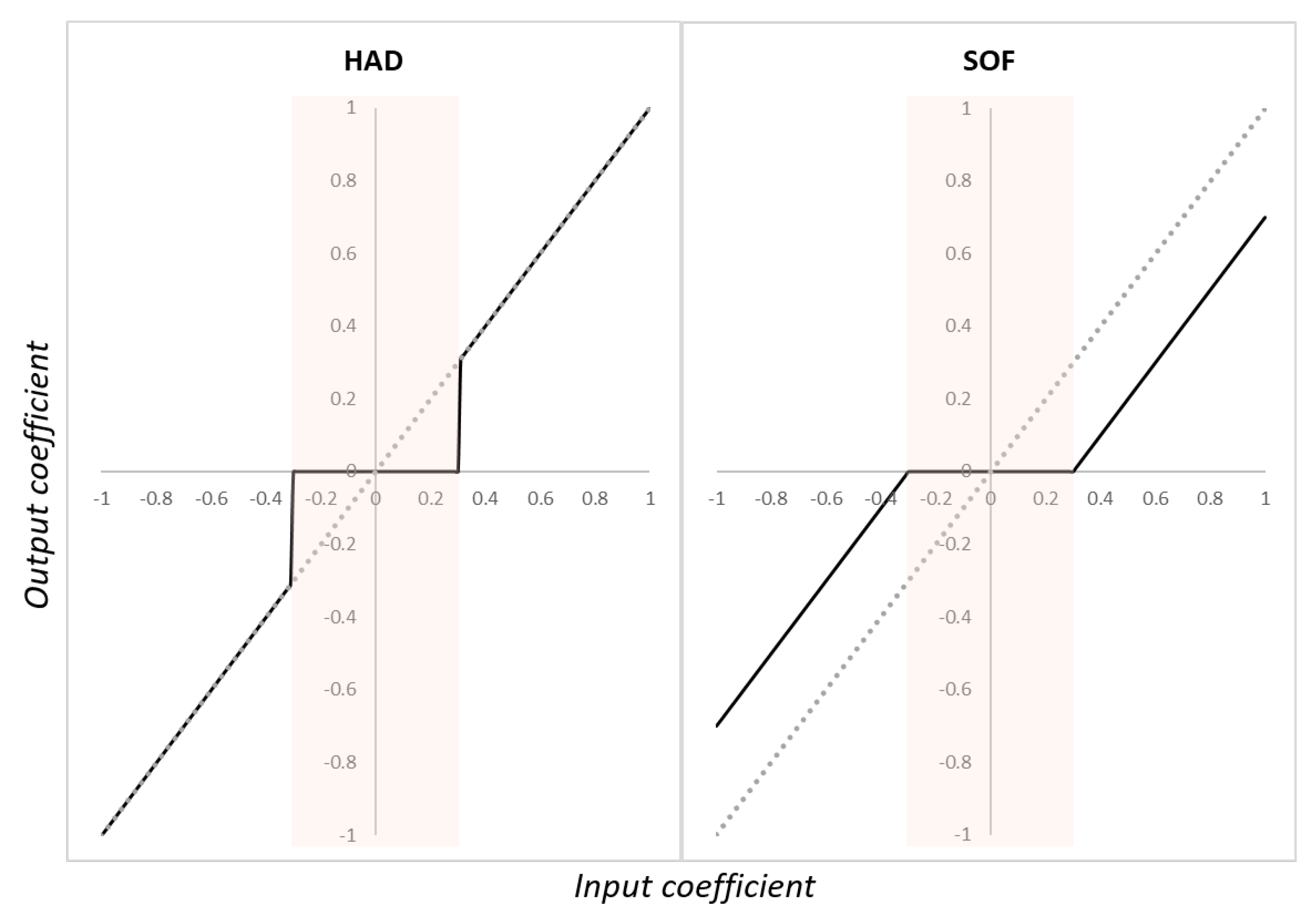
2.4.2. Denoising methods after wavelet decomposition
2.4.3. Denoising after empirical mode decomposition (EMD)
2.4.4. Denoising after variational mode decomposition (VMD)
2.5. Combining methods and hybrid methods
3. Performance evaluation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, B.; Saad, I.; Bolong, N.; Siew, K.E. A Review of Surface EMG in Clinical Rehabilitation Care Systems Design. 2021 IEEE 19th Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD). IEEE, 2021, pp. 371–376. [CrossRef]
- Rozaqi, L.; Nugroho, A.; Sanjaya, K.H.; Simbolon, A.I. Design of Analog and Digital Filter of Electromyography. 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA). IEEE, 2019, pp. 186–192. [CrossRef]
- Corvini, G.; D’Anna, C.; Conforto, S. Estimation of mean and median frequency from synthetic sEMG signals: Effects of different spectral shapes and noise on estimation methods. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Quantification and solutions of arm movements effect on sEMG pattern recognition. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2014, 13, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.; Naber, A.; Ortiz-Catalan, M. Improved Prosthetic Control Based on Myoelectric Pattern Recognition via Wavelet-Based De-Noising. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2018, 26, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Cerone, G.L. Tutorial. Surface EMG detection, conditioning and pre-processing: Best practices. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2020, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.O.; Nasuto, S.; Kyberd, P.; Sweeney-Reed, C.M.; Van Kanijn, F.R. EMG signal filtering based on Empirical Mode Decomposition. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2006, 1, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.D.; Chan, A.D.; Green, J.R.; Macisaac, D.T. Automated biosignal quality analysis for electromyography using a one-class support vector machine. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2014, 63, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, P.; Fraser, G.D.; Chan, A.D.; Petropoulakis, L.; Soraghan, J.J. Identification of contaminant type in surface electromyography (EMG) signals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2014, 22, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J.; Donald Gilmore, L.; Kuznetsov, M.; Roy, S.H. Filtering the surface EMG signal: Movement artifact and baseline noise contamination. Journal of Biomechanics 2010, 43, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huigen. E.; Peper, A.; Grimbergen, C.A. Investigation into the origin of the noise of surface electrodes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput 2002, 40, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.D.; Callaghan, J.P. Elimination of electrocardiogram contamination from electromyogram signals: An evaluation of currently used removal techniques. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology 2006, 16, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Reducing Motion Artifacts and Interference in Biopotential Recording. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1984, BME-31, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.R. Computational intelligence in electromyography analysis: a perspective on current applications and future challenges 2012.
- De Talhouet, H.; Webster, J.G. The origin of skin-stretch-caused motion artifacts under electrodes. Physiological Measurement 1996, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, E.A.; Morin, E.L.; Merletti, R. Sampling, noise-reduction and amplitude estimation issues in surface electromyography. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology 2002, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, R.V.; Solomonow, M.; Zhou, B.H.; Zhu, M. Methods to reduce the variability of EMG power spectrum estimates. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 1998, 8, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivanovic, M.; Niegowski, M.; Lecumberri, P.; Gómez, M. A low-rank matrix factorization approach for joint harmonic and baseline noise suppression in biopotential signals. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2017, 141, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayvargiya, A.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, R.; Dey, N.; Tavares, J.M.R. A hybrid WD-EEMD sEMG feature extraction technique for lower limb activity recognition. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 20431–20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A.; Rau, G.; Kadefors, R.; Broman, H.; De Luca, C. Units, terms and standards in the reporting of EMG research. International Society of Electrophysiological Kinesiology 1980. p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Merletti, R.; Di Torino, P. Standards for reporting EMG data. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 1999, 9, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Stegeman, D.; Hermens, H. Standards for surface electromyography: The European project Surface EMG for non-invasive assessment of muscles (SENIAM). Enschede: Roessingh Research and Development 2007, 10, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxtel, A. Optimal signal bandwidth for the recording of surface EMG activity of facial, jaw, oral, and neck muscles. Psychophysiology 2001, 38, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, E.A.; Farry, K.A. Adaptive whitening of the electromyogram to improve amplitude estimation. IEEE transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2000, 47, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, G.; Jiang, G.; Chen, D.; Liu, H. Surface EMG data aggregation processing for intelligent prosthetic action recognition. Neural Computing and Applications 2020, 32, 16795–16806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, S.; Raoof, K. Noise removal from surface respiratory EMG signal. International Journal of Computer, Information, and Systems Science, and Engineering 2008, 2, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer, T.; Fitzgerald, J.; Bowden, J.; Lynne-Davies, P. Spectral analysis of human inspiratory diaphragmatic electromyograms. Journal of Applied Physiology 1979, 46, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, M.S.; Hughes, R.E.; Chaffin, D.B. High-pass filtering to remove electrocardiographic interference from torso EMG recordings. Clinical Biomechanics 1993, 8, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: detection, processing, classification and applications. Biological procedures online 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Lock, B.; Kuiken, T.A. Real time ECG artifact removal for myoelectric prosthesis control. Physiological measurement 2007, 28, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhou, B.; Sawan, M.; Desilets, T.; Bellemare, F. Real-time filtering technique to remove ECG interference from recorded esophageal EMG. 2008 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference. IEEE, 2008, pp. 21–24. [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.W.; DeFreitas, J.M.; Cramer, J.T.; Stout, J.R. A comparison of adaptive and notch filtering for removing electromagnetic noise from monopolar surface electromyographic signals. Physiological measurement 2009, 30, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiana-Merino, J.J.; Ruiz-Fernandez, D.; Martinez-Espla, J.J. Power line interference filtering on surface electromyography based on the stationary wavelet packet transform. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine 2013, 111, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, M.; Gonzalez-Izal, M. Simultaneous powerline interference and baseline wander removal from ECG and EMG signals by sinusoidal modeling. Medical engineering & physics 2013, 35, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.D.; Chan, A.D.; Green, J.R.; Abser, N.; MacIsaac, D. CleanEMG—Power line interference estimation in sEMG using an adaptive least squares algorithm. 2011 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, 2011, pp. 7941–7944. [CrossRef]
- Bloch, R. Subtraction of electrocardiographic signal from respiratory electromyogram. Journal of applied physiology 1983, 55, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.; Gillen, J.; Weiser, P.; Gillen, M.; Kwatny, E. Description and validation of an ECG removal procedure for EMGdi power spectrum analysis. Journal of applied physiology 1986, 60, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, A.; Dzwonczyk, R.; Roberts, O.; Goldman, E. Description and validation of a technique for the removal of ECG contamination from diaphragmatic EMG signal. Medical and biological engineering and computing 1996, 34, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, J.D.C.; de Seixas, J.M.; others. A template subtraction method for reducing electrocardiographic artifacts in EMG signals of low intensity. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2019, 47, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, A.H.; Juffermans, R.; Doorduin, J.; Heunks, L.M.; Harlaar, J. Estimated ECG Subtraction method for removing ECG artifacts in esophageal recordings of diaphragm EMG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 69, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbrollini, A.; Agostinelli, A.; Morettini, M.; Verdini, F.; Nardo, F.D.; Fioretti, S.; Burattini, L. Separation of superimposed electrocardiographic and electromyographic signals. In EMBEC & NBC 2017; Springer, 2017; pp. 518–521. [CrossRef]
- Conforto, S.; D’Alessio, T. Optimal rejection of artifacts in the processing of surface EMG signals for movement analysis. In Computer Methods in Biomechanics & Biomedical Engineering–2; CRC Press, 2020; pp. 799–805.
- Conforto, S.; D’Alessio, T.; Pignatelli, S. Optimal rejection of movement artefacts from myoelectric signals by means of a wavelet filtering procedure. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 1999, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, G.D.; Chan, A.D.; Green, J.R.; MacIsaac, D. Detection of ADC clipping, quantization noise, and amplifier saturation in surface electromyography. MeMeA 2012 - 2012 IEEE Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Proceedings 2012. pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marker, R.J.; Maluf, K.S. Effects of electrocardiography contamination and comparison of ECG removal methods on upper trapezius electromyography recordings. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2014, 24, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widrow, B.; Glover, J.R.; McCool, J.M.; Kaunitz, J.; Williams, C.S.; Hearn, R.H.; Zeidler, J.R.; Dong, J.E.; Goodlin, R.C. Adaptive noise cancelling: Principles and applications. Proceedings of the IEEE 1975, 63, 1692–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkiraju, P.; Reddy, D. Adaptive cancellation technique in processing myoelectric activity of respiratory muscles. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1992, 39, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Ramahi, M.; Mittal, R. Adaptive cancellation of ECG artifacts in the diaphragm electromyographic signals obtained through intraoesophageal electrodes during swallowing and inspiration. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 1994, 6, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Kuiken, T.A. Eliminating cardiac contamination from myoelectric control signals developed by targeted muscle reinnervation. Physiological Measurement 2006, 27, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Peri, E.; Vullings, R.; Rabotti, C.; Van Dijk, J.P.; Mischi, M. Comparative review of the algorithms for removal of electrocardiographic interference from trunk electromyography. Sensors 2020, 20, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Brittain, J.S.; Holland, P.; Yianni, J.; Green, A.L.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z.; Wang, S. Removing ECG noise from surface EMG signals using adaptive filtering. Neuroscience letters 2009, 462, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marque, C.; Bisch, C.; Dantas, R.; Elayoubi, S.; Brosse, V.; Perot, C. Adaptive filtering for ECG rejection from surface EMG recordings. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology 2005, 15, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortolan, R.L.; Mori, R.N.; Pereira, R.R.; Cabral, C.M.; Pereira, J.C.; Cliquet, A. Evaluation of adaptive/nonadaptive filtering and wavelet transform techniques for noise reduction in EMG mobile acquisition equipment. IEEE transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering 2003, 11, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.H.; Tavares, M.C. Removing harmonic power line interference from biopotential signals in low cost acquisition systems. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2009, 39, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malboubi, M.; Razzazi, F.; Aliyari, S.M. Elimination of power line noise from EMG signals using an efficient adaptive Laguerre filter. ICSES 2010 International Conference on Signals and Electronic Circuits. IEEE, 2010, pp. 49–52.
- Deng, Y.; Wolf, W.; Schnell, R.; Appel, U. New aspects to event-synchronous cancellation of ECG interference: an application of the method in diaphragmatic EMG signals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2000, 47, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijila, C.K.S.; Kumar, C.E.S. Interference cancellation in EMG signal Using ANFIS. International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering 2009, 2, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, S.; Fallah, A.; Lindén, M.; Gholamhosseini, H. A novel approach for removing ECG interferences from surface EMG signals using a combined ANFIS and wavelet. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2016, 26, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Lin, Z.; Yin, F. Removal of ECG contamination from diaphragmatic EMG by nonlinear filtering. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2005, 63, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, Z.; Hua, T. Research on AR-AKF Model Denoising of the EMG Signal. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Moon, Y.; Hunt, J.; McKenzie, K.A.; Horin, A.; McGuire, M.; Kim, K.; Hargrove, L.J.; Jayaraman, A. A Novel Technique to Reject Artifact Components for Surface EMG Signals Recorded During Walking With Transcutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Pilot Study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2021, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschero, G.; Gizdulich, P. Denoising of surface EMG with a modified Wiener filtering approach. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2010, 20, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djellatou, M.E.F.; Nougarou, F.; Massicotte, D. Enhanced FBLMS algorithm for ECG and noise removal from sEMG signals. 2013 18th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP). IEEE, 2013, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Lee, C.; Lee, M. Ideal filtering approach on DCT domain for biomedical signals: Index blocked DCT filtering method (IB-DCTFM). Journal of Medical Systems 2010, 34, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewett, D.T.; Nazeran, H.; Reynolds, K.J. Removing power line noise from recorded EMG. 2001 conference proceedings of the 23rd annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, 2001, Vol. 3, pp. 2190–2193. [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.P. A frequency domain Hampel filter for blind rejection of sinusoidal interference from electromyograms. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2009, 177, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Tian, F.; Tang, G.; Wang, C. A wavelet-based method to predict muscle forces from surface electromyography signals in weightlifting. Journal of Bionic Engineering 2012, 9, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A wavelet tour of signal processing; Elsevier, 1999.
- Phinyomark, A.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. The usefulness of wavelet transform to reduce noise in the SEMG signal. EMG methods for evaluating muscle and nerve function 2012. pp. 107–132. [Google Scholar]
- Jamaluddin, F.N.; Ahmad, S.A.; Noor, S.B.M.; Hassan, W.Z.W.; Yaacob, A.; Adam, Y. Estimation of wavelet threshold value for surface EMG baseline removal. 2016 IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES). IEEE, 2016, pp. 102–105. [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Limsakul, C.; Phukpattaranont, P. EMG denoising estimation based on adaptive wavelet thresholding for multifunction myoelectric control. 2009 Innovative Technologies in Intelligent Systems and Industrial Applications. IEEE, 2009, pp. 171–176. [CrossRef]
- Limem, M.; Hamdi, M.A. Uterine Electromyography signals denoising using discrete wavelet transform. 2015 International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME). IEEE, 2015, pp. 101–103. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.F.; Kuo, S.L. A comparative study of wavelet denoising of surface electromyographic signals. 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, 2007, pp. 1868–1871. [CrossRef]
- Rampp, S.; Prell, J.; Thielemann, H.; Posch, S.; Strauss, C.; Romstöck, J. Baseline correction of intraoperative electromyography using discrete wavelet transform. Journal of clinical monitoring and computing 2007, 21, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A. Optimal Wavelet Functions in Wavelet Denoising for Multifunction Myoelectric Control. ECTI Transactions on Electrical Eng.Electronics, and Communications 2010, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, B.; Farooq, O.; Uzzaman, Y.; Khan, A.A.; Vyas, A. Enhancing classification accuracy of wrist movement by denoising sEMG signals. 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2013, pp. 5762–5764. [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeo, L.; Zecca, M.; Sessa, S.; Lin, Z.; Mukaeda, Y.; Ishii, H.; Takanishi, A. Baseline adaptive wavelet thresholding technique for sEMG denoising. AIP Conference Proceedings. American Institute of Physics, 2011, Vol. 1371, pp. 205–214. [CrossRef]
- Schimmack, M.; Mercorelli, P. Noise detection for biosignals using an orthogonal wavelet packet tree denoising algorithm. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications 2016, 62, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Sauer, J.; Graßhoff, J.; Rostalski, P. Removing cardiac artifacts from single-channel respiratory electromyograms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 30905–30917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirmazlaghani, M.; Amindavar, H. EMG signal denoising via Bayesian wavelet shrinkage based on GARCH modeling. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. IEEE, 2009, pp. 469–472. [CrossRef]
- Slim, Y.; Raoof, K. Removal of ECG interference from surface respiratory electromyography. IRBM 2010, 31, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Veer, K. Comparative study of wavelet denoising in myoelectric control applications. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology 2016, 40, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradolewski, D.; Tojza, P.M.; Jaworski, J.; Ambroziak, D.; Redlarski, G.; Krawczuk, M. Arm EMG wavelet-based denoising system. In Mechatronics-Ideas for Industrial Application; Springer, 2015; pp. 289–296. [CrossRef]
- Strazza, A.; Verdini, F.; Mengarelli, A.; Cardarelli, S.; Tigrini, A.; Fioretti, S.; Di Nardo, F. Wavelet Analysis-Based Reconstruction for sEMG Signal Denoising. Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing. Springer, 2019, pp. 245–252. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Reaz, M.; Ali, M.; Bakar, A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T. Surface Electromyography Signal Processing and Classification Techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guang-ying, Y.; Zhi-zeng, L. Surface electromyography disposal based on the method of wavelet de-noising and power spectrum. 2004 International Conference on Intelligent Mechatronics and Automation, 2004. Proceedings. IEEE, 2004, pp. 896–900. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.L. The SEMG analysis for the lower limb prosthesis using wavelet transformation. The 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, 2004, Vol. 1, pp. 341–344. [CrossRef]
- Qingju, Z.; Zhizeng, L. Wavelet de-noising of electromyography. 2006 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation. IEEE, 2006, pp. 1553–1558. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, G.F.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, G.Z.; Kong, J.Y.; Xu, S. Pretreatment of sEMG using wavelet threshold method. 2018 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC). IEEE, 2018, Vol. 2, pp. 638–643. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Bi, Z.Y.; Fan, W.J.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.X.; Li, F.; Wang, K.; Lü, X.Y.; Wang, Z.G. Real-Time Artifact Removal System for Surface EMG Processing during Ten-Fold Frequency Electrical Stimulation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68320–68331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, J.M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. Wavelet-based denoising algorithm for robust EMG pattern recognition. Fluctuation and Noise Letters 2011, 10, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Yeung, L.F.; Yang, Z. A wavelet-based adaptive filter for removing ECG interference in EMGdi signals. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2010, 20, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobahi, N. Denoising of EMG signals based on wavelet transform. Asian Transactions on Engineering 2011, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A: mathematical, physical and engineering sciences 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkar, R.; Yarossi, M.; Ramanujam, A.; Rajagopalan, V.; Bayram, M.B.; Mitchell, M.; Canton, S.; Forrest, G. Application of empirical mode decomposition combined with notch filtering for interpretation of surface electromyograms during functional electrical stimulation. IEEE transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2016, 25, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, M.; Firoozabadi, M.; Kahrizi, S. The Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition in Elimination of ECG contamination from EMG signals. 2011 18th Iranian Conference of Biomedical Engineering (ICBME). IEEE, 2011, pp. 77–80. [CrossRef]
- Kopsinis, Y.; McLaughlin, S. Development of EMD-based denoising methods inspired by wavelet thresholding. IEEE Transactions on signal Processing 2009, 57, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, H.; Waris, A.; Gilani, S.O.; Tariq, M.U.; Alquhayz, H. Threshold parameters selection for empirical mode decomposition-based EMG signal denoising. INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION AND SOFT COMPUTING 2021, 27, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, P. Filtering of surface EMG using ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Medical Engineering & Physics 2013, 35, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Advances in adaptive data analysis 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xi, X.; Yuan, C.; Yang, Y.; Hua, X. Surface electromyography signal denoising via EEMD and improved wavelet thresholds. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 2020, 17, 6945–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.R.; Shieh, J.S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Advances in adaptive data analysis 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; She, Q.; Luo, Z. Denoising of surface electromyogram based on complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition and improved interval thresholding. Review of Scientific Instruments 2019, 90, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasevicius, R.; Vasiljevas, M.; Martisius, I.; Jusas, V.; Birvinskas, D.; Wozniak, M. BoostEMD: an extension of EMD method and its application for denoising of EMG signals. Elektronika ir elektrotechnika 2015, 21, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Yang, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y. VMD-based denoising methods for surface electromyography signals. Journal of Neural Engineering 2019, 16, 056017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2014, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lv, B.; Lin, C.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. EMG signal filtering based on variational mode decomposition and sub-band thresholding. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics 2020, 25, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzerboni, B.; Carpentieri, M.; La Foresta, F.; Morabito, F. Neural-ICA and wavelet transform for artifacts removal in surface EMG. 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37541). IEEE, 2004, Vol. 4, pp. 3223–3228. [CrossRef]
- Taelman, J.; Van Huffel, S.; Spaepen, A. Wavelet-independent component analysis to remove electrocardiography contamination in surface electromyography. 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, 2007, pp. 682–685. [CrossRef]
- von Tscharner, V.; Eskofier, B.; Federolf, P. Removal of the electrocardiogram signal from surface EMG recordings using non-linearly scaled wavelets. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 2011, 21, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, S.; Lindén, M.; Gholamhosseini, H. ECG Artifact Removal from Surface EMG Signal Using an Automated Method Based on Wavelet-ICA. PHealth, 2015, pp. 91–97.
- Mijović, B.; De Vos, M.; Gligorijević, I.; Taelman, J.; Van Huffel, S. Source separation from single-channel recordings by combining empirical-mode decomposition and independent component analysis. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering 2010, 57, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Qiao, X.y. Removal of Motion Noise from Surface-electromyography Signal Using Wavelet Adaptive Filter. 2016 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control. Atlantis Press, 2016, pp. 1270–1274. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ying, D.; Zhou, P. Wiener filtering of surface EMG with a priori SNR estimation toward myoelectric control for neurological injury patients. Medical engineering & physics 2014, 36, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yeh, C.H.; Young, H.W.V.; Hu, K.; Lo, M.T. On the computational complexity of the empirical mode decomposition algorithm. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2014, 400, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




