1. Introduction
Working memory (WM) is a system for short-term storage and manipulation of information. WM underlies human thought processes and plays an important role in complex cognitive tasks such as language comprehension, learning, and reasoning. (Baddeley, 1992, 2003, 2010).
Neural circuits of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the brain are assumed to be responsible for WM implementation (Curtis and D’Esposito, 2003, Riley and Constantinidis, 2016). In classical concept, electrophysiological recordings of neural activity during WM tasks demonstrate that some PFC neurons remain active during delay period. This “persistent activity” is hypothesized as neural correlate of memorized stimulus hold in WM (Bray, 2017; Guo et al., 2017; Bolkan et al., 2017). This concept has its experimental proofs and mathematical models (Constantinidis et al., 2018; Lisman, and Idiart, 1995; Rolls et al., 2013; Dempere-Marco et al., 2012).
Other studies have hypothesized that the information in WM could be represented in form of complex sequences of different activity patterns, so called transient trajectories (Jun et al., 2010; Hussar and Pasternak, 2012; Rabinovich et al., 2015, 2008). Brief, sparse, bursts of spiking were registered in WM tasks rather than persistent spiking. Information about memorized items are held between bursts by spiking-induced changes in synaptic weights (Mongillo, et al., 2008, Lundqvist et al., 2016). Wang et al. (2016) showed that spiking in the PFC can produce fast synaptic enhancement that lasts hundreds of milliseconds.
Gordleeva et al. (2021) propose another interesting dynamical mechanism of WM formation where astrocytes operating at a time scale of a dozen of seconds can successfully store traces of neuronal activations corresponding to information patterns. The astrocytic network selectively modulates synaptic connections in the spiking neural networks in the retrieval stage leading to successful recall.
Both persistent activity and transient dynamics hypothesis have experimental validation (Nachstedt, 2017) and it is not clear which dynamical mechanisms actually underlies the neuronal implementation of WM. Thus, neural mechanisms are WM an open question to date.
One of defining characteristic of working memory is its flexibility. WM can store anything. This is relating with the formation of spatio-temporal structures, or clusters of neural activity. Such structures are formed due to the collective dynamics of the interacting neurons. That clusters and activity structures play an important role in the WM processes (Jensen and Lisman, 2005; Haken, 2000). The spatio-temporal information encoding in WM occurs due to self-sustaining clusters of periodic neural activity after a short-term external input. In papers (Lisman and Idiart, 1995; Jensen and Lisman, 2005) a WM circuit was developed in which such processes occur, and a dynamic model of this scheme was proposed in the papers (Klinshov and Nekorkin, 2005).
Most models of WM formation both persistent and transient do not take flexibility into account. These models contain pre-formed content-specific structures of neurons.
Bouchacourt and Buschman (2019) propose a flexible WM model that relies on random reciprocal connections to generate persistent activity. The random connections are untuned to the content being stored and do not need to be learned, allowing the network to maintain any representation. However, in this model, when multiple memories are stored in the network, they begin to interfere, resulting in a divisive-normalization-like reduction of responses and imposing a capacity limit on the network.
Some models that hypothesize working memory representations, are encoded in short-term synaptic plasticity or changes in single-cell biophysics capture the flexibility of working memory (Loewenstein and Sompolinsky, 2003; Hasselmo and Stern, 2006; Mongillo et al., 2008).
Pre-formed clusters that encode memorized objects don’t match WM mechanisms. In this paper, we show that clusters can be formed due to the mechanisms of spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) based on the model proposed in (Mongillo et al.,2008), where memorized object is maintained by short-term enhancement of strength of connections between cluster neurons that code for this object. STDP shows the change in synaptic connections depending on the relative time of presynaptic and postsynaptic spikes. In STDP, a repeated presynaptic impulse a few milliseconds before the postsynaptic impulse leads to an increase in synaptic transmission between two neurons, with the reverse order of impulses, the connection between neurons weakens. We first model a working memory in spiking neural network considering STDP and show the clusters formation in it by synchronous action of a stimulus on a group of neurons. Then, we model a WM considering two types of plasticity: short-term plasticity and STDP. We show that clusters in the WM model, encoding items, can be formed by external stimulation of a group of neurons for some time due to the mechanisms of STDP. Thus, we develop on previous research and propose the more biologically relevant WM model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spiking neural network model with SDTP
An Integrate-and-Fire neurons in an excitable mode are used as elements of the spiking neural network. Inhibitory neurons are connected to excitatory neurons in an unstructured way. All connections between excitatory neurons exhibit enhanced transmission as described by phenomenological models of STDP.
We sequentially stimulate some groups of neurons after a few seconds of spontaneous activity with a constant external current until the average weight in the group increases due to increased interaction between neurons during stimulation. Thus, clusters are formed by increasing the weights in the stimulated groups.
The network consists of
NE excitatory and
NI inhibitory Integrate-and-Fire neurons. Their subthreshold dynamics is described as
where 𝑖 = [1, 𝑁
𝐸 +
NI] is a neuron number,
τm refers to membrane time constant,
Ii(ext) is an external current provided by distant brain areas. Membrane resistance has been absorbed into the definition of the currents. Every time, the membrane potential reaches a fixed threshold 𝜃, neuron emits a spike and becomes refractory for a time
τarp, after which resumes from sub-threshold reset potential 𝑉
r. Recurrent current 𝐼
𝑖(𝑟𝑒𝑐)(𝑡) is a sum of postsynaptic currents from all the other neurons connected to neuron
i:
where
(𝑡) is the instantaneous efficacy of the synapse connecting neuron j to neuron i.
The instantaneous efficacy:
where
is the absolute synaptic efficiency of connection between excitatory neurons
j and
i, for the other neuronal connections -
,
is the weight of connection between presynaptic neuron j and postsynaptic neuron
i.
In papers (Morrison et al., 2008; Song et al, 2000), the dynamics of the synaptic weight
is regulated by STDP with two local variables and is described as
where
and
are variables that track impulses on the postsynaptic and presynaptic neuron respectively,
=10 ms is the characteristic decay time of local variables,
=0.001 is the learning rate,
=5 is the asymmetry parameter,
is the time delay of spike transmission between neurons
j and
i. A presynaptic spike that fires at time
and reaches neuron
i at time
causes a weight reduction proportional to the size of the postsynaptic trace
. Similarly, a postsynaptic spike at
causes a weight gain proportional to the value of the presynaptic trace
. The weight functions obey the multiplicative update rule.
The synaptic weight
is described by the equations (5) obtained from equations (4) by neglecting the time delay in the transmission of the spike between neurons
j and
i for simplification:
External noise currents are modeled as Gaussian white noise:
with <
ηi (
t)> = 0, <
ηi (
t)
ηj (
t′)> =
δijδ (
t −
t ′), so that
µext and
are respectively the mean and the variance of the external currents. Numerical simulations have been conducted using Euler-Maruyama scheme.
2.2. WM model with two types of plasticity
In that case, all connections between excitatory neurons exhibit enhanced transmission as described by phenomenological models of short-term plasticity (Tsodyks and Markram, 1997) and STDP.
Items are loaded into working memory through external sequential stimulation of certain groups of excitatory neurons. The neurons in the same group strongly influence each other due to external stimulation, the weights of connections between neurons in the same group are enhanced due to the mechanisms of STDP. An increase in the strength of connections between neurons with common stimulus is stronger than with other neurons, which leads to the formation of populations, which corresponds to memorization.
The network dynamics is formed as a result of interplay between excitation and inhibition. When some neurons of the same formed cluster emit spikes nearly simultaneously (as a result of local stimulation or noise-induced spontaneous activity), they excite both other neurons of the formed clusters through strong couplings and some of inhibitory neurons, that inhibits activity of other neurons of the network. When the activity in the excited cluster decays the activity of inhibitory neurons decays too and “releases” other neurons from suppression.
Information about memorized items are held in WM by changes in synaptic weights, ‘‘impressions’’ left in the network after stimulus presentation. A memory item can be reactivated by weak stimulation of network input due to the mechanisms of short-term plasticity even if neural activity is spontaneous. Item reactivation in working memory is expressed as a short period of synchronous activity, when almost every neuron within the population generates a spike. The neurons corresponding to the loaded item generate a population spike, the rest of non-specific neurons remain at the level of subthreshold or spontaneous activity. There is a short-term strengthening of connections within the population due to the population spike, which leads to the possibility of sequential reactivation of this image in memory.
Recurrent current in neural network with consideration of short-term plasticity and STDP:
where
(𝑡) is the instantaneous efficiency of the synapse connecting neuron
j with neuron
i; 𝑡
𝑘(j) – all times of spikes of presynaptic neuron
j.
The instantaneous efficacy of connection between excitatory neurons:
where
is the absolute synaptic efficiency of connection between neurons
j and
i, u and
x are parameters of short-term synaptic plasticity:
u is the synaptic efficiency,
x is the synaptic resource. For the other neuronal connections
,
Short-term synaptic plasticity is described by equations:
where
is the calcium level recovery time,
is the neurotransmitter recovery time. There are two types of short-term plasticity: depression and facilitation. Synaptic depression is caused by the depletion of neurotransmitters, used for signal transmission on presynaptic neuron, while facilitation is caused by inflow of calcium ions into axonal terminal right after spike generation that increase the probability of neurotransmitter release. For facilitating synapses τ
F > τ
D, and vice-versa τ
F < τ
D for depressing synapses. In PFC synapses demonstrates facilitation and temporal scale of τ
F is up to several seconds and for τ
D is about several hundreds of milliseconds (Mi et al., 2017).
External noise currents are described by equation (6). The means of the external currents for excitatory neurons µext_e and for inhibitory neurons µext_i are different. Numerical simulations have been conducted using Euler-Maruyama scheme.
3. Results
3.1. Clusters formation in spiking neural network with SDTP
Simulated spiking neural network dynamics with STDP are fully described by equations (1) - (3), (5) - (6). The biologically relevant values of the neuron parameters are the same as in the paper (Mi et al., 2017). Model parameters are presented in
Table 1 and
Table 2.
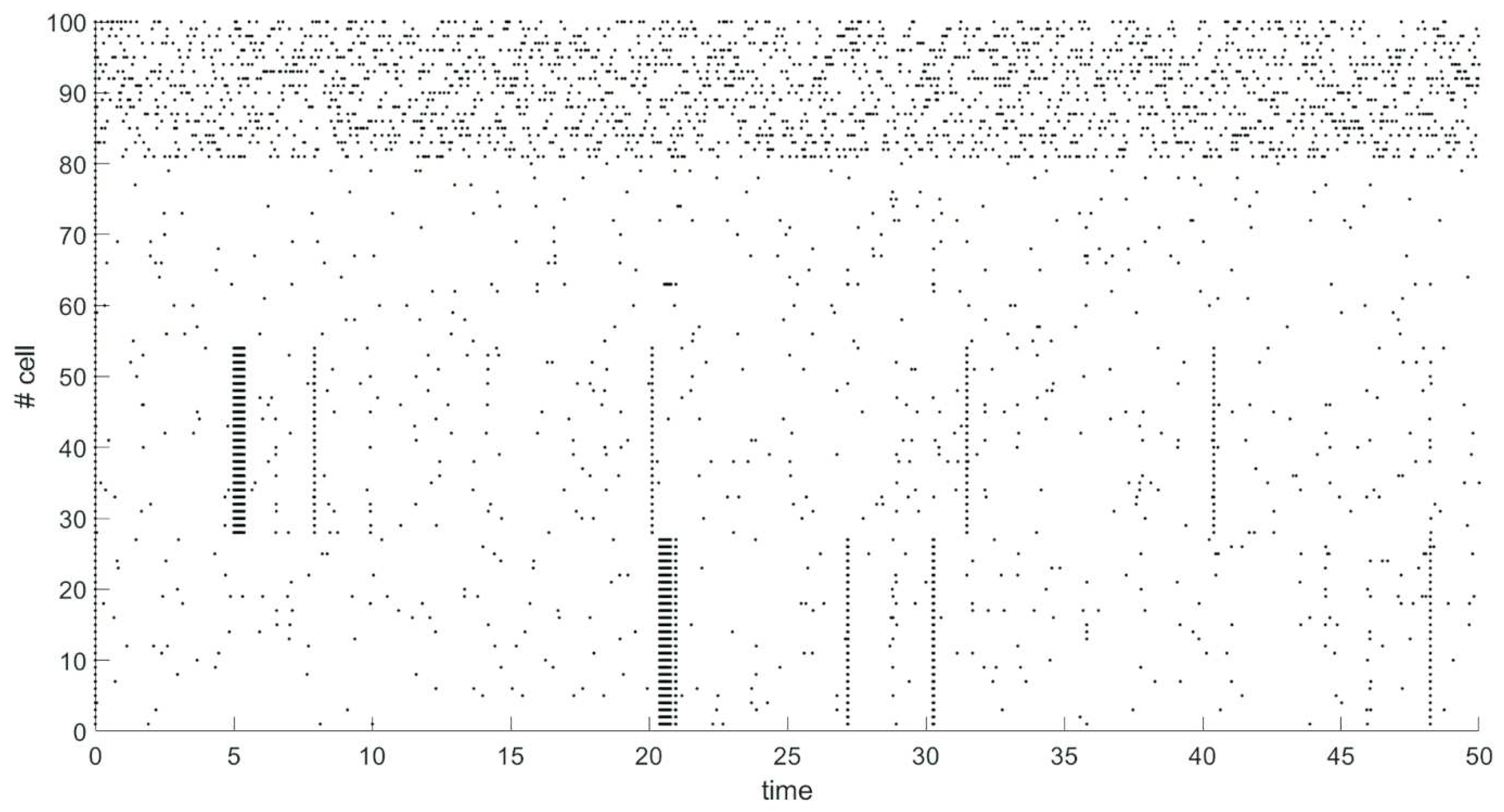
We have modeled spiking neural network of 100 neurons. Network contains 80 excitatory neurons (neurons 1-80), 20 neurons are inhibitory (neurons 81-100). Probability of connection between any two neurons is 80%. After 5 seconds of spontaneous activity from start of simulation a group of 27 excitatory neurons (neurons 28-54) has been stimulated by external signal of 30 mV for 0.376 seconds. 15 seconds after the end of the stimulus, another group of 27 excitatory neurons (neurons 1-27) is similarly stimulated. The dynamics of the network is shown on raster plot (
Figure 1), where every dot represents a spike.
The neurons in the same group strongly influence each other due to external stimulation. An increase in the strength of connections between neurons with common stimulus is stronger than with other neurons, which leads to the formation of clusters. Synchronous activity is observed in the clusters due to the strengthening of connections after the end of stimulation, as seen in
Figure 2. At the same time there is no synchronous activity for the rest of the excitatory neurons that do not belong to the formed clusters (neurons 55-80).
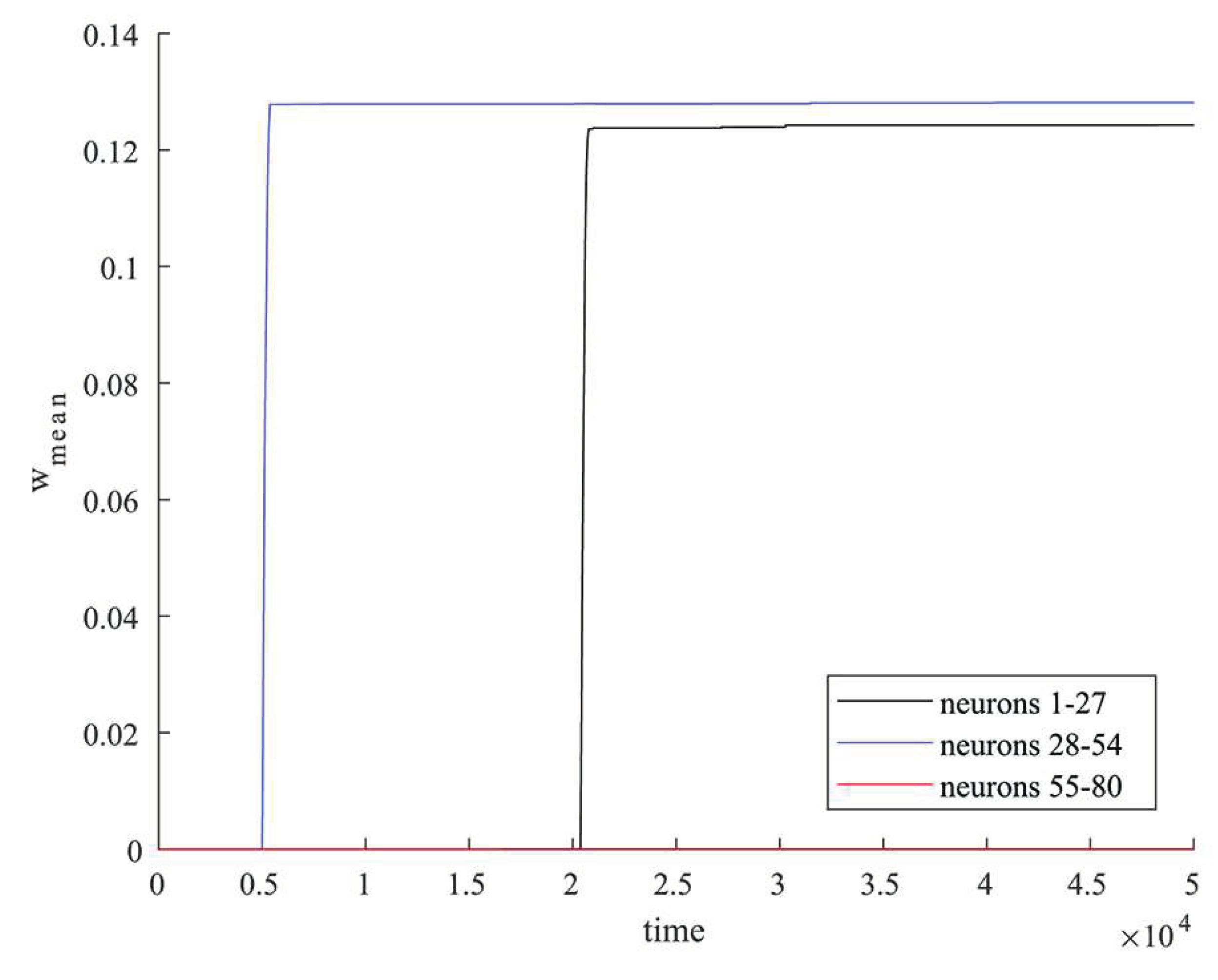
Average values of synaptic weights depending on time were calculated in groups of neurons that were simultaneously stimulated by an external current and in a group of the rest of excitatory neurons that were not simultaneously stimulated.
Figure 2 shows in black the graph of change in the average value of the synaptic weight in the group of neurons 1-27, in blue – in the group of neurons 28-54, in red – in the group of neurons 55-80. The rapid increase in the value of synaptic weight for connections within groups of neurons occurs at the time of external stimulation (neurons 1-27, 28-54) as shown in
Figure 2 which leads to the formation of clusters. As shown in
Figure 2 the synaptic weights between excitatory neurons that were not simultaneously stimulated by external current (neurons 55-80) changed negligibly little during the simulation.
Thus, clusters can be formed by synchronous stimulation of a group of neurons due to the mechanisms of STDP.
3.2. Clusters formation in WM model with two types of plasticity
Network dynamics of WM model with consideration of two types of plasticity are fully described by equations (1), (5) - (9). The biologically relevant values of the neuron parameters are the same as in the paper (Mi et al., 2017). Parameters of neurons are presented in
Table 1. Parameters of synaptic dynamics are presented in
Table 3.
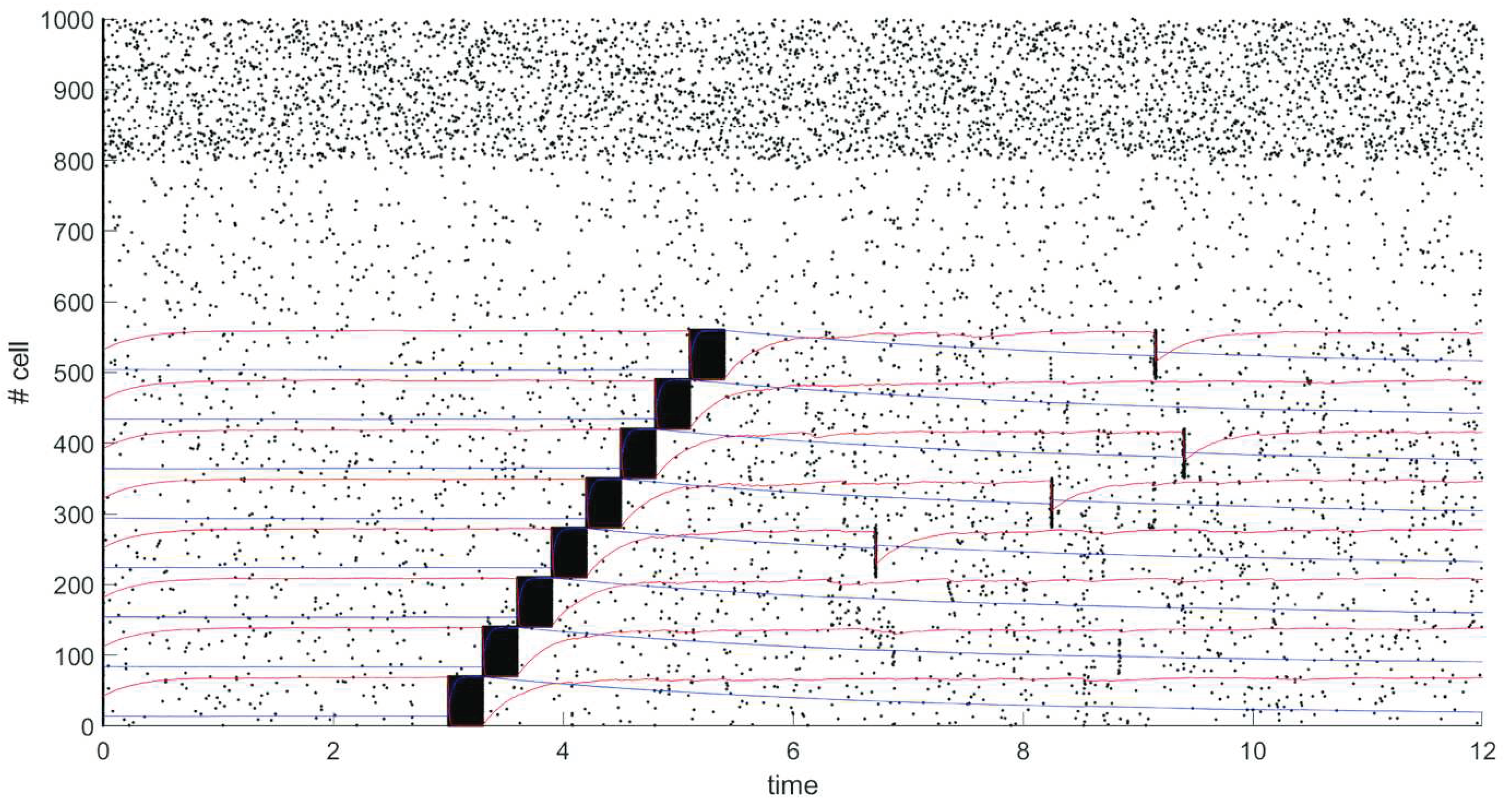
We have modeled spiking neural network of 1000 neurons. Network contains 800 excitatory neurons (neurons 1-800), 200 neurons are inhibitory (neurons 801-1000). Probability of connection between any two neurons is 20%.
After 5 seconds of spontaneous activity from start of simulation 8 different groups of neurons, each of which contains 70 neurons, are sequentially stimulated by external signal of 30 mV for 0.3 seconds. The dynamics of the network is shown on raster plot in
Figure 3, where every dot represents a spike, graphs of changes in the average values of synaptic efficiency u in stimulated groups are shown in blue, and changes in the average values of synaptic resource x in stimulated groups are shown in red.
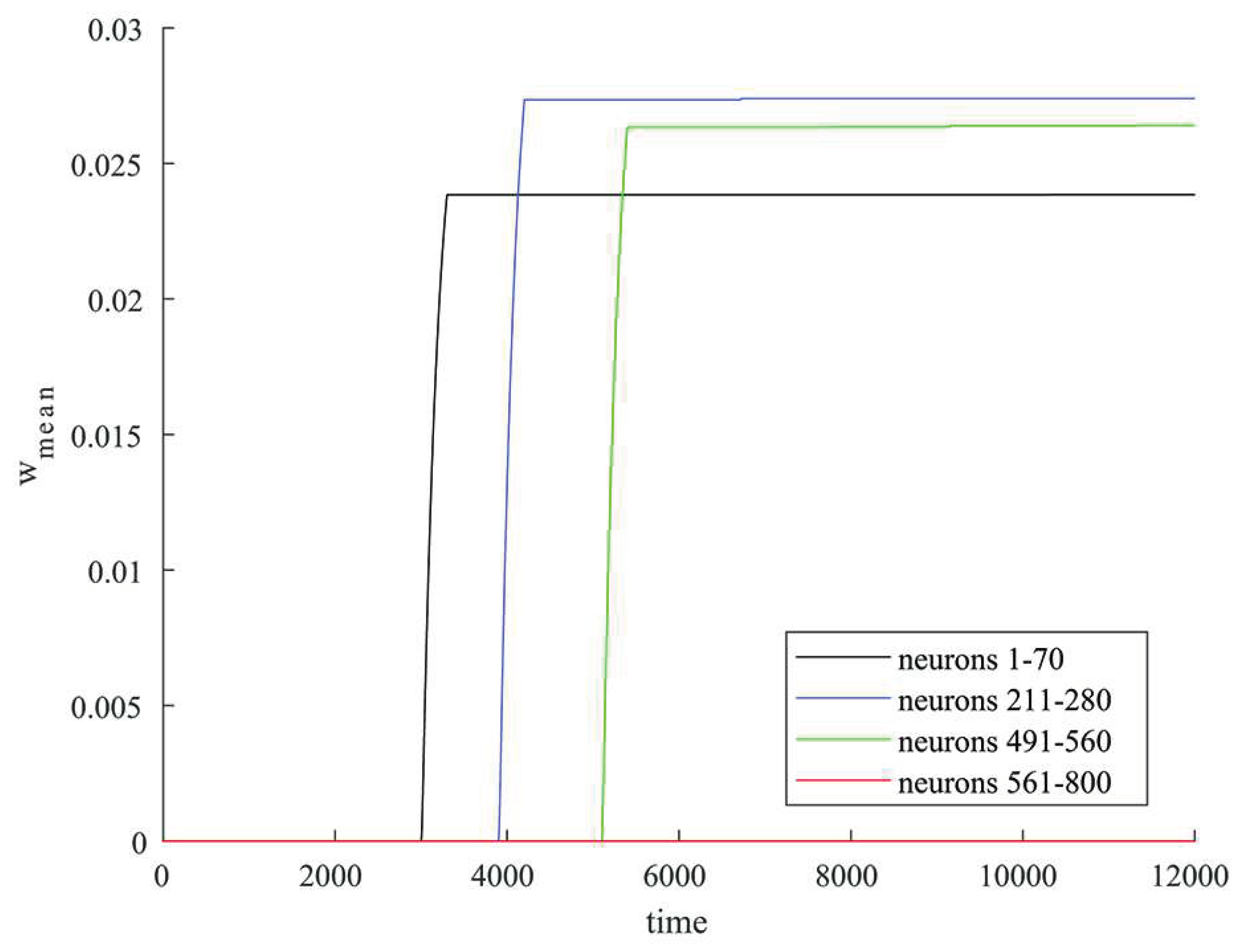
Average values of synaptic weights depending on time were calculated in some groups of neurons that were simultaneously stimulated by an external current and in a group of the rest of excitatory neurons that were not simultaneously stimulated.
Figure 4 shows in black the graph of change in the average value of the synaptic weight in the group of neurons 1-70, in blue – in the group of neurons 211-280, in green – in the group of neurons 491-560, in red – in the group of neurons 561-800. The rapid increase in the value of synaptic weight for connections within groups of neurons occurs at the time of stimulation by external current (neurons 1-70, 211-280, 491-560) as shown in
Figure 4. For the rest of excitatory neurons 561-800 excitatory neurons that were not simultaneously stimulated by external current the synaptic weight grows negligibly little during the simulation as shown in
Figure 4.
There is an increase in the weight of connections within groups of neurons which were sequentially stimulated by an external current due to the mechanisms of STDP. Neuronal clusters are formed, which corresponds to memorization of stimulus. A periodic spontaneous reactivation of the stored items occurs due to short-term plasticity after the items are loaded into memory and there is no synchronous activity outside the formed clusters as we can see in figure 3.
Thus, the clusters that encodes loaded items in the network in the working memory model can be preliminarily formed by synchronous stimulation of a group of neurons due to the mechanisms of STDP.
4. Discussion
The mechanisms of WM remain discussing today. Persistent activity and transient dynamics hypothesis have experimental validation. However, typical models of WM formation both persistent and transient are inflexible. Persistent models of WM formation rely on fine-tuning of connections to embed stable fixed points in the network dynamics specific to the content being stored. These connections must be hardwired or learned for each type of information, and so the network cannot flexibly represent novel, unexpected stimuli. Indeed, networks of this type in the brain seem to encode ecologically relevant information, such as heading direction (Kim et al., 2017).
Models that represent working memory as a result of transient dynamics in neural activity are similarly inflexible. They require learning to embed the dynamics, to decode the temporally evolving representations, or to ensure the dynamics are orthogonal to mnemonic representations (Vogels et al., 2005; Druckmann and Chklovskii, 2012).
Some models that hypothesize working memory representations, are encoded in short-term synaptic plasticity or changes in single-cell biophysics capture the flexibility of working memory (Loewenstein and Sompolinsky, 2003; Hasselmo and Stern, 2006; Mongillo et al., 2008).
Bouchacourt and Buschman (2019) propose a flexible WM model that relies on random reciprocal connections to generate persistent activity. However, in this model, when multiple memories are stored in the network, they begin to interfere, resulting in a divisive-normalization-like reduction of responses and imposing a capacity limit on the network. Thus, this model provides a mechanistic explanation for the limited WM capacity. Perhaps this is a necessary compromise for its flexibility.
Our approach allows to get rid of the strong WM capacity limitation, while maintaining flexibility. We develop a model based on model proposed in (Mongillo et al. (2008)) where memorized object is maintained in the WM by short-term enhancement of strength of connections between neurons that code for this item. Our model considering two types of plasticity: short-term and STDP, where clusters encoding memorized object are formed due to STDP. Memory encoding processes in neural networks are associated with the formation of spatio-temporal structures. The STDP mechanisms allow the formation of such structures. We have considered how clusters are formed in a spiking neural network with STDP. We have modeled WM with two types of plasticity, which is original research and showed how clusters encoding loaded items are formed by external stimulation of a group of neurons. Thus, we develop on previous research and move closer to a more accurate mathematical description of the WM model.
Acknowledgments
The work was performed by the support of the federal academic leadership program “Priority 2030” of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. All authors contributed substantially to this study; all contributed to the conception and design of the study, and interpretation of the results. NK performed the computations, VM and MM performed the analysis. NK and MM drafted the manuscript. VM revised the manuscript critically. All authors gave final approval of the submission.
References
- Baddeley, A. (1992). Working Memory. Science. 255, 556–559. [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. (2003). Working Memory: Looking Back and Looking Forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. (2010). Working Memory. Curr. Biol. 20, 136–140. [CrossRef]
- Bolkan, S.S., Stujenske, J.M., Parnaudeau, S., Spellman, T.J., Rauffenbart, C., Abbas, A.I., Harris, A.Z., Gordon, J.A., and Kellendonk, C. (2017). Thalamic Projections Sustain Prefrontal Activity during Working Memory Maintenance. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 987–996. [CrossRef]
- Bouchacourt, F., and Buschman, T.J. (2019). A Flexible model of Working Memory. Neuron. 103, 147-160. [CrossRef]
- Bray, N. (2017). Working Memory: Persistence Is Key. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 385–385. [CrossRef]
- Constantinidis, C., Funahashi, S., Lee, D., Murray, J.D., Qi, X.-L., Wang, M., and Arnsten, A.F.T. (2018). Persistent Spiking Activity Underlies Working Memory. J. Neurosci. 38, 7020–7028. [CrossRef]
- Curtis, C.E., and D’Esposito, M. (2003). Persistent Activity in the Prefrontal Cortex during Working Memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 7, 415–423. [CrossRef]
- Dempere-Marco, L. , Melcher, D.P., and Deco, G. (2012). Effective Visual Working Memory Capacity: An Emergent Effect from the Neural Dynamics in an Attractor Network. PLoS One 7, e42719. [CrossRef]
- Druckmann, S., and Chklovskii, D.B. (2012). Neuronal circuits underlying persistent representations despite time varying activity. Curr. Biol. 22, 2095-2103. [CrossRef]
- Gordleeva, S.Y. , Tsybina, Y.A., Krivonosov, M.I., Ivanchenko, M. V., Zaikin, A.A., Kazantsev, V.B., and Gorban, A.N. (2021). Modeling Working Memory in a Spiking Neuron Network Accompanied by Astrocytes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. V., Inagaki, H.K., Daie, K., Druckmann, S., Gerfen, C.R., and Svoboda, K. (2017). Maintenance of Persistent Activity in a Frontal Thalamocortical Loop. Nature 545, 181–186. [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. (2000). Principles of Brain Functioning. A Synergetic Approach to Brain Activity, Behavior and Cognition. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
- Hasselmo, M.E. and Stern, E.C., (2006). Mechanisms underlying working memory for novel information. Trends Cogn Sci. 10, 487-493. [CrossRef]
- Hussar, C.R. , and Pasternak, T. (2012). Memory-Guided Sensory Comparisons in the Prefrontal Cortex: Contribution of Putative Pyramidal Cells and Interneurons. J. Neurosci. 32, 2747–2761. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O. , and Lisman, J. E. (2005). Hippocampal sequence-encoding driven by a cortical multi-item working memory buffer. Trends in Neurosci. 28, 67–72. [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.K. , Miller, P., Hernández, A., Zainos, A., Lemus, L., Brody, C.D., and Romo, R. (2010). Heterogenous Population Coding of a Short-Term Memory and Decision Task. J. Neurosci. 30, 916–929. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S., Rouault, H., Druckmann, S., and Jayaraman, V. (2017). Ring attractor dynamics in the Drosophila central brain. Science 356, 849–853. [CrossRef]
- Klinshov, V. V. , and Nekorkin, V. I. (2005). Model of a neuron with after depolarization and short-term memory. Radiophys. Quant. Electron. 48, 203–211. [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J. E. , and Idiart, M. A. P. (1995). Storage of 7±2 short-term memories in oscillatory subcycles. Science. 267, 1512–1515. [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.E. , and Idiart, M.A.P. (1995). Storage of 7 ± 2 Short-Term Memories in Oscillatory Subcycles. Science (80-. ). 267, 1512–1515. [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, Y., and Sompolinsky, H. (2003). Temporal integration by calcium dynamics in a model neuron. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 961-967. [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M., Rose, J., Herman, P., Brincat, S.L.L., Buschman, T.J.J., and Miller, E.K.K. (2016). Gamma and Beta Bursts Underlie Working Memory. Neuron 90, 152–164. [CrossRef]
- Mongillo, G., Barak, O., and Tsodyks, M. (2008). Synaptic Theory of Working Memory. Science. 319, 1543–1546. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A., Diesmann, M., and Gerstner, W. (2008). Phenomenological Models of Synaptic Plasticity Based on Spike Timing. Biol. Cybern. 98, 459–478. [CrossRef]
- Nachstedt, T. (2017). The Processing and Storage of Information in Neuronal Memory Systems Across Time Scales. [dissertation/ doctoral thesis]. [Goettingen]: Georg-August-University Goettingen.
- Rabinovich, M.I., Huerta, R., and Laurent, G. (2008). Neuroscience. Transient Dynamics for Neural Processing. Science 321, 48–50. [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, M.I., Simmons, A.N., and Varona, P. (2015). Dynamical Bridge between Brain and Mind. Trends Cogn. Sci. 19, 453–461. [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.R., and Constantinidis, C. (2016). Role of Prefrontal Persistent Activity in Working Memory. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 9, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. , Dempere-Marco, L., and Deco, G. (2013). Holding Multiple Items in Short Term Memory: A Neural Mechanism. PLoS One 8, e61078. [CrossRef]
- Song, S. , Miller, K.D., and Abbott, L.F. (2000) Competitive Hebbian Learning through Spike-Timing-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 919–926. [CrossRef]
- Tsodyks, M. V. , and Markram, H. The neural code between neocortical pyramidal neurons depends on neurotransmitter release probability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94, 719–723. [CrossRef]
- Vogels, T.P., Rajan K., and L.F. Abbott (2005). Neural Network Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28, 357-376. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Markram, H., Goodman, P.H., Berger, T.K., Ma, J., and Goldman-Rakic, P.S. (2006). Heterogeneity in the Pyramidal Network of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 534–542. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).