1. Introduction
At present, large language model (LLM) is widely used in various tasks of natural language processing, and has achieved the performance of state-of-the-art on many mainstream lists [
1,
2,
3]. However, this does not mean that LLM can achieve good results in various specific businesses. Engineers need to fine tune the business data to determine the performance that LLM can achieve. Whether the final effect matches the cost of manpower and calculation required for fine-tuning is a problem that technical decision-makers need to consider.
Compared with LLM, classical computational linguistic features are considered to be unable to describe semantics well [
4]. But its advantage is that the development and calculation costs are very low. Therefore, decision makers need to make a choice between LLM and classical methods according to business requirements. For example, Zhu et al.[
5,
6] compiled a series of benchmarks for CTR tasks to help engineers determine whether certain methods are competitive in business. Weimao et al.[
7] sorted out multiple benchmarks of text classification tasks. They conducted classification experiments on this basis, so as to compare and analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various methods. Lai T M et al.[
8] proposed a baseline for coreference resolution, which provides evidence for the necessity of justifying the complexity of existing or newly proposed models. Huliyah et al.[
9] compared the benchmark of random forest and naive bayes algorithm to know which modeling process has the best value of accuracy for sentiment classification in texts. Salemi et al.[
10,
11] introduced RTAnews benchmark dataset and conducted extensive benchmarking tests of most of the well-known multi-label learning algorithms for Arabic text classification, so as to compare the effectiveness of these algorithms. Naseem et al.[
12] benchmarked the performance of different state-of-the-art ML text classification mechanisms, which can assist governments worldwide in analyzing public sentiment and its dynamic during the pandemic, so as to plan effective public health responses.
In this paper, we study the performance upper bound of classical computational linguistic metrics for specific tasks. We conduct research based on the contest model of Baidu Search Technology Innovation Challenge 2022 (STI) [
13]. This competition suggested that participating teams make fine-tuning based on LLM ERNIE [
14] proposed by Baidu to complete the reading comprehension task under specific business data. But we study the performance upper bound of classical information retrieval methods under this business task, and compare with the cost and performance of participating teams based on LLM. Our work attempts to provide insight into the potential of classical computational linguistics algorithms to help decision-makers make reasonable choices in business development.
2. Reading Comprehension Task of STI
Baidu Search Technology Innovation Challenge 2022 requires the participating teams to complete several reading comprehension tasks based on ERNIE, and the dataset provided was built on the basis of Baidu search desensitization business data.
ERNIE is the NLP pre-training model proposed by Baidu. It has been proven to have superior performance over BERT in various Chinese NLP tasks such as named entity recognition and natural language inference. The application of ERNIE has significantly improved the performance of Baidu’s decimated intelligent question answering system. However, in the open domain search scenario, there are problems such as the length of web documents is different, the quality level is uneven, the length of questions and answers is long, and the distribution is scattered. This brings challenges to the extraction of answers and the calculation of answer confidence.
The dataset provided by the competition contains the training set, the verification set and the test set. Among them, the training set contains about 900 queries and 30,000 query-document pairs; the verification set and test set each contains about 100 queries and 3,000 query-document pairs. The main characteristics of the data are:
The length of documents is generally long, the quality is uneven, and there is often a lot of noise inside the document.
Answer fragments are of sentence-level. An answer usually consists of several sentences that contain the complete context.
The annotated data only guarantees the relevance between answer fragments and searched questions. It does not guarantee correctness, and there exist documents that do not contain any answer.
The competition task requires that the participating team should take the query and the document in the test set as model input, find reasonable answer fragments in the corresponding document according to the query, and output them as answer sets after integration. More specifically, the test set gives a set of searched questions. Based on each searched question , a set of web documents retrieved by a search engine is given, including up to 40 web documents. For each pair, the contest model is required to extract answer fragments that can answer the query from . If the model forecasts that documents do not contain any answer, “NoAnswer” is returned. The contest model should achieve good and robust answer extraction effect in the data environment with variable document lengths and long answer lengths.
3. Evaluation Metrics
Each contest model predicts the answers of each pair, and submits them to the evaluation system after integration. The evaluation system calculates precision, recall and F1 value according to the character granularity of the answer corresponding to each pair and the character granularity of groundtruth. Ultimately it takes the average F1 valve of test data as final score of a contest model.
When both the standard answer and predicted answer are “NoAnswer”, , and are all 1; when only one of them is not “NoAnswer”, , and are all 0; when they are not “NoAnswer”, the evaluation system calculates the character-granularity similarity of the two texts:
Firstly remove the punctuation marks in the two texts, and then calculate precision
and recall
:
Among which
and
are the number of characters in the standard answer and predicted answer, and
is the number of characters of the same kind in both. On the basis of getting
and
,
is further calculated as a comprehensive index to measure the performance of the model:
The baseline provided by STI is based on ERNIE with full fine-tuning. Based on the evaluation method above, the evaluation results corresponding to baseline are as follows:
Table 1.
Evaluation Result of Baseline.
Table 1.
Evaluation Result of Baseline.
| F1 |
Precision |
Recall |
| 0.35335 |
0.36416 |
0.48317 |
4. Upper Bound Analysis of BM25
In this paper, we analyze the upper bound that the classical information retrieval method BM25 [
16] can reach on the reading comprehension task. It is generally believed that such classical metrics are only calculated based on the statistics of word frequency. They can only calculate the relevance of text without understanding semantics, so they are not suitable for reading comprehension tasks. However, the raw results (as shown in
Table 1) show that the end-to-end generation of ERNIE is not good without meticulous fine-tuning.
BM25 calculates the correlation between text paragraphs and queries. Because we only filter text based on BM25 metrics, and do not use other metrics. Therefore, the algorithm has no ability to exclude texts that are highly relevant but cannot answer questions. We can only exclude the text that cannot answer the question because of low relevance based on the minimum BM25 score related to the query. The steps of this process are:
Split the document into a set of paragraphs.
Calculate the BM25 score of the corresponding query for this set of paragraphs (each paragraph will have a BM25 score).
Filter out the paragraph whose BM25 score is greater than as an answer to the query.
The key point of this process is that for each pair, what value should threshold take to obtain the best result.
Obviously, the minimum BM25score of paragraphs in the answer is the correlation boundary of “whether the paragraph is in the answer”.Namely:
In the training data, we have groundtruth answer for each pair. However, some groundtruth answers in the reading comprehension task are derived directly from candidate document , while some groundtruth answers reorganize the language. This means that there are paragraphs in A that do not have a corresponding BM25 score, so BM25 estimate is required.
For document
, we can map each paragraph to one of the most similar paragraphs in
. This gives a BM25 estimate for each paragraph in the document
. Let:
Among which is the BM25 estimate of the paragraph in document .To implement this method, we also need to consider how to calculate the most similar paragraph of in .
Same as the evaluation indicators of the task, for each paragraph in , we calculate the character-granularity similarity with it and each paragraph in . If the similarity is bigger than threshold , the paragraphs are regarded as similar paragraphs:
- 1)
For in
- 2)
For in
- 3)
If
- 4)
Add to
However, for each pair, the threshold is different. If a is preset without adjustment, it may cause no result to be added to SimilarParagraphs, which in turn will cause the paragraph in A cannot be mapped to the most similar paragraph in D. To solve the problem, we first set an initial value for , and if no similar paragraphs are found, will be automatically adjusted downward by step . Therefore, the final algorithm is:
- 1)
For in
- 2)
For in
- 3)
If
- 4)
Add to
- 5)
If is empty
- 6)
- 7)
Repeat this algorithm
and are hyperparameters of this algorithm. Due to ,we can try all combinations of and . The algorithm will search hyperparameter that can make the evaluation result best. The effect achieved at this time is the upper bound of our estimation. The final result is:
Table 2.
Final Evaluation Result of BM25 Method’s Upper Bound.
Table 2.
Final Evaluation Result of BM25 Method’s Upper Bound.
|
|
|
F1 |
Precision |
Recall |
| 0.9 |
0.1 |
0.61666 |
0.64045 |
0.68939 |
5. Experiment Result
B. Calculation Cost Comparison
In order for the BM25 algorithm to reach this upper bound, it is necessary to accurately select the threshold
according to the groundtruth data. If this problem is regarded as the problem of stopping point estimation of autocorrelation random process, by using the method proposed by Liu et al.[
18], the sequence pattern of the BM25 score can be learned to infer the threshold
for each
pair.
We compare the calculation cost based on this method with that of fine-tuning ERNIE. According to statistics, participating teams train 118 epochs on average, and the calculation duration on Tesla V100 GPU is 2.5h (only the last training-inferencing duration is counted, excluding the time for hyperparameter adjustment). Since the method in [
18] only models the BM25 score sequence, its network size is far smaller than ERNIE. The network only needs 0.884h to train 118 epochs on RTX3060 GPU. Considering that the performance gap between the Tesla V100 and the RTX3060 is more than 1.23 times (FP32 floating-point performance estimation is used here [
19]), this means that the cost of fine-tuning LLM is at least 3.48 times of the method in [
18].
However, it was also pointed out in [
18] that only using BM25 sequence on STI dataset maybe could not provide enough information for inferring stopping point. This means that the upper bound cannot be reached directly by the model in [
18], and text is still needed to provide auxiliary information. Therefore, the network structure that reaches the upper bound is more complex than this one. The performance cost estimate made here does not represent the final result.
6. Conclusion
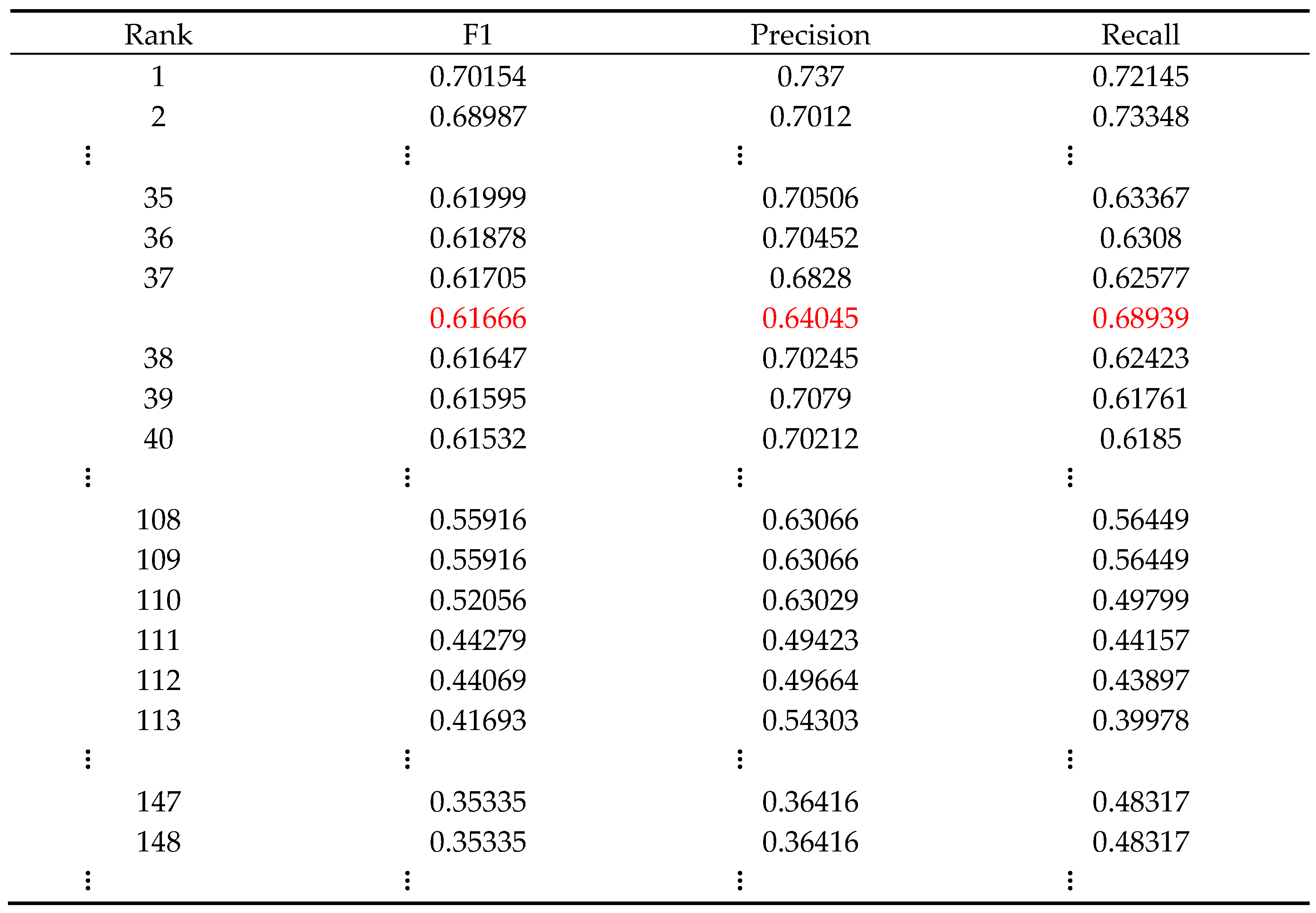
According to experimental results, the effect of fine-tuning LLM in specific tasks is uncertain. For instance, out of 168 participating teams, most teams have not got satisfactory fine-tuning results, and only 37 teams are able to make their results beyond the upper bound of the BM25 method. Whereas the average computility they use far exceeds the encoder architecture of the estimated BM25 sequence stopping point, which means that paying excessive costs on LLM does not necessarily lead to better effects. Basing on this observation, we recommend that technical decision-maker reasonably determine the expected indicators firstly that the algorithm needs to achieve according to business requirements. If fairly precise results are not required, whether costs should be spent on LLM needs to be carefully considered.
References
- Chen W . Large Language Models are few(1)-shot Table Reasoners[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Xu R, Luo F, Zhang Z, et al. Raise a Child in Large Language Model: Towards Effective and Generalizable Fine-tuning[J]. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wei J, Tay Y, et al. Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Manshadi M H . Towards a Robust Deep Language Understanding System[C]// Twenty-fourth Aaai Conference on Artificial Intelligence. DBLP, 2010.
- Zhu J, Liu J, et al. Open Benchmarking for Click-Through Rate Prediction, in Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2021. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Mao K, et al. BARS: Towards Open Benchmarking for Recommender Systems, in Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR), 2022. [CrossRef]
- Weimao, Ke. Least information document representation for automated text classification[J]. Proceedings of the American Society for Information Science & Technology, 2012,49(1):1-10. [CrossRef]
- Lai T M, Bui T, Kim D S . End-to-end Neural Coreference Resolution Revisited: A Simple yet Effective Baseline[J]. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hulliyah K, Bakar N, Ismail A R , et al. A Benchmark of Modeling for Sentiment Analysis of The Indonesian Presidential Election in 2019[C]// 2019 7th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management (CITSM). 2019. [CrossRef]
- Al-Salemi B , Ayob M,Kendall G , et al. RTAnews: A Benchmark for Multi-label Arabic Text Categorization[Dataset]. Mendeley, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Al-Salemi B, Ayob M, Kendall G, et al. Multi-label Arabic text categorization: A benchmark and baseline comparison of multi-label learning algorithms[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2019, 56(1):212-227. [CrossRef]
- Naseem U, Razzak I, Khushi M, et al. COVIDSenti: A Large-Scale Benchmark Twitter Data Set for COVID-19 Sentiment Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 8(4):1003-1015. [CrossRef]
- Baidu AI Studio. Baidu Search Technology Innovation Challenge 2022[EB/OL]. December 6, 2022. http://sti.baidu.com/.
- Sun Y, Wang S, Feng S , et al. ERNIE 3.0: Large-scale Knowledge Enhanced Pre-training for Language Understanding and Generation[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Xiong Q, Zhang S. STI BM25 Sequence Dataset[Dataset]. figshare. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Robertson S , Zaragoza H . The Probabilistic Relevance Framework: BM25 and Beyond[J]. Foundations & Trends in Information Retrieval, 2009, 3(4):333-389. [CrossRef]
- Xiong Q. Ranking List of STI[Dataset]. figshare. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Zhang S, Xiong Q. Sequence Encoder for Stopping Point Prediction of Autoregressive Processes[J]. ResearchGate, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gadget Versus. Processor[EB/OL]. February 25, 2021. https://gadgetversus.com/graphics-card/nvidia-tesla-v100-pcie-16gb-vs-nvidia-geforce-rtx-3060/.
Table 3.
Part of The STI 2022 Ranking List [
17].
Table 3.
Part of The STI 2022 Ranking List [
17].
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).