Submitted:
09 January 2023
Posted:
12 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
- (A)
- Firstly, the research team selected the nurses and speech therapists who would participate in the fieldwork phase. Three nurses were selected using a convenience sampling method: two from the Primary Care Management Board of the Tenerife Healthcare Area and one from the Management Board of the Nuestra Señora de La Candelaria University Hospital. The instruction phase for the professionals comprised five joint explanatory meetings of approximately 60 minutes each. Their content focused on explaining the objectives and methodology of the study, the instructions for administering the CEECCA and the proxy instruments, as well as other methodological and ethical considerations. Each collaborator was given a field notebook with all the documents required for the administration of the tests and data collection.
- (B)
- Secondly, participants were selected to form the study sample. Participants were selected using a convenience sampling method in various settings: The University Hospital of the Canary Islands (HUC), primary healthcare facilities in the Tenerife Healthcare Area, as well as private rehabilitation centres and associations. Inclusion criteria were persons of legal age; diagnosed with aphasia as a consequence of acquired brain damage; with Spanish as their mother tongue; who agreed to participate in the study. The exclusion criteria were: patients with a low level of consciousness (in a vegetative state and/or minimally conscious); a personal history of neurological or neurodegenerative disease prior to the brain injury that caused the aphasia; a psychiatric-psychological history of communication disorder prior to the brain damage; with a cognitive level preventing them from taking the test; pre-morbid reading and writing disability; severe visual or hearing impairment that hinders the correct administration of the instrument; behavioural problems that impede communication with the researchers; history of alcoholism and/or other drug abuse.
- (C)
- Subsequently, the proxy instruments used to carry out the validity tests of the questionnaire were selected and applied. The three proxy instruments used in the validation phase of the CEECCA questionnaire had previously been used in the design and construction phase of the questionnaire, enabling consistency to be maintained between the two processes: The Boston test for diagnosing aphasia. Spanish adaptation. Second edition [36]; the selected indicators of the four communication-related Nursing Outcomes Classification (NOC) outcomes [37]; the selected defining characteristics (DCs) of the 2012-2014 NANDA-I nursing diagnosis “Impaired verbal communication” [38]. The standardised nursing classifications used were the latest revisions available at the time of administration.
- Conversational speech.
- Descriptive speech.
- Visual confrontation naming.
- Writing mechanics.
- Written confrontation naming.
- Auditory discrimination of words.
- Auditory comprehension of commands.
- Reading comprehension. Matching pictures and words.
- Reading comprehension. Reading sentences and paragraphs.
- (D)
- A nurse administers the CEECCA to each subject in the sample. The CEECCA was administered at the primary healthcare facilities in the Tenerife Healthcare Area, at the HUC rehabilitation units, in the rehabilitation departments of the collaborating centres and associations, and in the participants’ own homes. The CEECCA is administered once again by another nurse under the same conditions at an interval of one to seven days. Alternatively, one of the nurses who previously administered the questionnaire repeats the process four weeks later.
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Description
2.2.2. Validity Tests
- Construct validity
- Convergent criterion validity
2.2.3. Inter-Observer Reliability, Intra-Observer Reliability, and Internal Consistency
2.2.4. Responsiveness
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Administration of the CEECCA
3.3. Construct Validity
3.4. Convergent Criterion Validity
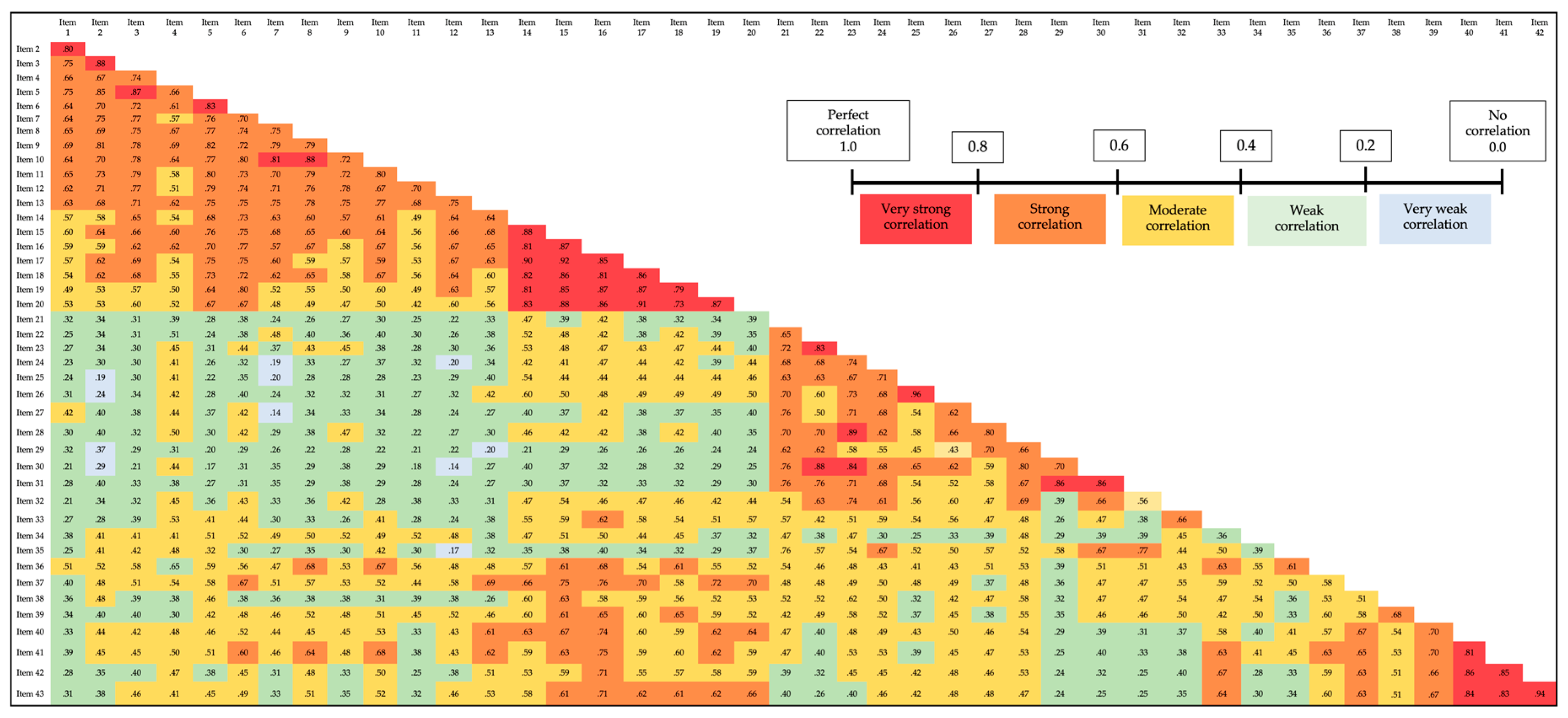
3.5. Reliability through Internal Consistency
3.6. Test-Retest Reliability
3.6.1. Inter-Nurse Reliability in Administering the CEECCA
3.6.2. Intra-Nurse Reliability when Administering the CEECCA
3.5. Responsiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNeil, M.R.; Pratt, S.R. Defining aphasia: Some theoretical and clinical implications of operating from a formal definition. Aphasiology 2001, 15, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthier, M.L. Poststroke Aphasia. Drugs Aging 2005, 22, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelter, S.T.; Gostynski, M.; Papa, S.; Frei, M.; Born, C.; Ajdacic-Gross, V.; Gutzwiller, F.; Lyrer, P.A. Epidemiology of Aphasia Attributable to First Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersano, A.; Burgio, F.; Gattinoni, M.; Candelise, L. Aphasia Burden to Hospitalised Acute Stroke Patients: Need for an Early Rehabilitation Programme. Int. J. Stroke 2009, 4, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauhanen, M.-L.; Korpelainen, J.; Hiltunen, P.; Määttä, R.; Mononen, H.; Brusin, E.; Sotaniemi, K.; Myllylä, V. Aphasia, Depression, and Non-Verbal Cognitive Impairment in Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen PM, Stig Jørgensen H, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS. Aphasia in acute stroke: incidence, determinants, and recovery. Annals of neurology [Internet]. 1995 [citado 2 de septiembre de 2022];38(4):659-66. Available online: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ana.410380416/full.
- Dickey, L.; Kagan, A.; Lindsay, M.P.; Fang, J.; Rowland, A.; Black, S. Incidence and Profile of Inpatient Stroke-Induced Aphasia in Ontario, Canada. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2010, 91, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra i Raventós, M. Comunicación y lenguaje; Universitat de Barcelona, Publicacions i Edicions: Barcelona, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Code, C. The quantity of life for people with chronic aphasia. Neuropsychol. Rehabilitation 2003, 13, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilari, K.; Needle, J.J.; Harrison, K.L. What Are the Important Factors in Health-Related Quality of Life for People With Aphasia? A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2012, 93, S86–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, T.; Johansson, U. The lived experience of engaging in everyday occupations in persons with mild to moderate aphasia. Disabil. Rehabilitation 2013, 35, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, C., Parr, S., Lindsay, J., & Woolf, C. (2017). Beyond Aphasia: Therapies for Living with Communication Disability. Sppechmark.
- Gordon, C.; Ellis-Hill, C.; Ashburn, A. The use of conversational analysis: nurse–patient interaction in communication disability 512 after stroke. J. Adv. Nurs. 2016, 65, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.; Mckeever, M. The impact of stroke aphasia on health and well-being and appropriate nursing interventions: an exploration using the Theory of Human Scale Development. J. Clin. Nurs. 2014, 23, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito Brito, PR. Redes y diagnósticos enfermeros. El Ejido: Círculo; 2013.
- Hemsley, B.; Sigafoos, J.; Balandin, S.; Forbes, R.; Taylor, C.; Green, V.A.; Parmenter, T.; BAppSc, B.H.; BAppSc, C.T.; Ralph Forbes RN B(Health). Nursing the patient with severe communication impairment. J. Adv. Nurs. 2001, 35, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGilton, K.; Sorin-Peters, R.; Sidani, S.; Rochon, E.; Boscart, V.; Fox, M. Focus on communication: increasing the opportunity for successful staff–patient interactions. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2011, 6, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitworth A, Webster J, Howard D. A Cognitive Neuropsychological Approach to Assessment and Intervention in Aphasia: A Clinician’s Guide. 2nd ed. Psychology Press; 2013. [CrossRef]
- E Poslawsky, I.; Schuurmans, M.J.; Lindeman, E.; Hafsteinsdóttir, T.B. A systematic review of nursing rehabilitation of stroke patients with aphasia. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terradillos E, López-Higes Sánchez R. Guía de intervención logopédica en las afasias. Síntesis; 2016.
- Martín-Dorta, W.-J.; Brito-Brito, P.-R.; García-Hernández, A.-M. Development and Content Validation of the CEECCA Questionnaire to Assess Ability to Communicate among Individuals with Aphasia Based on the NANDA-I and NOC. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal A, Centeno C, Watson R, Martínez M, Sanz Rubiales Á. ¿Cómo validar un instrumento de medida de la salud? Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra [Internet]. 2011 [citado 26 de spetiembre de 2016];34(1):63-72. Disponible en: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S1137-66272011000100007&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=pt.
- Ramada-Rodilla, J.M.; Serra-Pujadas, C.; Delclós-Clanchet, G.L. Adaptación cultural y validación de cuestionarios de salud: revisión y recomendaciones metodológicas. 2013, 55, 57–66. [CrossRef]
- Brito-Brito, P.R.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, C.; Sierra-López, A.; Rodríguez-Gómez, J.; Aguirre-Jaime, A. Diseño y validación de un cuestionario para el diagnóstico enfermero psicosocial en Atención Primaria. 2012, 22, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Sánchez, J.M.; Brito-Brito, P.R.; Martínez-Alberto, C.E.; Martín-García, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Rodríguez-Álvaro, M.; Paloma-Castro, O.; CoNocidiet-Research Group. A New Instrument for Measuring Dietary Knowledge in Patients With Diabetes: Psychometric Testing of the CoNOCidiet-Diabetes. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2021, 32, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hachioui, H.; Visch-Brink, E.G.; de Lau, L.M.L.; van de Sandt-Koenderman, M.W.M.E.; Nouwens, F.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Dippel, D.W.J. Screening tests for aphasia in patients with stroke: a systematic review. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enderby, P.M.; Wood, V.A.; Wade, D.T.; Hewer, R.L. The Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test: a short, simple test for aphasia appropriate for non-specialists. Int. Rehabilitation Med. 1987, 8, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khawaja, I.; Wade, D.T.; Collin, C.F. Bedside screening for aphasia: a comparison of two methods. J. Neurol. 1996, 243, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommessen, B.; Thoresen, G.E.; Bautz-Holter, E.; Laake, K. Screening by nurses for aphasia in stroke- the Ullevaal Aphasia Screening (UAS) test. Disabil. Rehabilitation 1999, 21, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doesborgh, S.J.C.; van de Sandt-Koenderman, W.M.E.; Dippel, D.W.J.; van Harskamp, F.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Visch-Brink, E.G. Linguistic deficits in the acute phase of stroke. J. Neurol. 2003, 250, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Košťálová, M.; Bártková, E.; Šajgalíková, K.; Dolenská, A.; Dušek, L.; Bednařík, J. A standardization study of the Czech version of the Mississippi Aphasia Screening Test (MASTcz) in stroke patients and control subjects. Brain Inj. 2008, 22, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamand-Roze, C.; Falissard, B.; Roze, E.; Maintigneux, L.; Beziz, J.; Chacon, A.; Join-Lambert, C.; Adams, D.; Denier, C.; R, V.H.; et al. Validation of a New Language Screening Tool for Patients With Acute Stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Heo, J. Differentiating between Aphasic and Nonaphasic Stroke Patients Using Semantic Verbal Fluency Measures with Administration Time of 30 Seconds. Eur. Neurol. 2011, 65, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, M.; Sánchez, A.; Marín, C.; Navarro, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Ferri, J.; Noé, E. Utilidad clínica de la versión en castellano del Mississippi Aphasia Screening Test (MASTsp): validación en pacientes con ictus. 2012, 27, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Park, H.K.; Ahn, K.-H.; Son, Y.-J.; Paik, N.-J. A Telescreening Tool to Detect Aphasia in Patients with Stroke. Telemed. e-Health 2015, 21, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodglass H, Kaplan E, García-Albea JE, Sánchez Bernardos ML. Evaluación de la afasia y de trastornos relacionados. Editorial Médica Panamericana; 1998.
- Moorhead S, Johnson M, Maas ML, Swanson E. Clasificación de Resultados de Enfermería (NOC): Medición de Resultados en Salud. Elsevier España; 2013.
- Herdman TH, Carter DP, Martín Iglesias S, North American Nursing Diagnosis Association. NANDA International, diagnósticos enfermeros: definiciones y clasificación, 2012-2014.; 2012.
- Luján-Tangarife, A J, Cardona-Arias, A J. Construcción y validación de escalas de medición en salud: revisión de propiedades psicométricas. Archivos de Medicina. 2015;11(3). Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=5178935.
- Brtio-Brito, PR. Investigación sobre el proceso de valoración enfermera. En: Investigación en metodología y lenguajes enfermeros; Echevarría-Pérez, P., directora. Barcelona: Elsevier España; 2016; p.p. 159-70.
- Morilla-Herrera, J.C.; Morales-Asencio, J.M.; Fernández-Gallego, M.C.; Cobos, E.B.; Romero, A.D. Utilidad y validez de un instrumento basado en indicadores de la Nursing Outcomes Classification como ayuda al diagnóstico de pacientes crónicos de Atención Primaria con gestión ineficiente de la salud propia. An. del Sist. Sanit. de Navar. 2011, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Bath, P.M.; Lyden, P.D.; Bernhardt, J.; Brady, M. Representation of People with Aphasia in Randomized Controlled Trials of Acute Stroke Interventions. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, M.C.; Fredrick, A.; Williams, B. People with Aphasia: Capacity to Consent, Research Participation and Intervention Inequalities. Int. J. Stroke 2013, 8, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, A.; Brown, L.; Smith, J.; House, A.; Knapp, P.; Wright, J.J.; Young, J. Information provision for stroke patients and their caregivers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, 11, CD001919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. A second generation little jiffy. Psychometrika 1970, 35, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero KP, Mora OM. Análisis factorial exploratorio mediante el uso de las medidas de adecuación muestral kmo y esfericidad de Bartlett para determinar factores principales. Journal of Science and Research: Revista Ciencia e Investigación ISSN 2528-8083. 2020;5(CININGEC):903-924.
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, DG. Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman & Hall/CRC; 1999.
- González Lázaro P, González Ortuño B. Afasia: de la teoría a la práctica. Editorial Medica Panamericana; 2012.
- Tomás-Sábado, J. Fundamentos de bioestadística y análisis de datos para enfermería. Univ. Autónoma de Barcelona; 2010.
- Bellido-Vallejo, J.C.; Rodríguez-Torres, M.C.; López-Medina, I.M.; Pancorbo-Hidalgo, P.L. Psychometric Testing of the Spanish Version of the Pain Level Outcome Scale in Hospitalized Patients With Acute Pain. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2016, 27, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Mayoral, A.; Peña-Casanova, J. [Test-retest and interrater reliability of Barcelona Test]. Neurología 2006, 21, 277–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matias-Guiu, J.; de Bobadilla, R.F.; Escudero, G.; Pérez-Pérez, J.; Cortés, A.; Morenas-Rodríguez, E.; Valles-Salgado, M.; Moreno-Ramos, T.; Kulisevsky, J. Validación de la versión española del test Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination III para el diagnóstico de demencia. Neurología 2015, 30, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero-Arias, J.; Turrión-Rojo, M. Validación de una versión española del Test Your Memory. Neurología, 2016; 31, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalemans, R.J.; de Witte, L.P.; Beurskens, A.J.; Heuvel, W.J.v.D.; Wade, D.T. Psychometric Properties of the Community Integration Questionnaire Adjusted for People With Aphasia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2010, 91, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhogal, S.K.; Teasell, R.; Speechley, M. Intensity of Aphasia Therapy, Impact on Recovery. Stroke 2003, 34, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, M.C.; Kelly, H.; Godwin, J.; Enderby, P.; Campbell, P. Speech and language therapy for aphasia following stroke. Cochrane 2016, 2016, CD000425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016;(6). [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ge, L.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, P.; Xiang, J. Constraint-induced aphasia therapy for patients with aphasia: A systematic review. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2020, 7, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, M.L.; Pulvermüller, F. Neuroscience insights improve neurorehabilitation of poststroke aphasia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simic, T.; Leonard, C.; Laird, L.; Stewart, S.; Rochon, E. The effects of intensity on a phonological treatment for anomia in post-stroke aphasia. J. Commun. Disord. 2021, 93, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, E.; Ciccone, N.; Godecke, E. An exploration of aphasia therapy dosage in the first six months of stroke recovery. Neuropsychol. Rehabilitation 2021, 31, 1254–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozeiko, J.; Coelho, C.A.; Myers, E.B. The role of intensity in constraint-induced language therapy for people with chronic aphasia. Aphasiology 2016, 30, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozeiko, J.; Myers, E.B.; Coelho, C.A. Treatment Response to a Double Administration of Constraint-Induced Language Therapy in Chronic Aphasia. J. Speech, Lang. Hear. Res. 2018, 61, 1664–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Hernández AM, Brito Brito PR, Rodríguez Álvaro M, et al. Adaptación al español y validación de la Escala de Continuidad de Vínculos (ECV) con el ser querido fallecido. Spanish adaptation and validation of the Continuig Bonds Scale (CBS) with the deceased loved one. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, IS. Validación y adaptación de un instrumento de medida de funcionalidad biopsicosocial en ámbito sanitario rural. http://purl.org/dc/dcmitype/Text. Universidad de La Laguna; 2017. Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/tesis?codigo=175175.
- Badia, X.; Baró, E. Cuestionarios de salud en España y su uso en atención primaria. Aten Primaria. 2001; 28, 249–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Participants with aphasia (n) |
Participants without aphasia (n) |
Sample size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test: a short, simple test for aphasia appropriate for non-specialists [27]. | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Bedside screening for aphasia: A comparison of two methods [28]. | 45 | 5 | 50 |
| Screening by nurses for aphasia in stroke--the Ullevaal Aphasia Screening (UAS) test [29]. | 8 | 29 | 37 |
| Linguistic deficits in the acute phase of stroke [30]. | 14 | 49 | 63 |
| A standardization study of the Czech version of the Mississippi Aphasia Screening Test (MASTcz) in stroke patients and control subjects [31]. | 149 | 45 | 194 |
| Validation of a new language screening tool for patients with acute stroke: the Language Screening Test (LAST) [32]. | 52 | 50 | 102 |
| Differentiating between aphasic and nonaphasic stroke patients using semantic verbal fluency measures with administration time of 30 seconds [33]. | 27 | 26 | 53 |
| Utilidad clínica de la versión en castellano del Mississippi Aphasia Screening Test (MASTsp): Validación en pacientes con ictus [34]. | 29 | 29 | 58 |
| A Telescreening Tool to Detect Aphasia in Patients with Stroke [35]. | 30 | 30 | 60 |
| Areas in the CEECCA questionnaire | Areas in the Boston test |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Areas in the CEECCA questionnaire | Defining characteristics. Impaired verbal communication (2015-2017) |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Areas in the CEECCA questionnaire | NOC outcome. Indicator |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Areas in the CEECCA questionnaire | Frequency | Percentage (%) of dysfunctionality |
| Verbal expression: conversational speech | 15 | 31.9 |
| Verbal expression: descriptive speech | 27 | 57.4 |
| Naming objects verbally | 20 | 42.6 |
| Naming actions verbally | 18 | 38.3 |
| Written expression: writing name and surname(s) | 20 | 42.6 |
| Naming objects in writing | 27 | 57.4 |
| Naming actions in writing | 34 | 72.3 |
| Expressing actions through pictograms | 7 | 14.9 |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms | 14 | 29.8 |
| Auditory comprehension of words | 8 | 17.0 |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences | 21 | 44.7 |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands | 21 | 44.7 |
| Reading comprehension of words | 18 | 38.3 |
| Reading comprehension of sentences | 27 | 57.4 |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin sampling adequacy measure | .30 | |
| Bartlett’s sphericity test | chi-squared approximation | 3190 |
| df | 903 | |
| Sig. | .000 | |
| Component | Initial eigenvalues | ||
| Total | % of the variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 22.4 | 52.1 | 52.0 |
| 2 | 5.6 | 13.1 | 65.2 |
| 3 | 2.9 | 6.8 | 72.0 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 3.6 | 75.6 |
| 5 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 78.6 |
| Items in the CEECCA | Components | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Conversational speech. Item 3 | .87 | ||||
| Conversational speech. Item 5 | .86 | ||||
| Conversational speech. Item 2 | .85 | ||||
| Naming actions verbally. Item 11 | .85 | ||||
| Naming objects verbally. Item 9 | .84 | ||||
| Naming objects verbally. Item 8 | .82 | ||||
| Naming objects verbally. Item 10 | .82 | ||||
| Naming objects verbally. Item 7 | .82 | ||||
| Naming actions verbally. Item 12 | .79 | ||||
| Conversational speech. Item 1 | .77 | ||||
| Naming actions verbally. Item 13 | .74 | ||||
| Descriptive speech. Item 6 | .73 | ||||
| Conversational speech. Item 4 | .66 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 36 | .50 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of words. Item 30 | .90 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of words. Item 31 | .87 | ||||
| Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 21 | .83 | ||||
| Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 23 | .81 | ||||
| Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 22 | .79 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of words. Item 28 | .79 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of words. Item 29 | .77 | ||||
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 24 | .76 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 35 | .74 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of words. Item 27 | .74 | ||||
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 25 | .71 | ||||
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 26 | .70 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 32 | .62 | ||||
| Naming actions in writing. Item 20 | .75 | ||||
| Naming objects in writing. Item 17 | .74 | ||||
| Naming actions in writing. Item 19 | .71 | ||||
| Writing name and surname(s). Item 14 | .71 | ||||
| Naming objects in writing. Item 15 | .67 | ||||
| Naming actions in writing. Item 18 | .59 | ||||
| Naming objects in writing. Item 16 | .58 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 37 | .45 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 42 | .88 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 43 | .85 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 41 | .79 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of words. Item 40 | .76 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 33 | .52 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of words. Item 39 | .55 | ||||
| Reading comprehension of words. Item 38 | .55 | ||||
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 34 | .50 | ||||
| Theoretical dimensions | Component items of each theoretical dimension | Dimensions resulting from the factor analysis | Items that are components of the dimensions according to factor analysis | Final dimensions | Component items of each final dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verbal expression | 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10, 11,12,13 |
Verbal expression/ Auditory comprehension |
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, 10,11,12,13/36 |
Verbal expression | 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10, 11,12,13 |
| Written expression | 14,14,16,17,18,19,20 | Written expression/ Auditory comprehension |
14,15,16,17,18, 19,20/37 |
Written expression | 14,14,16,17,18,19,20 |
| Expression through pictograms | 21,22,23,24,25,26 | Expression through pictograms/ Auditory comprehension |
21,22,23,24,25,26/27,28,29,30,31,32,35 | Expression through pictograms | 21,22,23,24,25,26 |
| Auditory comprehension | 27,28,29,30,31,32, 33,34,35,36,37 |
Reading comprehension/ Auditory comprehension |
40,41,42,43/33 | Auditory comprehension | 27,28,29,30,31,32, 33,34,35,36,37 |
| Reading comprehension | 38,39,40,41,42,43 | Reading comprehension/ Auditory comprehension |
38,39/33 | Reading comprehension | 38,39,40,41,42,43 |
|
CEECCA (Areas) |
BOSTON TEST (Areas) |
70th percentile | 60th percentile | ||||||||
| Functionality concordance (%) | Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value |
p-value |
Functionality concordance (%) | Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value |
p-value |
||
| Conversational speech | Conversational speech | 48.9 | 29.8 | 78.7 | 0.57 | <0.001 | 61.7 | 29.8 | 91.5 | 0.81 | <0.001 |
| Descriptive speech | Descriptive speech | 42.6 | 51.1 | 93.7 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 42.6 | 40.4 | 83 | 0.67 | <0.001 |
| Naming objects verbally | Visual confrontation naming | 25.5 | 44.7 | 70.2 | 0.43 | <0.001 | 34.0 | 44.7 | 78.7 | 0.49 | <0.001 |
| Naming actions verbally | Visual confrontation naming | 25.5 | 38.3 | 63.8 | 0.35 | 0.002 | 34.0 | 38.3 | 72.3 | 0.49 | <0.001 |
| Writing name and surname(s) | Writing mechanics: name | 17.0 | 44.7 | 61.7 | 0.26 | 0.017 | 44.7 | 44.7 | 89.4 | 0.79 | <0.001 |
| Naming objects in writing | Written confrontation naming | 31.9 | 55.3 | 87.2 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 32.6 | 50.0 | 82.6 | 0.64 | <0.001 |
| Naming actions in writing | Written confrontation naming | 25.5 | 59.6 | 85.1 | 0.67 | <0.001 | 26.1 | 54.3 | 80.4 | 0.59 | <0.001 |
| Auditory comprehension of words | Auditory discrimination of words | 38.3 | 17.0 | 55.3 | 0.23 | 0.014 | 40.4 | 17.0 | 57.4 | 0.24 | 0.011 |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences | Auditory comprehension of verbal commands | 29.8 | 40.4 | 70.2 | 0.42 | 0.001 | 36.2 | 36.2 | 72.4 | 0.45 | 0.001 |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands | Auditory comprehension of commands | 34.0 | 44.7 | 78.7 | 0.59 | <0.001 | 40.4 | 40.4 | 80.8 | 0.62 | <0.001 |
| Reading comprehension of words | Reading comprehension: Matching pictures and words | 25.5 | 38.3 | 63.8 | 0.35 | 0.002 | 34.0 | 38.3 | 72.3 | 0.49 | <0.001 |
| Reading comprehension of sentences | Reading comprehension: Reading sentences and paragraphs. | 31.9 | 55.3 | 87.2 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 55.3 | 87.2 | 0.73 | <0.001 |
| CEECCA (Area) | NANDA-I diagnosis Impaired verbal communication (DCs) |
Functionality concordance (%) |
Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conversational speech | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 8.5 | 31.9 | 40.4 | 0.08 | 0.152 |
| DC3. Difficulty forming sentences. | 21.3 | 31.9 | 53.2 | 0.23 | 0.015 | |
| DC4. Difficulty forming words (e.g., aphonia, dyslalia, dysarthria). | 34.0 | 31.9 | 65.9 | 0.39 | 0.001 | |
| DC5. Difficulty speaking. | 23.4 | 29.8 | 53.2 | 0.21 | 0.042 | |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication | 23.4 | 31.9 | 55.3 | 0.25 | 0.009 | |
| DC9. Difficulty verbalizing. | 23.4 | 29.8 | 53.2 | 0.21 | 0.042 | |
| DC13. Slurred speech. | 36.2 | 29.8 | 66.0 | 0.37 | 0.002 | |
| DC14. Inappropriate verbalization. | 31.9 | 31.9 | 63.8 | 0.36 | 0.001 | |
| Descriptive speech | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 8.5 | 57.4 | 65.9 | 0.22 | 0.015 |
| DC3. Difficulty forming sentences. | 19.1 | 55.3 | 74.4 | 0.44 | 0.001 | |
| DC4. Difficulty forming words (e.g., aphonia, dyslalia, dysarthria). | 27.7 | 51.1 | 78.8 | 0.55 | <0.001 | |
| DC5. Difficulty speaking. | 19.1 | 51.1 | 70.2 | 0.36 | 0.008 | |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 23.4 | 57.4 | 80.8 | 0.58 | <0.001 | |
| DC9. Difficulty verbalizing. | 14.9 | 46.8 | 61.7 | 0.17 | 0.200 | |
| DC13. Slurred speech. | 27.7 | 46.8 | 74.5 | 0.47 | 0.001 | |
| DC14. Inappropriate verbalization. | 27.7 | 53.2 | 80.9 | 0.60 | <0.001 | |
| Naming objects verbally | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 8.5 | 44.7 | 53.2 | 0.14 | 0.060 |
| DC4. Difficulty forming words (e.g., aphonia, dyslalia, dysarthria). | 31.9 | 42.6 | 76.6 | 0.51 | <0.001 | |
| DC5. Difficulty speaking. | 23.4 | 42.6 | 66.0 | 0.35 | 0.003 | |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 23.4 | 44.7 | 68.1 | 0.40 | 0.001 | |
| DC9. Difficulty verbalizing. | 23.4 | 42.6 | 66.0 | 0.35 | 0.003 | |
| DC13. Slurred speech. | 34.0 | 40.4 | 74.4 | 0.50 | <0.001 | |
| DC14. Inappropriate verbalization. | 29.8 | 42.6 | 72.4 | 0.47 | <0.001 | |
| Naming actions verbally |
DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 8.5 | 38.3 | 46.8 | 0.11 | 0.099 |
| DC4. Difficulty forming words (e.g., aphonia, dyslalia, dysarthria). | 34.0 | 38.3 | 72.3 | 0.49 | <0.001 | |
| DC5. Difficulty speaking. | 25.5 | 38.3 | 63.8 | 0.35 | 0.002 | |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 23.4 | 38.4 | 61.8 | 0.32 | 0.003 | |
| DC9. Difficulty verbalizing. | 23.4 | 36.2 | 59.6 | 0.28 | 0.013 | |
| DC13. Slurred speech. | 36.2 | 36.2 | 72.4 | 0.48 | <0.001 | |
| DC14. Inappropriate verbalization. | 31.9 | 38.3 | 70.2 | 0.45 | <0.001 | |
| Writing name and surname(s) | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 6.4 | 44.7 | 51.1 | 0.07 | 0.361 |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 19.1 | 42.6 | 61.7 | 0.26 | 0.300 | |
| Naming objects in writing | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 6.4 | 59.6 | 66.0 | 0.16 | 0.114 |
| DC6.Difficulty maintaining communication. | 17.0 | 55.3 | 72.3 | 0.37 | 0.007 | |
| Naming actions in writing | DC2. Difficulty expressing thoughts verbally (e.g., aphasia, dysphasia, apraxia, dyslexia). | 6.4 | 70.2 | 76.6 | 0.26 | 0.027 |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 12.8 | 61.7 | 74.5 | 0.33 | 0.023 | |
| Expressing actions through pictograms | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 44.7 | 14.9 | 59.6 | 0.25 | 0.010 |
| DC7. Difficulty in use of body expressions. | 48.9 | 12.8 | 61.7 | 0.22 | 0.035 | |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 38.3 | 23.4 | 61.7 | 0.27 | 0.037 |
| DC7. Difficulty in use of body expressions. | 42.6 | 21.3 | 63.9 | 0.27 | 0.045 | |
| Auditory comprehension of words | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 44.7 | 17.0 | 61.7 | 0.28 | 0.005 |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 23.4 | 17.0 | 40.4 | 0.12 | 0.086 | |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 38.3 | 38.3 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 |
| DC6.Difficulty maintaining communication. | 21.3 | 42.6 | 63.9 | 0.32 | 0.007 | |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 38.3 | 38.3 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 |
| DC6. Difficulty maintaining communication. | 21.3 | 42.6 | 63.9 | 0.31 | 0.007 | |
| Reading comprehension of words | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 42.6 | 36.2 | 78.8 | 0.59 | <0.001 |
| Reading comprehension of sentences | DC1. Difficulty comprehending communication. | 31.9 | 46.8 | 78.7 | 0.57 | <0.001 |
|
CEECCA (Areas) |
NOC OUTCOMES. Indicators | When a score of 1 or 2 on the Likert scale of the NOC taxonomy is considered dysfunctional | When a score of 1, 2, or 3 on the Likert scale of the NOC taxonomy is considered dysfunctional | ||||||||
| Functionality concordance (%) | Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
Functionality concordance (%) | Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
||
| Conversational speech | Communication. Indicator 2 | 46.8 | 29.8 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 31.9 | 63.8 | 0.36 | 0.001 |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 51.1 | 31.9 | 83.0 | 0.66 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 31.9 | 61.7 | 0.33 | 0.002 | |
| Communication. Indicator 9 | 51.1 | 29.8 | 80.9 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 31.9 | 68.1 | 0.42 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 2 | 46.8 | 29.8 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 29.8 | 61.7 | 0.31 | 0.007 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 3 | 46.8 | 31.9 | 78.7 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 31.9 | 61.7 | 0.33 | 0.002 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 2 | 51.1 | 31.9 | 83.0 | 0.66 | <0.001 | 25.5 | 31.9 | 57.4 | 0.28 | 0.006 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 9 | 46.8 | 29.8 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 31.9 | 63.8 | 0.36 | 0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 10 | 46.8 | 31.9 | 78.7 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 31.9 | 63.8 | 0.36 | 0.001 | |
| Descriptive speech | Communication. Indicator 2 | 40.4 | 48.9 | 89.3 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 57.4 | 89.3 | 0.78 | <0.001 |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 40.4 | 46.8 | 87.2 | 0.75 | <0.001 | 27.7 | 55.3 | 83 | 0.64 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 9 | 40.4 | 44.7 | 85.1 | 0.71 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 53.2 | 85.1 | 0.69 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 2 | 31.9 | 55.3 | 87.2 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 40.4 | 51.1 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 3 | 29.8 | 57.4 | 87.2 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 42.6 | 48.9 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 2 | 42.6 | 48.9 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 25.5 | 57.4 | 82.9 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 3 | 42.6 | 10.6 | 53.2 | 0.16 | 0.042 | 40.4 | 48.9 | 89.3 | 0.79 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 4 | 42.6 | 8.5 | 51.1 | 0.13 | 0.072 | 40.4 | 48.9 | 89.3 | 0.79 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 9 | 40..4 | 48.9 | 89.3 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 55.3 | 85.1 | 0.69 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 10 | 40.4 | 51.1 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 55.3 | 85.1 | 0.69 | <0.001 | |
| Naming objects verbally | Communication. Indicator 2 | 46.8 | 42.6 | 89.4 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 44.7 | 76.6 | 0.55 | <0.001 |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 48.9 | 42.6 | 92.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 44.7 | 74.5 | 0.51 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 9 | 48.9 | 40.4 | 89.3 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 44.7 | 80.9 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 2 | 48.9 | 44.7 | 93.6 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 34.0 | 44.7 | 78.7 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 3 | 46.8 | 44.7 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 44.7 | 74.5 | 0.51 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 1 | 53.2 | 19.1 | 72.3 | 0.41 | 0.001 | 36.2 | 42.6 | 78.8 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 2 |
51.1 | 44.7 | 95.8 | 0.92 | <0.001 | 25.5 | 44.7 | 70.2 | 0.43 | <0.001 | |
| Naming actions verbally |
Communication. Indicator 2 | 48.9 | 38.3 | 87.2 | 0.75 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 38.3 | 70.2 | 0.45 | <0.001 |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 46.8 | 34.0 | 80.8 | 0.62 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 38.3 | 68.1 | 0.42 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 9 | 51.1 | 36.2 | 87.3 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 38.3 | 74.5 | 0.52 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 2 | 48.9 | 38.3 | 87.2 | 0.75 | <0.001 | 34.0 | 38.3 | 72.3 | 0.49 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 3 | 46.8 | 38.3 | 85.1 | 0.71 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 38.3 | 68.1 | 0.74 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 1 | 57.4 | 17.0 | 74.4 | 0.41 | 0.002 | 36.2 | 36.2 | 72.4 | 0.48 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 2 | 48.9 | 12.8 | 61.7 | 0.70 | <0.001 | 25.5 | 38.3 | 63.8 | 0.35 | <0.001 | |
| Writing name and surname(s) | Communication. Indicator 1 | 36.2 | 46.8 | 83.0 | 0.67 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 46.8 | 68.1 | 0.38 | <0.001 |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 1 | 31.9 | 46.8 | 78.7 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 46.8 | 68.1 | 0.38 | <0.001 | |
| Naming objects in writing | Communication. Indicator 1 | 31.9 | 57.4 | 89.3 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 61.7 | 83.0 | 0.61 | <0.001 |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 1 | 27.7 | 57.4 | 85.1 | 0.68 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 61.7 | 83.0 | 0.61 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 1 | 34.0 | 17.0 | 51.0 | 0.14 | 0.180 | 29.8 | 53.2 | 83.0 | 0.64 | <0.001 | |
| Naming actions in writing | Communication. Indicator 1 | 23.4 | 59.6 | 83.0 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 19.1 | 70.2 | 89.3 | 0.71 | <0.001 |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 1 | 23.4 | 63.8 | 87.2 | 0.70 | <0.001 | 19.1 | 70.2 | 89.3 | 0.71 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 3 | 27.7 | 21.3 | 49.0 | 0.19 | 0.028 | 25.5 | 59.6 | 85.1 | 0.67 | <0.001 | |
| Expressing actions through pictograms | Communication. Indicator 3 | 57.4 | 10.6 | 68.0 | 0.24 | 0.051 | 38.3 | 14.9 | 53.2 | 0.20 | 0.024 |
| Communication. Indicator 6 | 74.5 | 10.6 | 85.1 | 0.50 | <0.001 | 51.1 | 14.9 | 66 | 0.31 | 0.003 | |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 66.0 | 10.6 | 76.6 | 0.35 | 0.009 | 38.3 | 14.9 | 53.2 | 0.20 | 0.024 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 4 | 55.3 | 10.6 | 65.9 | 0.21 | 0.070 | 34.0 | 14.9 | 48.9 | 0.17 | 0.039 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 3 | 72.3 | 10.6 | 82.9 | 0.46 | 0.001 | 55.3 | 12.8 | 68.1 | 0.29 | 0.012 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 5 | 80.9 | 8.5 | 89.4 | 0.56 | <0.001 | 63.8 | 10.6 | 74.4 | 0.32 | 0.015 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 6 | 68.1 | 12.8 | 80.9 | 0.47 | <0.001 | 46.8 | 14.9 | 61.7 | 0.27 | 0.007 | |
| Information processing: Indicator 1 | 78.7 | 14.9 | 93.6 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 14.9 | 53.2 | 0.20 | 0.024 | |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms | Communication. Indicator 3 | 51.1 | 19.1 | 70.2 | 0.34 | 0.017 | 36.2 | 27.7 | 63.9 | 0.34 | 0.004 |
| Communication. Indicator 6 | 63.8 | 14.9 | 78.7 | 0.45 | 0.002 | 42.6 | 21.3 | 63.9 | 0.27 | 0.045 | |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 57.4 | 17.0 | 74.4 | 0.39 | 0.008 | 34.0 | 25.5 | 59.5 | 0.26 | 0.027 | |
| Communication: expressive. Indicator 4 | 48.9 | 19.1 | 68.0 | 0.31 | 0.030 | 29.8 | 25.5 | 55.3 | 0.21 | 0.063 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 3 |
61.7 | 14.9 | 76.6 | 0.40 | 0.005 | 48.9 | 21.3 | 70.2 | 0.37 | 0.009 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 5 | 68.1 | 10.6 | 78.7 | 0.39 | 0.002 | 55.3 | 17.0 | 72.3 | 0.35 | 0.016 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 6 | 57.4 | 17.0 | 74.4 | 0.39 | 0.008 | 42.6 | 25.5 | 68.1 | 0.38 | 0.004 | |
| Information processing. Indicator1 | 63.8 | 14.9 | 78.7 | 0.45 | 0.002 | 34.0 | 25.5 | 59.5 | 0.26 | 0.027 | |
| Auditory comprehension of words | Communication. Indicator 6 | 76.6 | 14.9 | 91.5 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 51.1 | 17.0 | 68.1 | 0.35 | 0.002 |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 68.1 | 14.9 | 83.0 | 0.54 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 17.0 | 55.3 | 0.23 | 0.014 | |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 51.1 | 17.0 | 68.1 | 0.35 | 0.002 | 29.8 | 17.0 | 46.8 | 0.16 | 0.043 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 2 | 72.3 | 17.0 | 89.3 | 0.70 | <0.001 | 42.6 | 17.0 | 59.6 | 0.26 | 0.008 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 6 | 70.2 | 17.0 | 87.2 | 0.65 | <0.001 | 46.8 | 17.0 | 63.8 | 0.31 | 0.004 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 1 | 78.7 | 17.0 | 95.7 | 0.86 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 17.0 | 55.3 | 0.23 | 0.014 | |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences | Communication. Indicator 6 | 51.1 | 17.0 | 68.1 | 0.32 | 0.011 | 42.6 | 36.2 | 78.8 | 0.57 | <0.001 |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 51.1 | 25.5 | 76.6 | 0.51 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 42.6 | 78.8 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 40.4 | 34.0 | 74.4 | 0.49 | 0.001 | 27.7 | 42.6 | 70.3 | 0.43 | 0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 2 | 48.9 | 21.3 | 70.2 | 0.38 | 0.006 | 38.3 | 40.4 | 78.7 | 0.58 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 6 | 46.8 | 21.3 | 68.1 | 0.33 | 0.016 | 38.3 | 36.2 | 74.5 | 0.49 | 0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 5 | 51.1 | 31.9 | 83.0 | 0.65 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 42.6 | 80.9 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 6 | 44.7 | 34.0 | 78.7 | 0.57 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 42.6 | 78.8 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 7 | 42.6 | 36.2 | 78.8 | 0.57 | <0.001 | 27.7 | 42.6 | 70.3 | 0.43 | 0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 6 | 55.3 | 21.3 | 76.6 | 0.50 | <0.001 | 42.6 | 48.9 | 91.5 | 0.57 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 53.2 | 27.7 | 80.9 | 0.60 | <0.001 | 31.9 | 38.3 | 70.2 | 0.42 | 0.002 | |
| Communication. Indicator 8 | 46.8 | 40.4 | 87.2 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 27.7 | 42.6 | 70.3 | 0.43 | 0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 2 | 53.2 | 25.5 | 78.7 | 0.55 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 40.4 | 78.7 | 0.58 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 6 | 53.2 | 27.7 | 80.9 | 0.60 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 36.2 | 74.5 | 0.49 | 0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 5 | 53.2 | 34.0 | 87.2 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 42.6 | 80.9 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 6 | 48.9 | 38.3 | 87.2 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 36.2 | 42.6 | 78.8 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 7 | 46.8 | 40.4 | 87.2 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 27.7 | 42.6 | 70.3 | 0.43 | <0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of words | Communication. Indicator 1 | 36.2 | 38.3 | 74.5 | 0.52 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 38.3 | 59.6 | 0.29 | 0.005 |
| Communication. Indicator 6 | 59.6 | 19.1 | 78.7 | 0.51 | <0.001 | 46.8 | 34.0 | 80.8 | 0.62 | <0.001 | |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 57.4 | 25.5 | 82.9 | 0.62 | <0.001 | 34.0 | 34.0 | 68.0 | 0.40 | 0.003 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 1 | 46.8 | 36.2 | 83.0 | 0.66 | <0.001 | 25.5 | 38.3 | 63.8 | 0.35 | 0.002 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 1 | 59.6 | 19.1 | 78.7 | 0.51 | <0.001 | 38.3 | 38.3 | 76.6 | 0.56 | <0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of sentences | Communication. Indicator 1 | 25.5 | 48.9 | 74.4 | 0.46 | 0.002 | 17.0 | 55.3 | 72.3 | 0.38 | 0.004 |
| Communication. Indicator 6 | 40.4 | 21.3 | 61.7 | 0.31 | 0.003 | 31.9 | 40.4 | 72.3 | 0.45 | 0.002 | |
| Communication. Indicator 7 | 40.4 | 29.8 | 70.2 | 0.45 | <0.001 | 27.7 | 51.1 | 78.8 | 0.55 | <0.001 | |
| Communication: receptive. Indicator 1 | 34.0 | 44.7 | 78.7 | 0.57 | <0.001 | 23.4 | 57.4 | 80.8 | 0.58 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 5 | 36.2 | 31.9 | 68.1 | 0.39 | 0.003 | 29.8 | 48.9 | 78.7 | 0.56 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 6 | 36.2 | 40.4 | 76.6 | 0.54 | <0.001 | 29.8 | 51.1 | 80.9 | 0.60 | <0.001 | |
| Information processing. Indicator 7 | 34.0 | 42.6 | 76.6 | 0.53 | <0.001 | 21.3 | 51.1 | 72.4 | 0.41 | 0.005 | |
| Spearman’s rho | BOSTON_SUM | NANDACDSUM | NOCINDSUM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEESUMTOT | Correlation coefficient | .914** | -.845** | .914** |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | .000 | .000 | .000 | |
| N | 47 | 47 | 47 | |
| Areas in the CEECCA | Functionality concordance (%) |
Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nurse (a) |
Nurse (b) |
|||||
| Verbal expression: Conversational speech. | 66.0 | 29.8 | 95.8 | 0.90 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Descriptive speech. | 40.4 | 57.4 | 97.8 | 0.96 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming objects verbally. | 55.3 | 40.4 | 95.7 | 0.91 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming actions verbally. | 57.4 | 31.9 | 89.3 | 0.77 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Writing name and surname(s). | 48.9 | 42.6 | 91.5 | 0.83 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming objects in writing. | 36.2 | 57.4 | 93.6 | 0.87 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming actions in writing. | 25.5 | 66.0 | 91.5 | 0.80 | <0.001 | |
| Expressing actions through pictograms. | 83.0 | 8.5 | 91.5 | 0.62 | <0.001 | |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. | 68.1 | 19.1 | 87.2 | 0.67 | <0.001 | |
| Auditory comprehension of words | 83.0 | 17.0 | 100 | 1.00 | <0.001 | |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. | 42.6 | 29.8 | 72.4 | 0.44 | 0.003 | |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. | 44.7 | 29.8 | 74.5 | 0.48 | 0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of words. | 55.3 | 36.2 | 91.5 | 0.82 | <0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of sentences. | 36.2 | 55.3 | 91.5 | 0.82 | <0.001 | |
| Areas in the CEECCA | Functionality concordance (%) |
Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nurse (a) at baseline |
Nurse (a) at one month |
|||||
| Verbal expression: Conversational speech. | 63.6 | 24.2 | 87.8 | 0.71 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Descriptive speech. | 39.4 | 48.5 | 87.9 | 0.76 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming objects verbally. | 48.5 | 36.9 | 85.4 | 0.69 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming actions verbally. | 60.6 | 33.3 | 93.9 | 0.87 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Writing name and surname(s). | 57.6 | 33.3 | 90.9 | 0.81 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming objects in writing. | 42.4 | 48.5 | 90.9 | 0.82 | <0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming actions in writing. | 30.3 | 63.6 | 93.9 | 0.86 | <0.001 | |
| Expressing actions through pictograms. | 87.9 | 3.0 | 90.9 | 0.35 | 0.038 | |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. | 69.7 | 6.1 | 75.8 | 0.18 | 0.287 | |
| Auditory comprehension of words |
84.8 | 9.1 | 93.9 | 0.72 | <0.001 | |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. | 42.4 | 24.2 | 66.6 | 0.31 | 0.073 | |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. | 48.5 | 33.3 | 81.8 | 0.63 | <0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of words. | 63.6 | 27.3 | 90.9 | 0.79 | <0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of sentences. | 42.4 | 39.4 | 81.8 | 0.64 | <0.001 | |
| Areas in the CEECCA | Functionality concordance (%) |
Dysfunctionality concordance (%) |
Total concordance (%) |
Cohen’s κ value | Sig. p |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nurse (b) at baseline |
Nurse (b) at one month |
|||||
| Verbal expression: Conversational speech. | 64.3 | 35.7 | 100 | 1.00 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Descriptive speech. | 42.9 | 50.0 | 92.9 | 0.86 | 0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming objects verbally. | 57.1 | 42.9 | 100 | 1.00 | <0.001 | |
| Verbal expression: Naming actions verbally. | 57.1 | 35.7 | 92.8 | 0.85 | 0.001 | |
| Written expression: Writing name and surname(s). | 35.7 | 57.1 | 92.8 | 0.85 | 0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming objects in writing. | 28.6 | 64.3 | 92.9 | 0.84 | 0.001 | |
| Written expression: Naming actions in writing. | 14.3 | 71.4 | 85.7 | 0.58 | 0.031 | |
| Expressing actions through pictograms. | 78.6 | 21.4 | 100 | 1.00 | <0.001 | |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms. | 50.0 | 28.6 | 78.6 | 0.55 | 0.036 | |
| Auditory comprehension of words. | 71.4 | 28.6 | 100 | 1.00 | <0.001 | |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences. | 42.9 | 42.9 | 85.8 | 0.71 | 0.008 | |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. | 42.9 | 28.6 | 71.5 | 0.43 | 0.094 | |
| Reading comprehension of words. | 42.9 | 50.0 | 92.9 | 0.86 | 0.001 | |
| Reading comprehension of sentences. | 14.3 | 78.6 | 92.9 | 0.76 | 0.003 | |
| Areas in the CEECCA | Status of the area pre-intervention |
Status of the area post- intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Conversational speech | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Descriptive speech | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Naming objects verbally | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Naming actions verbally | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Writing name and surname(s) | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Naming objects in writing | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Naming actions in writing | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Expressing actions through pictograms | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Expressing emotions through pictograms | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Auditory comprehension of words | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Auditory comprehension of sentences | DYSFUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Auditory comprehension of verbal commands | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Reading comprehension of words | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Reading comprehension of sentences | FUNCTIONAL | FUNCTIONAL |
| Areas in the Boston test | Status of the area pre-intervention |
Status of the area post- intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Conversational speech | 2 / 5 | 2 / 5 |
| Descriptive speech | 1 / 5 | 2 / 5 |
| Visual confrontation naming | 26 / 96 | 51 / 96 |
| Writing mechanics | 2 / 5 – 2 / 5 – 2/ 5 | 3 / 5 – 2 / 5 – 3 / 5 |
| Written confrontation naming | 1 / 10 | 6 / 10 |
| Auditory comprehension of words | 43 / 72 | 63,5 / 72 |
| Auditory comprehension of commands | 8 / 15 | 12 / 15 |
| Reading comprehension of words. Matching pictures and words | 0 / 10 | 6 / 10 |
| Reading comprehension of sentences and paragraphs | 0 / 10 | 5 / 10 |
| Items in the CEECCA | Mean of the scale if the item is removed | Scale variance if the item is removed | Item-total correlation corrected | Cronbach’s alpha if the item is removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEECCA (a). Conversational speech. Item 1 | 113.09 | 596.56 | .68 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Conversational speech. Item 2 | 113.34 | 585.06 | .76 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Conversational speech. Item 3 | 113.45 | 584.69 | .80 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Conversational speech. Item 4 | 113.19 | 590.38 | .73 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Conversational speech. Item 5 | 113.66 | 577.58 | .82 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Descriptive speech. Item 6 | 114.04 | 578.39 | .84 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects verbally. Item 7 | 113.45 | 584.30 | .74 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects verbally. Item 8 | 113.64 | 581.63 | .80 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects verbally. Item 9 | 113.38 | 583.89 | .77 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects verbally. Item 10 | 113.64 | 580.67 | .80 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions verbally. Item 11 | 113.64 | 584.63 | .71 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions verbally. Item 12 | 113.62 | 582.72 | .75 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions verbally. Item 13 | 113.72 | 582.6 | .78 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Writing name and surname(s). Item 14 | 113.89 | 577.36 | .84 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects in writing. Item 15 | 113.98 | 573.93 | .88 | .97 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects in writing. Item 16 | 114.11 | 573.27 | .87 | .97 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming objects in writing. Item 17 | 114.11 | 575.58 | .85 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions in writing. Item 18 | 114.26 | 581.15 | .83 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions in writing. Item 19 | 114.34 | 583.40 | .80 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Naming actions in writing. Item 20 | 114.26 | 580.98 | .78 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 21 | 113.74 | 610.89 | .56 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 22 | 113.74 | 610.46 | .58 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing actions through pictograms. Item 23 | 113.77 | 608.84 | .63 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 24 | 113.79 | 609.87 | .57 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 25 | 113.89 | 609.10 | .54 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Expressing emotions through pictograms. Item 26 | 113.91 | 607.43 | .60 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of words. Item 27 | 113.70 | 612.00 | .56 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of words. Item 28 | 113.72 | 610.51 | .60 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of words. Item 29 | 113.66 | 615.53 | .43 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of words. Item 30 | 113.70 | 612.82 | .51 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of words. Item 31 | 113.70 | 612.74 | .52 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 32 | 113.94 | 606.45 | .58 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 33 | 114.15 | 602.70 | .62 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of sentences. Item 34 | 114.43 | 606.86 | .59 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 35 | 113.79 | 608.48 | .53 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 36 | 114.11 | 599.97 | .75 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Auditory comprehension of verbal commands. Item 37 | 114.30 | 602.21 | .78 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of words. Item 38 | 113.98 | 602.67 | .63 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of words. Item 39 | 114.11 | 599.36 | .69 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of words. Item 40 | 114.21 | 596.78 | .72 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 41 | 114.30 | 594.48 | .74 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 42 | 114.34 | 598.01 | .66 | .98 |
| CEECCA (a). Reading comprehension of sentences. Item 43 | 114.36 | 598.37 | .69 | .98 |
| Instrument | Sample size (n) | CVI/RI | Total variance explained | Criterion validity | Test-retest reliability | CI | ||
| Inter-observer | Intra- observer |
|||||||
| CEECCA |
47 | 0.90/0.90 | 79% | 0.23-0. 87a* p<0.014 - p<0.001 0.11-0.60b* p<0.10 - p<0.001 0.14-0.91c* p<0.18 - p<0.001 |
0. 92 a *** p<0.001 -0.85 b *** p<0.001 0.91 c *** p<0.001 |
0.50-1.00* | 0.19-0.87* | 0.98 |
| Adaptación al español y validación de la Escala de Continuidad de Vínculos (EVC) con el ser querido fallecido [64]. | 255 | − / − | 57% | -0.40 **** p<0.001 |
0.79-0.94 **** | − | 0.91 | |
| A new instrument for measuring dietary knowledge in patients with diabetes: Psychometric Testing of the CoNOCidiet-Diabetes [25]. | 350 | 0.87/0.87 | − | 0.72 *** p<0.001 |
0.70-0.90 **** | − | 0.67 | |
| Validación y adaptación de un instrumento de medida de funcionalidad biopsicosocial en el ámbito sanitario rural [65]. | 354 | 0.83/0.81 | − | 0.53 d *** p<0.001 0.62 e *** p<0.001 0.73 f *** p<0.001 |
0.17-0.91* | − | 0.92 | |
| Diseño y validación de un cuestionario para el diagnóstico enfermero psicosocial en Atención Primaria [24]. | 188 | − / − | 91% | 0.15-0.89 * p<0.049- p<0.001 |
0.38-0.89* | 0.67-0.91* | 0.93 | |
| Utilidad y validez de un instrumento basado en indicadores de las Nursing Outcomes Classification como ayuda al diagnóstico de pacientes crónicos de Atención Primaria con gestión ineficiente de la salud propia [41]. | 228 | − / − | − | 0.16 ** p<0.001 |
0.61-0.90* | − | 0.81 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





