Submitted:
05 January 2023
Posted:
06 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background and Scope
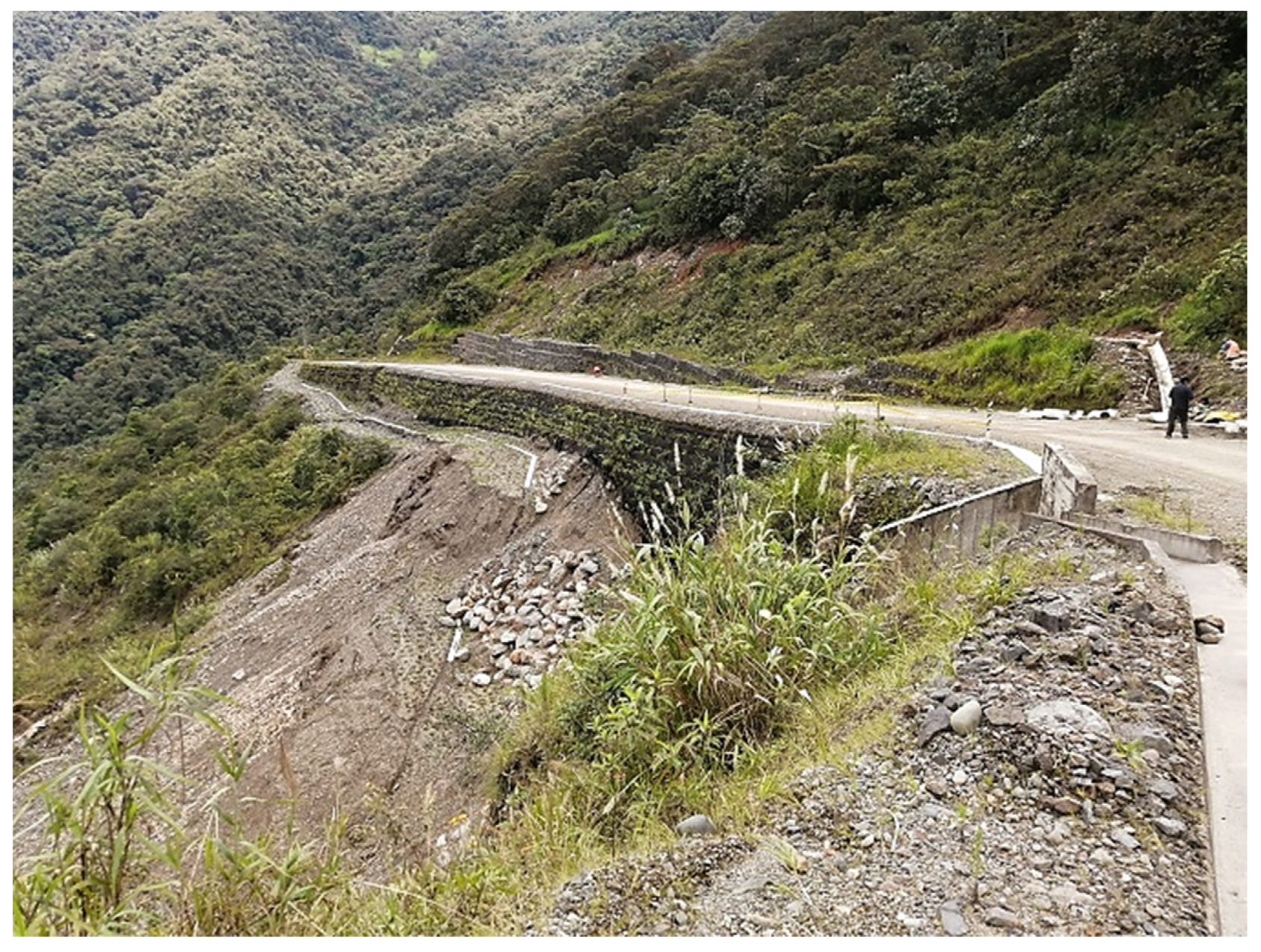
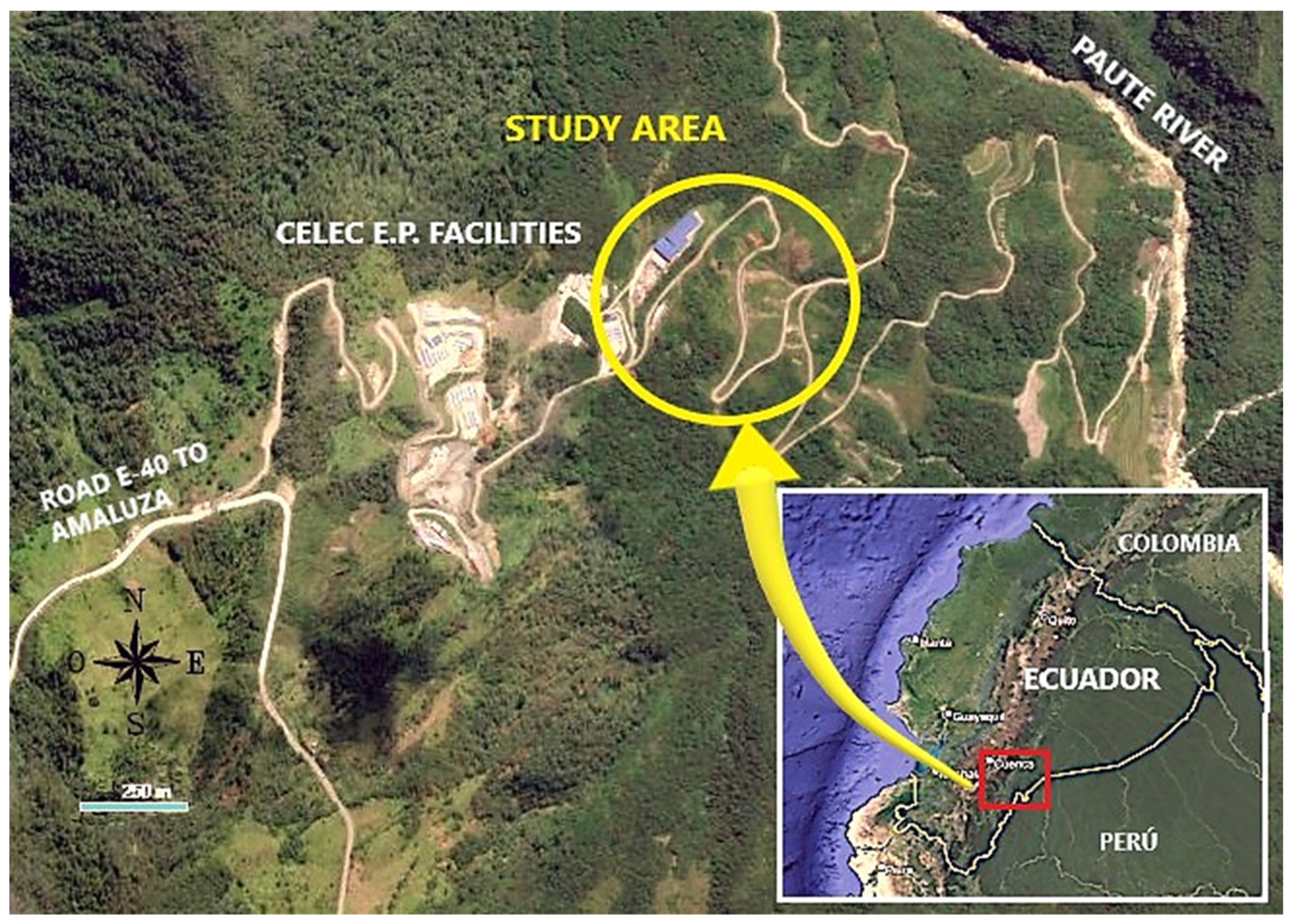
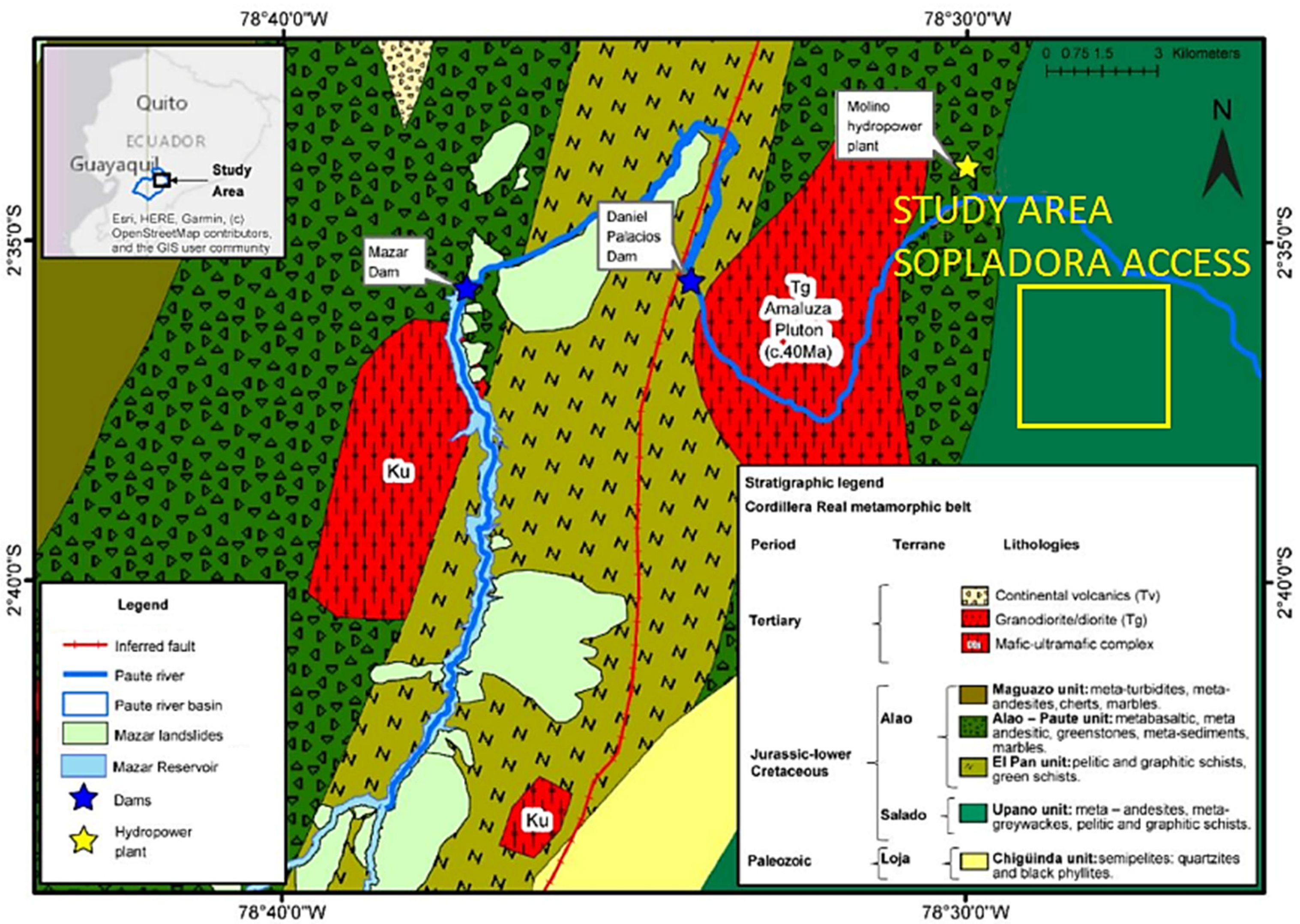
2.1. Geographical Situation
2.2. Geophysical Background and Scope
3. Geological Knowledge
4. Geophysical Research and Applied Methodology
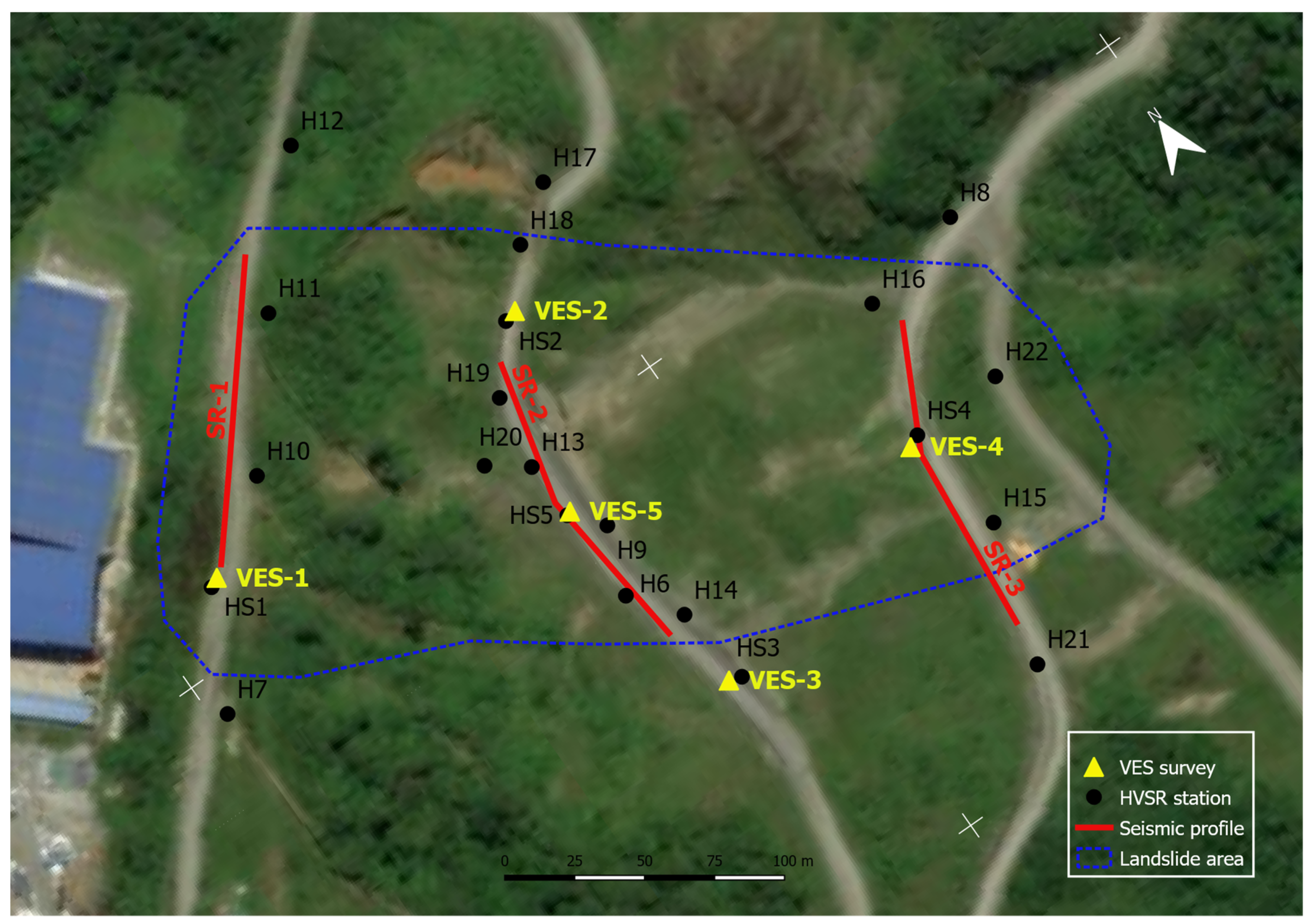
4.1. Geophysical Surveys
4.2. Applied Methodology
5. Results
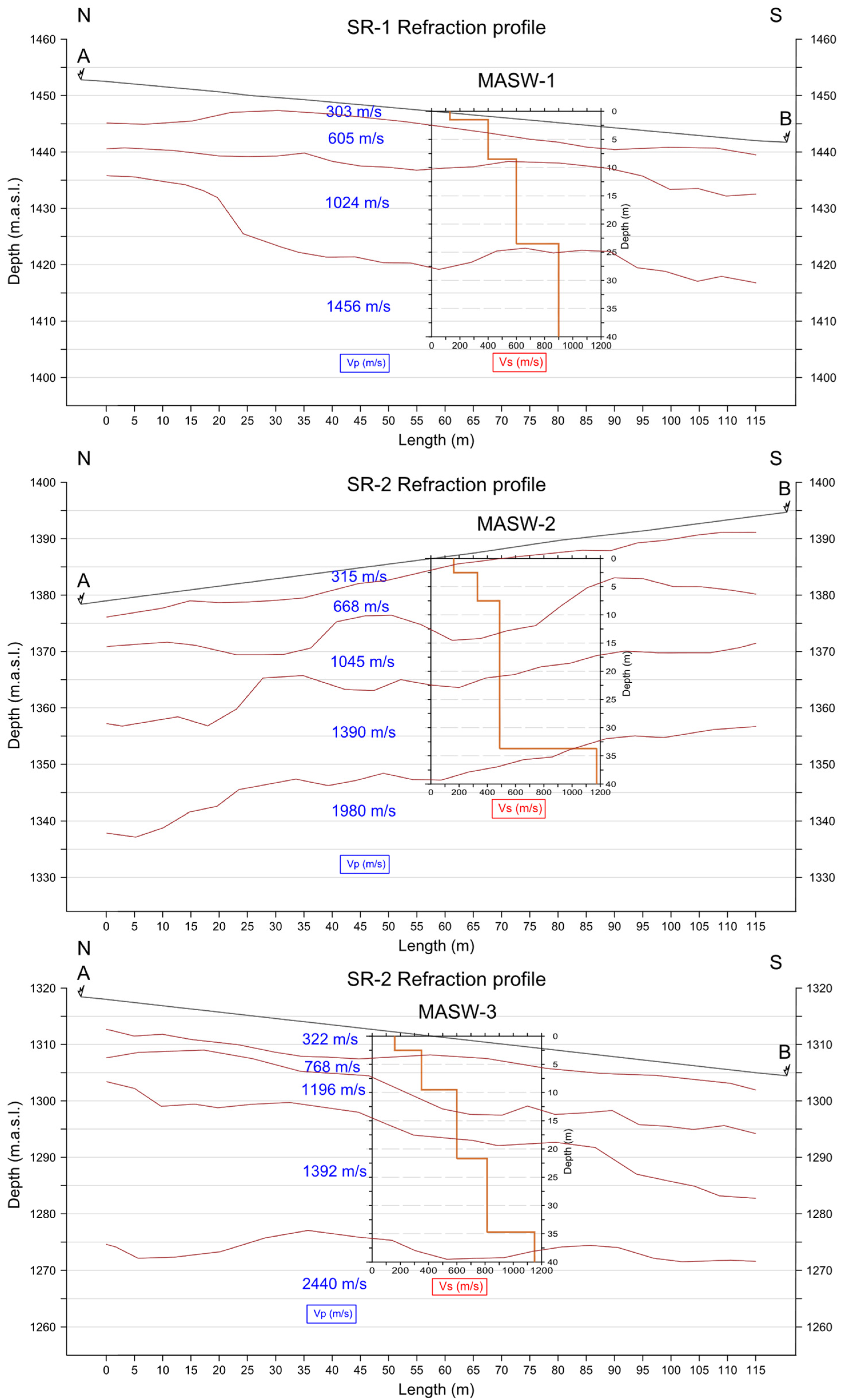
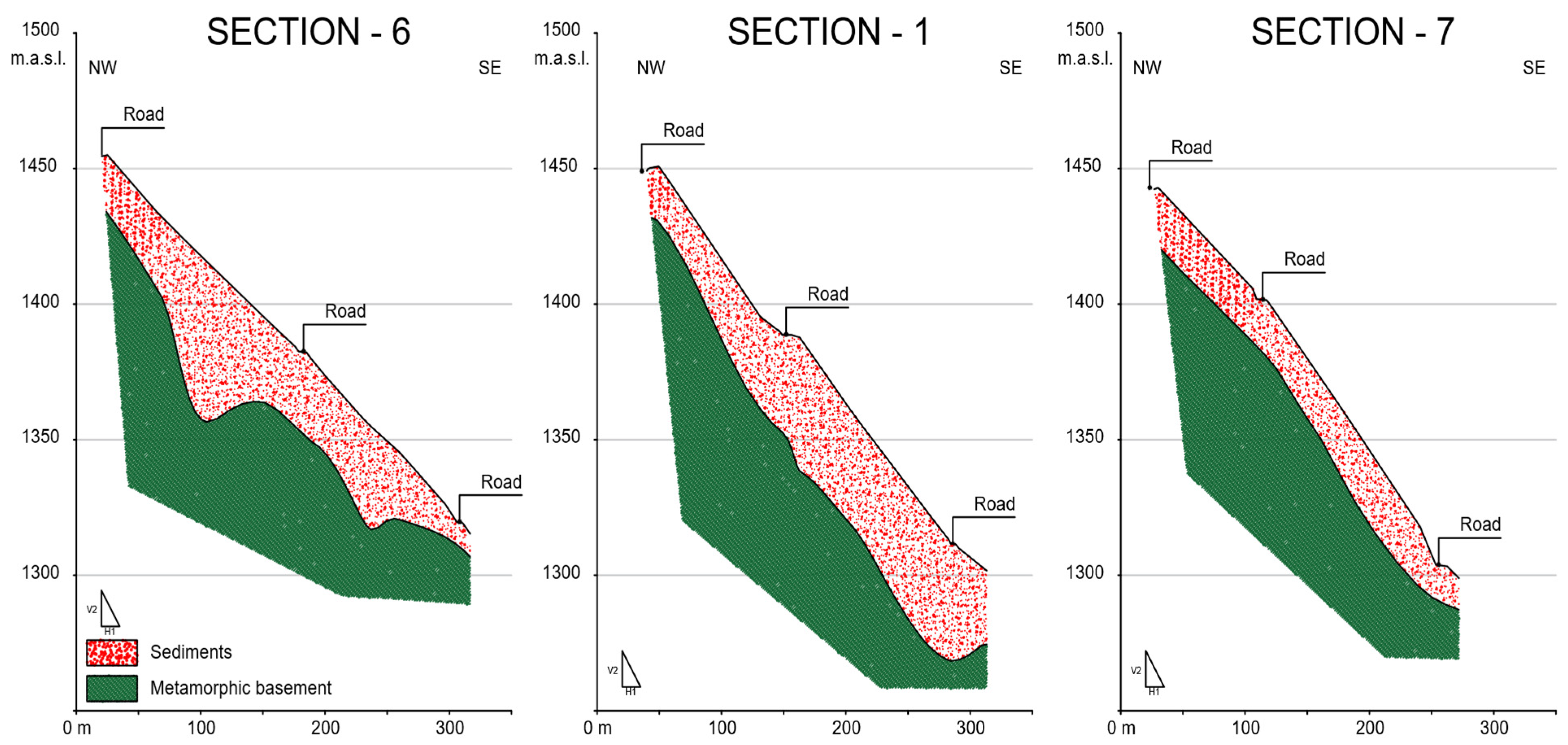
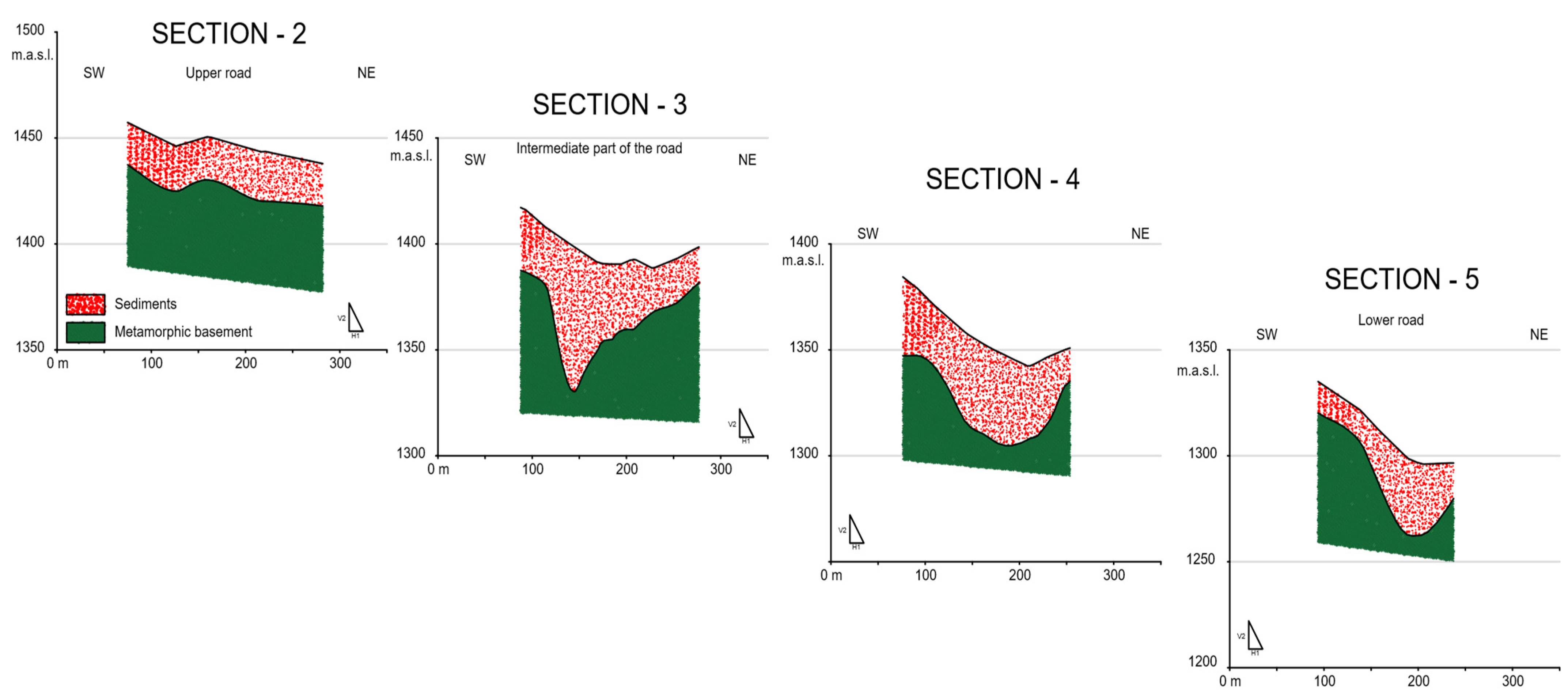
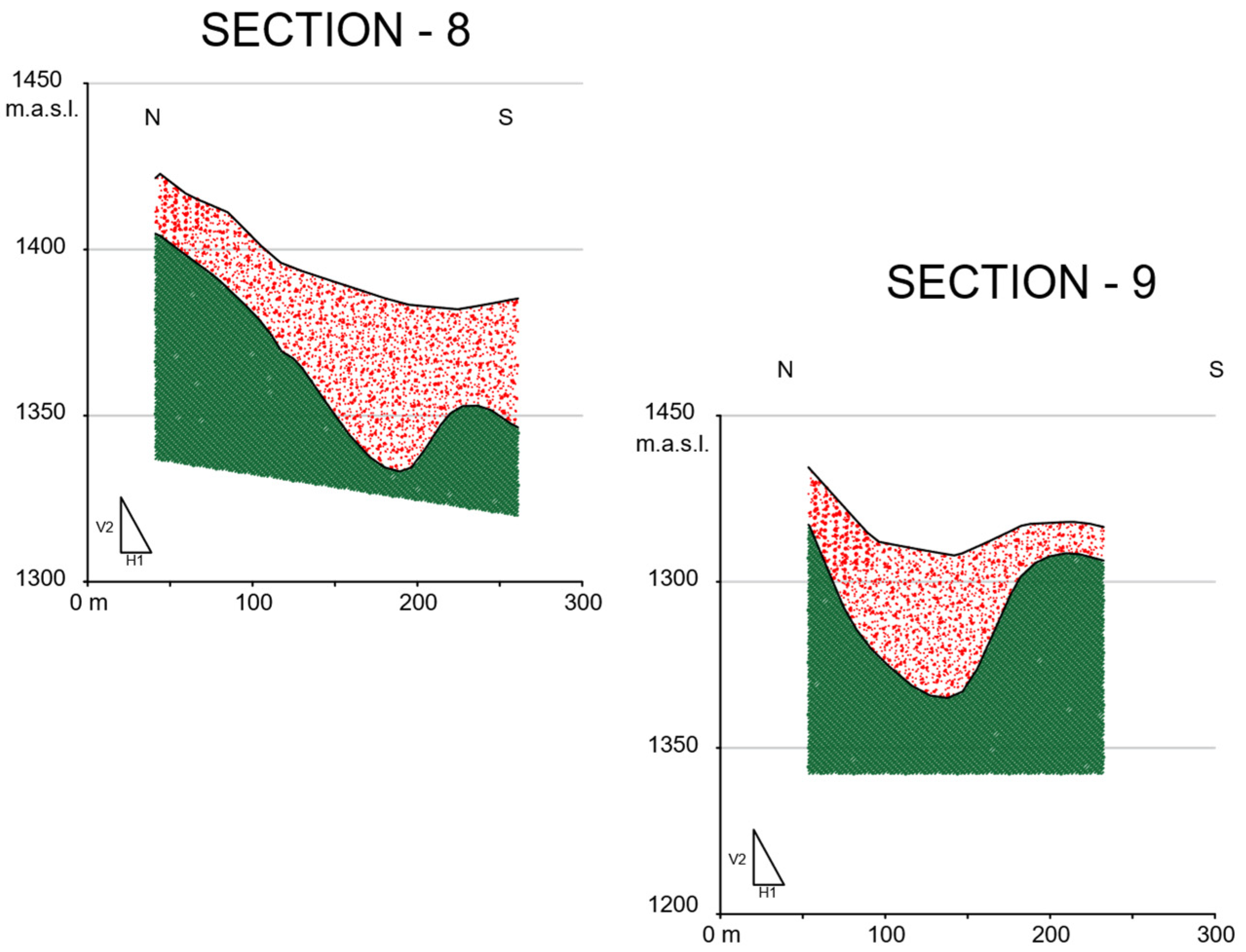
5.1. Seismic Refraction Technique
5.2. MASW Seismic Technique
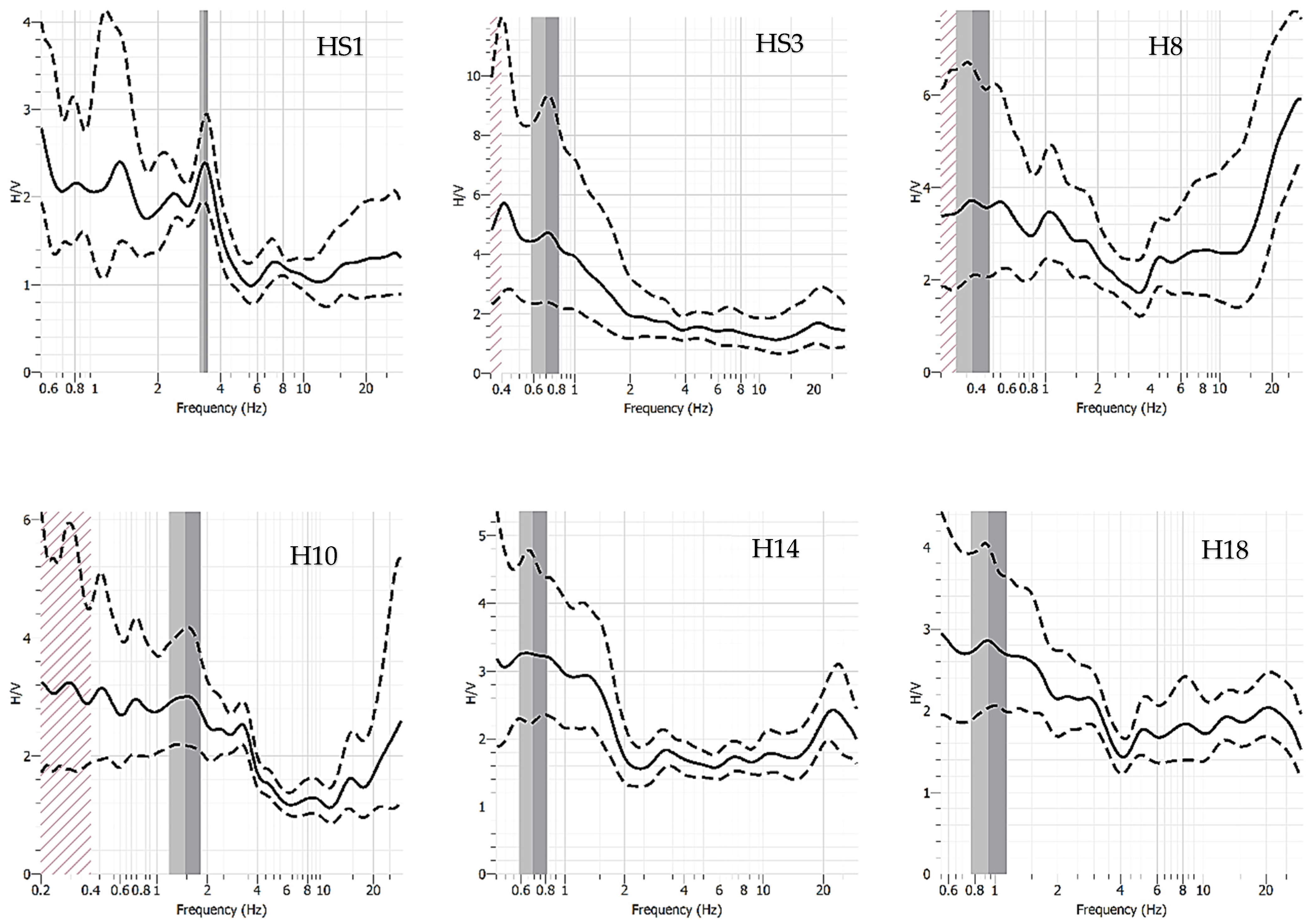
5.3. HVSR Seismic Passive Technique
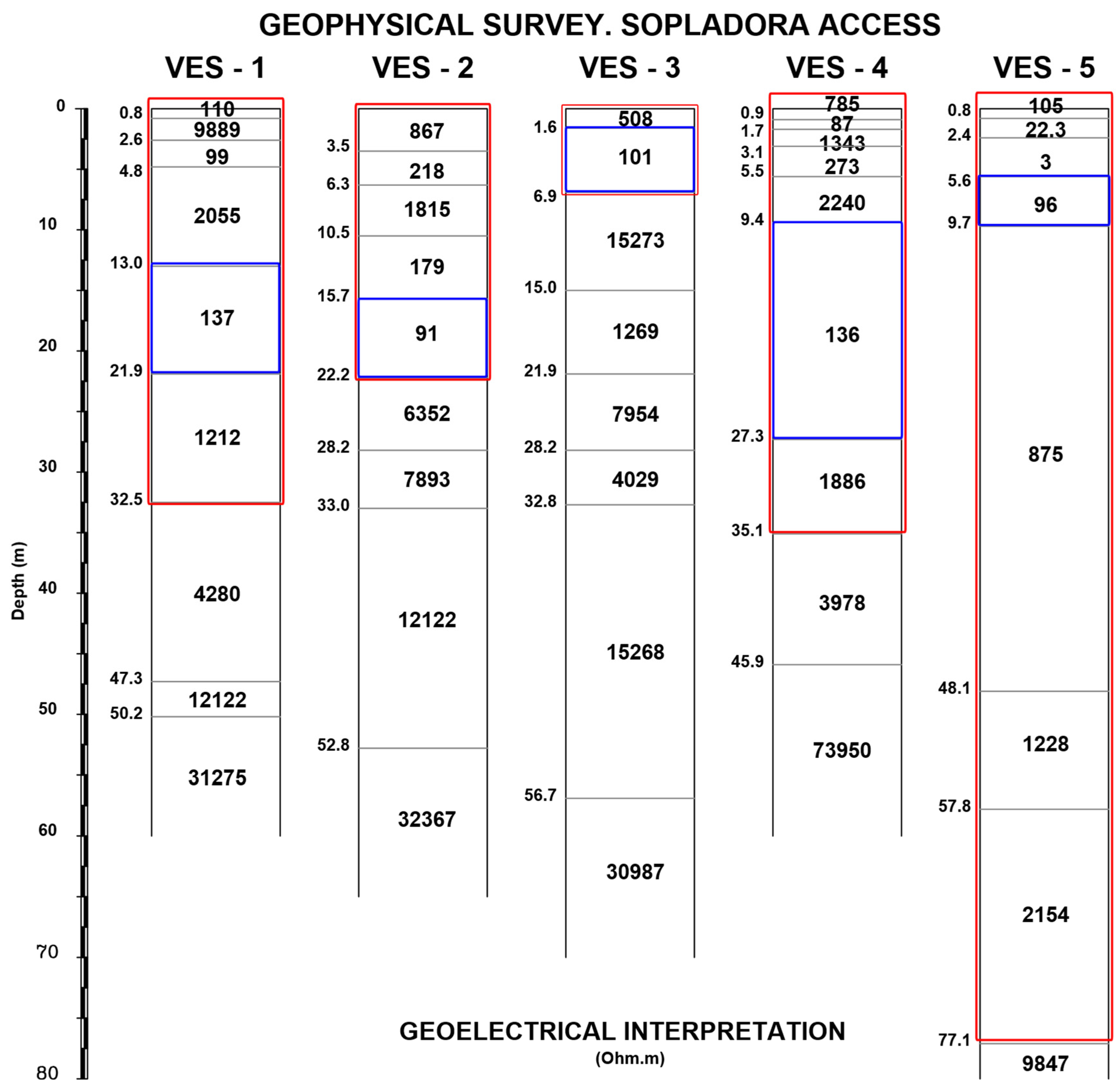
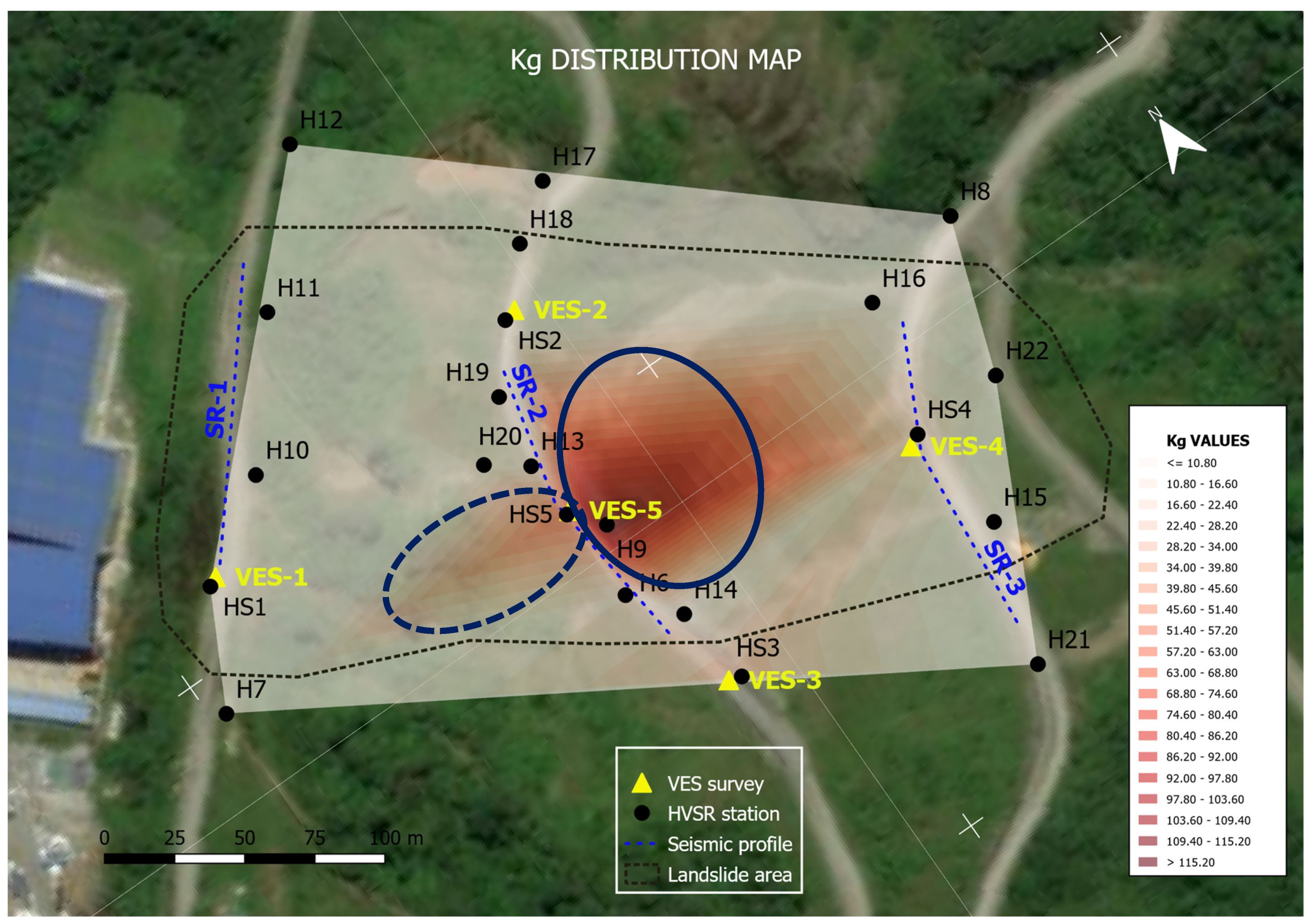
5.4. VES Geoelectrical Surveys
6. Discussion
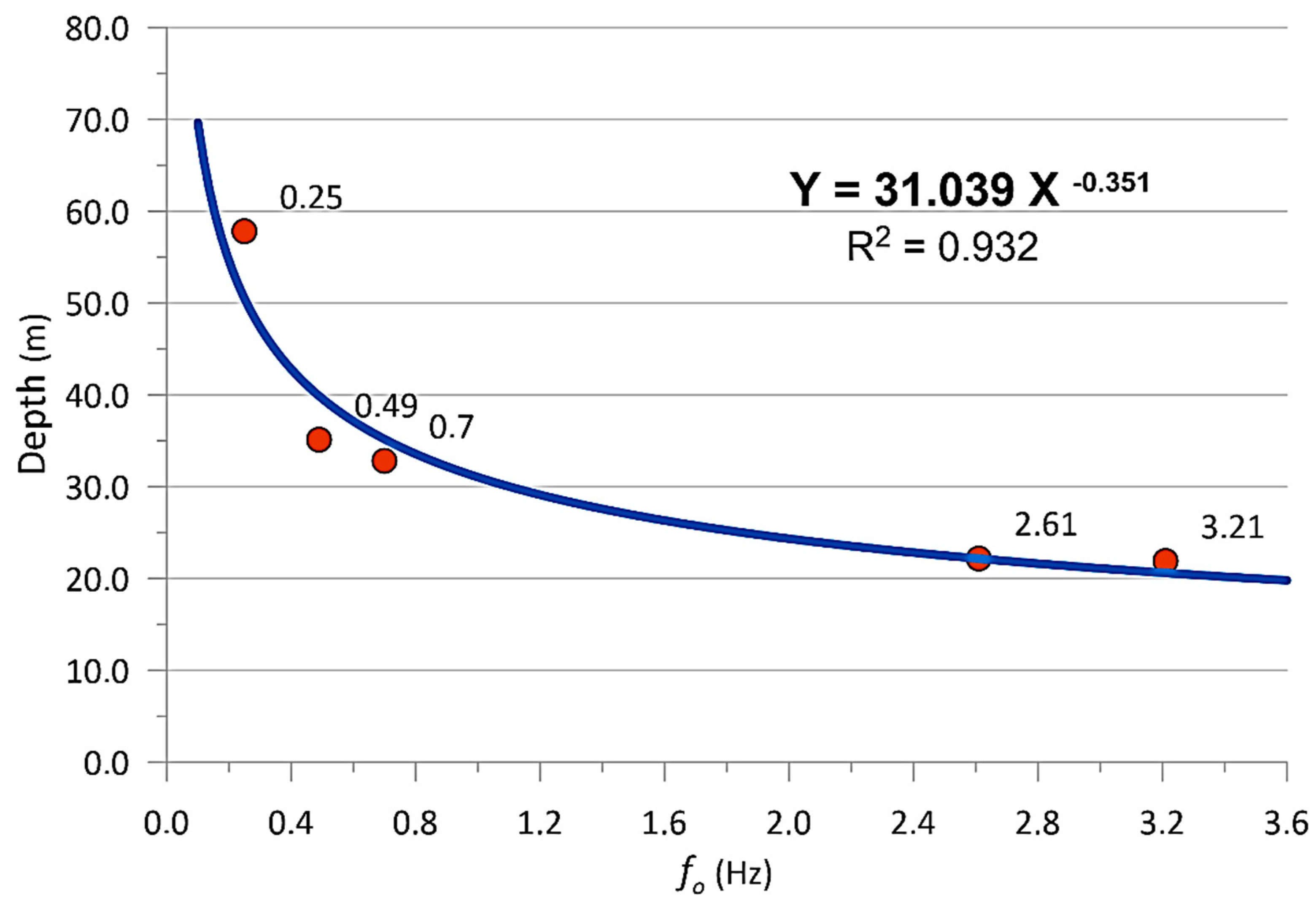
6.1. Data Integration and Calculation
6.2. Data Correlation and Reliability Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tibaldi, A.; Ferrari, L.; Pasquarè, G. Landslides Triggered by Earthquakes and Their Relations with Faults and Mountain Slope Geometry: An Example from Ecuador. Geomorphology 1995, 11, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ercole, R.; Trujillo, M. Amenazas, Vulnerabilidad, Capacidades y Riesgos En El Ecuador. Los Desastres, Un Reto Para El Desarrollo, 2003; ISBN 9978-42-972-7.
- Hussain, Y.; Schlögel, R.; Innocenti, A.; Hamza, O.; Iannucci, R.; Martino, S.; Havenith, H.-B. Review on the Geophysical and UAV-Based Methods Applied to Landslides. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León Gómez, A.M.; Tijera Carrión, A.; Ruiz Bravo, R. Utilización de Técnicas Geofísicas en la Identificación de Deslizamientos de Ladera. Revista Digital Del CEDEX Ingeniería Civil 2014, 175, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jongmans, D.; Garambois, S. Geophysical Investigation of Landslides: A Review. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 2007, 178, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, V.; Morelli, S.; Fanti, R. A Review of the Advantages and Limitations of Geophysical Investigations in Landslide Studies. International Journal of Geophysics 2019, 2019, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burjánek, J.; Gassner-Stamm, G.; Poggi, V.; Moore, J.R.; Fäh, D. Ambient Vibration Analysis of an Unstable Mountain Slope. Geophysical Journal International 2010, 180, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, A. Use HVSR Method at Studying Structure of Landslides. Geophysical Research Abstracts 2010, 12, 6191. [Google Scholar]
- Mainsant, G.; Larose, E.; Brönnimann, C.; Jongmans, D.; Michoud, C.; Jaboyedoff, M. Ambient Seismic Noise Monitoring of a Clay Landslide: Toward Failure Prediction: Seismic Noise Monitoring of a Landslide. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, n/a-n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Garrido, J.; Lenti, L.; Lopez-Casado, C.; Martino, S.; Sierra, F.J. Unconventional Pseudostatic Stability Analysis of the Diezma Landslide (Granada, Spain) Based on a High-Resolution Engineering-Geological Model. Engineering Geology 2015, 184, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, S.; Grassi, S.; Fazio, F.; Rannisi, G.; Cino, P. Geophysical Surveys to Study a Landslide Body (North-Eastern Sicily). Nat Hazards 2017, 86, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, V.; Tanteri, L.; Bicocchi, G.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Caselli, A.; Fanti, R. H/V Measurements as an Effective Tool for the Reliable Detection of Landslide Slip Surfaces: Case Studies of Castagnola (La Spezia, Italy) and Roccalbegna (Grosseto, Italy). Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2017, 98, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Galiana-Merino, J.J.; García-Tortosa, F.J.; Garrido, J.; Lenti, L.; Martino, S.; Peláez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Peces, M.J.; de Galdeano, C.S.; Soler-Llorens, J.L. Ambient Noise Measurements to Constrain the Geological Structure of the Güevéjar Landslide (S Spain). Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.; Schmitz, M. Caracterización dinámica de perfiles geotécnicos de Cariaco (estado Sucre, Venezuela), partiendo de datos de refracción sísmica. Revista de la Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad Central de Venezuela 2008, 23, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y. A Method for Dynamic Characteristics Estimation of Subsurface Using Microtremor on the Ground Surface. Quarterly Report of Railway Technical Research 1989, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y. What Is the Nakamura Method? Seismological Research Letters 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarello, D.; Lunedei, E. Alternative Interpretations of Horizontal to Vertical Spectral Ratios of Ambient Vibrations: New Insights from Theoretical Modeling. Bull Earthquake Eng 2010, 8, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibs-von Seht, M.; Wohlenberg, J. Microtremor Measurements Used to Map Thickness of Soft Sediments. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 1999, 89, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, M.A. Mapping Sediment Thickness of Islamabad City Using Empirical Relationships: Implications for Seismic Hazard Assessment. J Earth Syst Sci 2016, 125, 623–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Pandavenes, O.; Torres, G.; Torrijo, F.J.; Garzón-Roca, J. Basement Tectonic Structure and Sediment Thickness of a Valley Defined Using HVSR Geophysical Investigation, Azuela Valley, Ecuador. Bull Eng Geol Environ 2022, 81, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelouh, A.; Bensalem, R.; Zaourar, N.; Machane, D.; Moulouel, H.; Oubaiche, E.H. The Miocene Roof Mapping Using Microtremor Recording and Electrical Survey Method in Blida City, Algeria. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing maps. https://www.bing.com/maps/ (accessed on 13-6-2022).
- Google Earth https://www.google.com/intl/es/earth/ (accessed on 13-6-2022). 2022.
- McCann, D.M.; Forster, A. Reconnaissance Geophysical Methods in Landslide Investigations. Engineering Geology 1990, 29, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefoy-Claudet, S.; Cornou, C.; Bard, P.-Y.; Cotton, F.; Moczo, P.; Kristek, J.; Fäh, D. H/V Ratio: A Tool for Site Effects Evaluation. Results from 1-D Noise Simulations. Geophysical Journal International 2006, 167, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathelet, M.; Chatelain, J.-L.; Cornou, C.; Giulio, G.D.; Guillier, B.; Ohrnberger, M.; Savvaidis, A. Geopsy: A User-Friendly Open-Source Tool Set for Ambient Vibration Processing. Seismological Research Letters 2020, 91, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, M.; Lapenna, V.; Lorenzo, P.; Mucciarelli, M.; Perrone, A.; Piscitelli, S.; Sdao, F. Comparison of Geological and Geophysical Prospecting Techniques in the Study of a Landslide in Southern Italy. European Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics 2000, 4, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Méric, O.; Garambois, S.; Malet, J.-P.; Cadet, H.; Guéguen, P.; Jongmans, D. Seismic Noise-Based Methods for Soft-Rock Landslide Characterization. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 2007, 178, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, F.; Lombardo, G.; DAmico, S.; Gale, P. Speedy Techniques to Evaluate Seismic Site Effects in Particular Geomorphologic Conditions: Faults, Cavities, Landslides and Topographic Irregularities. In Engineering Seismology, Geotechnical and Structural Earthquake Engineering; DAmico, S., Ed.; InTech, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1038-5.
- Sánchez-Sesma, F.J.; Rodríguez, M.; Iturrarán-Viveros, U.; Luzón, F.; Campillo, M.; Margerin, L.; García-Jerez, A.; Suarez, M.; Santoyo, M.A.; Rodríguez-Castellanos, A. A Theory for Microtremor H/V Spectral Ratio: Application for a Layered Medium: Theory for Microtremor H/V Spectral Ratio. Geophysical Journal International 2011, 186, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lermo, J.; Chávez-García, F.J. Site Effect Evaluation Using Spectral Ratios with Only One Station. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 1993, 83, 1574–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, P.-Y. Foreword: The H/V Technique: Capabilities and Limitations Based on the Results of the SESAME Project. Bull Earthquake Eng 2008, 6, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; López Casado, C.; Giner, J.; Estévez, A.; Cuenca, A.; Molina, S. Microtremors as a Geophysical Exploration Tool: Applications and Limitations. Pure appl. geophys. 2000, 157, 1445–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolai, S. New Relationships between Vs, Thickness of Sediments, and Resonance Frequency Calculated by the H/V Ratio of Seismic Noise for the Cologne Area (Germany). Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 2002, 92, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzen, K.-G.; Weber, B.; Scherbaum, F. On the Resolution of H/V Measurements to Determine Sediment Thickness, a Case Study across a Normal Fault in the Lower Rhine Embayment, Germany. Journal of Earthquake Engineering 2004, 8, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainsant, G.; Larose, E.; Brönnimann, C.; Jongmans, D.; Michoud, C.; Jaboyedoff, M. Ambient Seismic Noise Monitoring of a Clay Landslide: Toward Failure Prediction: Seismic Noise Monitoring of a Landslide. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, n/a-n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, V.; Wasowski, J.; Muscillo, S. New Developments in Ambient Noise Analysis to Characterise the Seismic Response of Landslide-Prone Slopes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, V.; Muscillo, S.; Wasowski, J. What We Can Learn about Slope Response to Earthquakes from Ambient Noise Analysis: An Overview. Engineering Geology 2014, 182, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, F.; D’Amico, S.; Lotteri, A.; Galea, P.; Lombardo, G. Seismic Site Response of Unstable Steep Slope Using Noise Measurements: The Case Study of Xemxija Bay Area, Malta. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Xia, J. Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves. Geophysics 1999, 64, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Xia, J.; Ivanov, J. Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW)—Active and Passive Methods. The Leading Edge 2007, 26, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, J.S.; Watlet, A.; Uhlemann, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Boyd, J.P.; Jordan, C.; Kendall, J.M.; Chambers, J.E. Rapid Characterisation of Landslide Heterogeneity Using Unsupervised Classification of Electrical Resistivity and Seismic Refraction Surveys. Engineering Geology 2021, 290, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.; Spillmann, T.; Heincke, B.; Hauck, C.; Loew, S.; Springman, S.M.; Green, A.G. Geophysical Characterization of Slope Instabilities. First Break 2010, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgilez Vinueza, A.; Robles, J.; Bakker, M.; Guzman, P.; Bogaard, T. Characterization and Hydrological Analysis of the Guarumales Deep-Seated Landslide in the Tropical Ecuadorian Andes. Geosciences 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IIGE Instituto de Investigación Geológico y Energético Mapa Geológico de Azogues. Escala 1:100.000, 2008.
- Nakamura, Y. Clear Identification of Fundamental Idea of Nakamura’s Technique and Its Applications. The 12th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, M.; Mirzakurdeh, A.V. Fault Detection Using Microtremor Data (HVSR-Based Approach) and Electrical Resistivity Survey. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2019, 11, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, A.; Lenart, A. Mapping the Thickness of Sediments in the Ljubljana Moor Basin (Slovenia) Using Microtremors. Bull Earthquake Eng 2010, 8, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

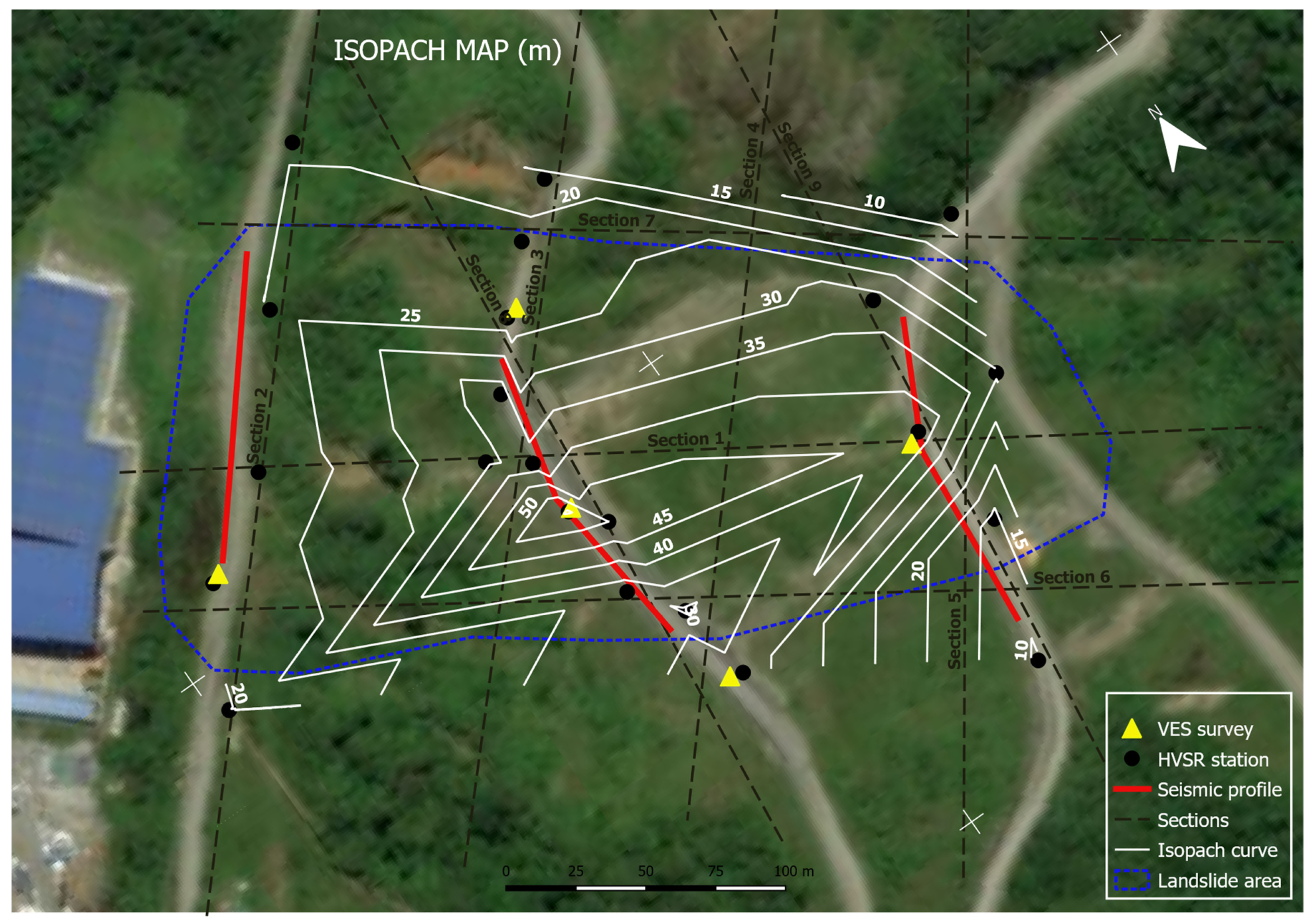
| GEOPHYSICAL METHOD | SURVEY TECHNIQUE |
DIMENSION | NUMBER OF SURVEYS | PARAMETER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REFRACTION | 2D profile | 115 m | 3 | Vp |
| MASW | 1D profile | 115 m | 3 | Vs |
| VES | Application point | 400 m (A-B) | 5 | Resistivity |
| HVSR | Single station | Point | 22 | fo, Ao |
| HVSR POINT | fo (Hz) | Ao (adim) |
| S1 | 3.21 | 2.37 |
| S2 | 2.61 | 2.05 |
| S3 | 0.70 | 4.70 |
| S4 | 0.49 | 3.42 |
| S5 | 0.25 | 3.91 |
| 6 | 1.07 | 4.19 |
| 7 | 3.66 | 2.28 |
| 8 | 57.67 | 12.66 |
| 9 | 0.34 | 6.49 |
| 10 | 3.28 | 2.53 |
| 11 | 2.42 | 1.90 |
| 12 | 3.76 | 1.54 |
| 13 | 0.73 | 3.18 |
| 14 | 0.60 | 2.99 |
| 15 | 9.37 | 2.34 |
| 16 | 1.04 | 2.99 |
| 17 | 4.81 | 2.02 |
| 18 | 2.95 | 2.13 |
| 19 | 0.71 | 3.42 |
| 20 | 0.91 | 3.22 |
| 21 | 25.30 | 2.38 |
| 22 | 1.18 | 3.17 |
| VES NUMBER | ROCK DEPTH IN VES SURVEYS (m) | CORRESPONDING HVSR SURVEY | fo(Hz) |
| 1 | 21.9 | S1 | 3.21 |
| 2 | 22.2 | S2 | 2.61 |
| 3 | 32.8 | S3 | 0.70 |
| 4 | 35.1 | S4 | 0.49 |
| 5 | 57.8 | S5 | 0.25 |
| HVSR POINT |
fo (Hz) | THICKNESS (m) |
Kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 3.21 | 20.61 | 1.75 |
| S2 | 2.61 | 22.16 | 1.61 |
| S3 | 0.70 | 35.18 | 31.56 |
| S4 | 0.49 | 39.87 | 23.87 |
| S5 | 0.25 | 50.49 | 61.15 |
| 6 | 1.07 | 30.31 | 16.41 |
| 7 | 3.66 | 19.68 | 1.42 |
| 8 | 57.67 | 7.48 | 2.78 |
| 9 | 0.34 | 45.33 | 123.88 |
| 10 | 3.28 | 20.46 | 1.95 |
| 11 | 2.42 | 22.76 | 1.49 |
| 12 | 3.76 | 19.50 | 0.63 |
| 13 | 0.73 | 34.66 | 13.85 |
| 14 | 0.60 | 37.13 | 14.90 |
| 15 | 9.37 | 14.15 | 0.58 |
| 16 | 1.04 | 30.61 | 8.60 |
| 17 | 4.81 | 17.88 | 0.85 |
| 18 | 2.95 | 21.23 | 1.54 |
| 19 | 0.71 | 35.00 | 16.47 |
| 20 | 0.91 | 32.08 | 11.39 |
| 21 | 25.30 | 9.99 | 0.22 |
| 22 | 1.18 | 29.29 | 8.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





