1. Introduction
The development of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) after performing angiographic diagnostic and/or therapeutic procedures can have serious short-term consequences related to events such as myocardial infarction, bleeding, initiation of renal replacement therapy, prolongation of hospital stay and increased in-hospital mortality [
1,
2,
3]. The long-term consequences are also not to be underestimated, leading to an increased incidence of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events among patients with contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) within 8 years of follow-up (54% vs. 15% vs. without CI-AKI) [
4]. Although CIN is generally accepted as a transient and benign condition, data suggest that it may also have a long-term effect on kidney function [
4,
5]. According to the Alberta Registry [
5], the proportion of patients with a sustained loss of kidney function 3 months following coronary angiography occurring in 5.9% of patients without AKI, 28.2% of patients with mild AKI and 59.1% among patients with moderate or severe AKI. The progressive deterioration of renal function within 5 years may be accelerated and more severe in patients with CI-AKI according to other authors [
4].
Therefore, diagnostics and timely adequate measures can be essential for invasive cardiology and other radiological specialties. Although the existing in literature definitions of CIN or CI-AKI differ from the reference limit accepted for a significant increase in creatinine
(> 0.5 mg/dl [44.2 μmol /l ] and/or >25% in the classical definition of CIN or according to AKIN criteria for AKI >0.3 mg/dl [26.5 μmol /l] and/or ≥1.5- 2 times compared to baseline levels ) [
6,
7,
8,
9], as well as recommended time interval for its follow-up (from 48 hours to 72 hours after the contrast administration) [
8,
9], the diagnosis is always made on the basis of dynamic changes in serum creatinine. The influence of various external and internal factors, considering that change in creatinine levels after acute injury can be detected only when a new steady-state condition between its production and elimination through the glomerulus is reached, as well as the compensatory possibilities of the “renal reserve” (compensatory effect of remaining intact nephrons) turn it into a delayed and insensitive marker of renal dysfunction. Also, mainly reflecting glomerular function creatinine may not represent tubular damage and not provides a disease-specific phenotype of AKI [
10]. On the other hand, in the last 10 years, the existence of a number of molecules such as KIM-1 (
Kidney Injury Molecule-1), NGAL (
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin), L-FABP (
Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein) and others, which production increases rapidly after acute ischemic/toxic damage to the renal tubules, has been proven [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15] . Accumulating evidence for the application of new biomarkers and their ability to identify multiple additional processes in renal structures has led to the introduction of a new conceptual framework for AKI accepted on 10th Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) meeting [
16]. According this framework all biomarkers could be classified as “functional biomarkers” (reflecting changes at the functional level of glomerular filtration rate as serum creatinine and cystatin C) and “damage biomarkers” (different molecules as NGAL, KIM-1, L-FABP, IL-18
(Interleukin-18) which production reflecting structural kidney disorders).
The simultaneous combined investigation of the two types of biomarkers will lead not only to the diagnosis of acute kidney injury (acute tubular necrosis), where both functional and structural biomarkers (BM) are positive, but also to the differentiation of conditions such as “subclinical AKI” (independent positivity only of “damage biomarkers”) or “ hemodynamic AKI” (change only in functional markers due to pre-renal causes) [
17]. NGAL is one of the widely studied new biomarkers in different clinical conditions – contrast-induced nephropathy, critically ill patients in intensive care units, AKI after aorto-coronary bypass surgery, with demonstrated good diagnostic power in individual studies [
18,
19,
20] and some meta-analyses [
21,
22,
23]. On the other point of view some authors report that “NGAL (+)/serum creatinine (-)” result in critically ill patients is an independent predictor of adverse outcomes regardless of the presence or absence of functional impairment [
24]. According to other published data, the combined study of urine biomarkers (NGAL, Midkine, IL-6) can identify up to 60% more cases with subclinical AKI after cardiac surgery than the measurement based on classic definition of serum creatinine [
25]. In the setting of invasive coronary angiography and percutaneous interventions, the existence of subclinical kidney injury is rarely considered according to the ADQI conceptual framework [
16,
17] and these formulations remain mostly theoretical. In the literature there is still no consistent and clear definition of subclinical CI-AKI, a reliable single structural biomarker has not been proven, and not available specific description of the dynamics changes after contrast administration. Active comparison of dynamic changes in biomarkers between patients developing CIN and subclinical forms of kidney damage is not yet properly addressed. In that regard our aim is to investigate the diagnostic power of an established structural biomarker—NGAL for the early diagnosis of clinically manifested CI-AKI and the presence of a subclinical form of CI-AKI among patients undergoing a scheduled coronary angiography. The initial results of the development of CI-AKI in the whole studied sample and the significantly higher baseline levels of NGAL in the different stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD) were already reported elsewhere [
26]. Based on these data and a number of literature sources [
27,
28], a hypothesis was formed that in the settings of CKD biomarker NGAL can reflects persistent kidney damage and demonstrate different dynamic course of changes. The hypothesis was tested by means of more comprehensive analysis of NGAL at different levels of kidney function.
3. Results
In the current study, the 45 patients with preserved kidney function undergoing scheduled coronary angiography were separated into three main groups—controls (n=18/40%); group with development of CI-AKI (n=12/26.7%) and group of patients with subclinical CI-AKI (n=15/33.3%). The average age of the entire sample was 61.72±8.62 years, and the gender distribution was almost equally (men n=25/55% and women n=20/45% ).
The risk profile of the total sample is formed by arterial hypertension (n=45/100%), dyslipidemia (n=44/97.8%) , diabetes mellitus type 2 (n=41/91.1%) , overweight ( BMI 25-29.9 kg/m
2 at n=17 /37.8%) and obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m
2 in n= 21/46.7%). The distribution between the individual groups is presented in
Table 1, with no significant differences reported between them.
The main indication for the angiographic examination in the studied cohort of patients is stable angina pectoris (n=39 /86.6%), and some of them have a history of myocardial infarction (n=17/37.8%). Previous percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (n=15 /33.3%) or operative coronary revascularization (n=7/15.6%) and heart failure II-III by NYHA class (n=13/28.9 %) also contribute to the cardiac profile of the sample. Diagnostic angiography was performed in 48.89% of all selected patients, and in 51.11% it was necessary to switch to one-stage PCI. As evident from
Table 1, in patients with CI-AKI there is a trend for predominance of multivessel coronary disease and a significantly higher frequency of previous aorto-coronary bypass revascularization. The latter has an essential role in determining the need for the application of a larger amount of contrast media for angiographic visualization of anatomy among such patients.
The evaluation of renal function was carried out by the simultaneous measurement of serum creatinine and plasma NGAL in a series of blood samples obtained at baseline before, on the 4th and 24th hour after the coronary angiography. For the diagnosis of CI-AKI, creatinine was monitored until the 48th hour after the contrast administration. Detailed information on the values of these indicators for individual groups is presented in
Table 2.
In the control group of patients, serum creatinine and corresponding GFR remained unchanged after the contrast administration compared to baseline levels (
Table 2). Similar trend was registered with measurement of the new biomarker NGAL—values reported at baseline (76.40 ± 14.70 ng/ml), at the 4th hour (76.39±14.12 ng/ml ) and at the 24th hour (76.86±13.47 ng/ml ) are extremely close (p=0.943; p=0.653).
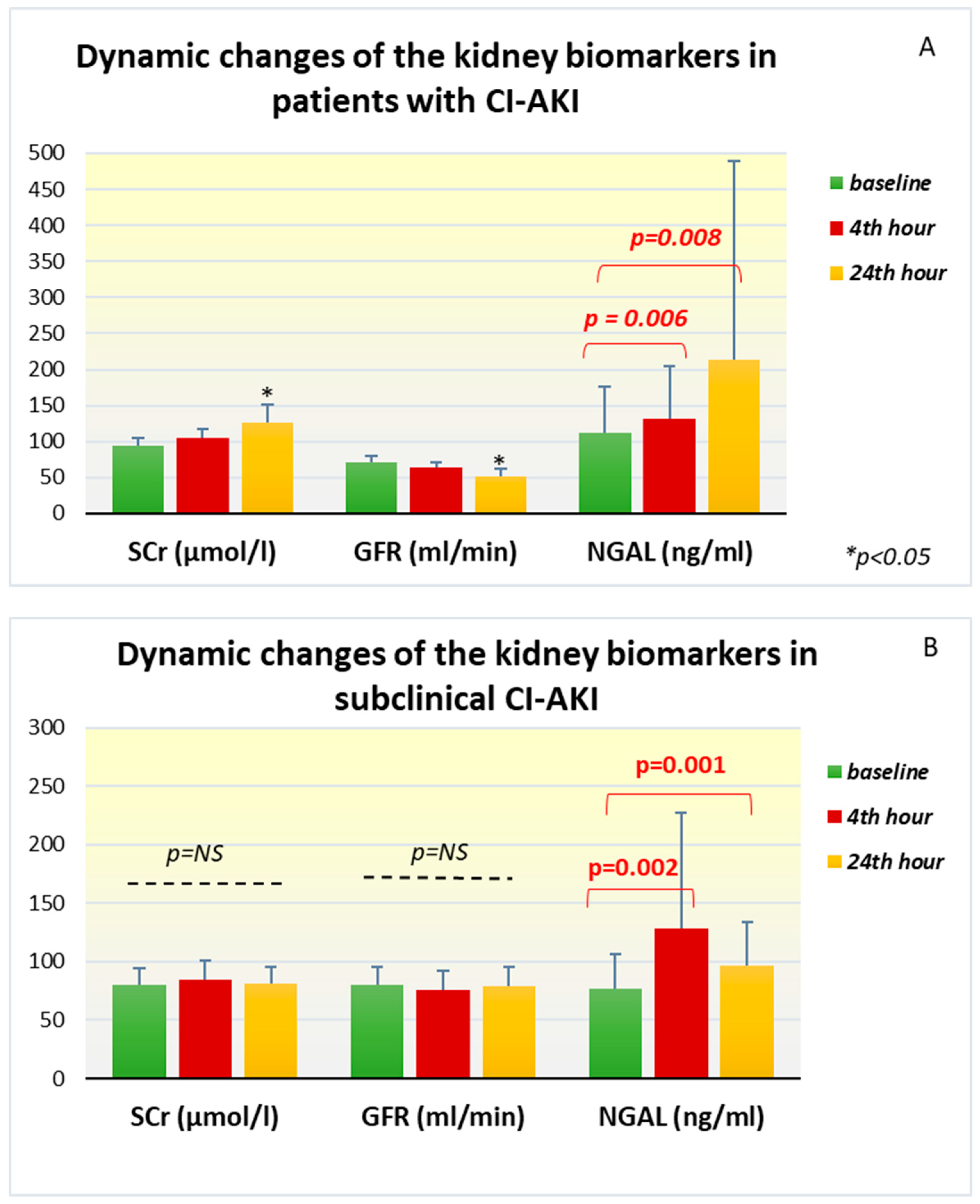
In patients with the development of CI-AKI, dynamic changes were found in all the investigated biomarkers. Serum creatinine from baseline levels of 94.90±10.63 µmol /l in this group increased 24 hours after the contrast angiography (126.46±24.17 µmol /l; p = 0.002) and remained high until the 48th hour (104.79±15.39 µmol/l; p = 0.007). The change in GFR follows the same trend, but in the opposite direction—compared to the initial levels (71.10±8.39 ml/min), a significant decrease was reported at the 24th hour (52.12±9.79 ml/min, p = 0.002). The laboratory measurements of plasma NGAL in this group of patients showed that the mean initial values were 111.48 ± 65.06 ng/ml, but they increased very quickly already at the 4th hour after the contrast administration to 132.33 ± 72.83 ng/ml (p=0.006). A significant increase in the biomarker continued at the 24th hour, where the reported levels were even higher and reached an average of 212.93±276.61 ng/ml (p=0.008) (
Figure 1A).
In the group with subclinical CI-AKI, the standard marker of renal function, serum creatinine, maintained its levels almost unchanged at the 24th hour (81.72±14.08 μmol/l, p=0.292) and the 48th hour (81.74 ±17.87 μmol /l, p=0.889) compared to the baseline values. GFR calculated for the corresponding time intervals also does not show significant change (
Table 2). However, the changes in plasma NGAL among this group of patients are interesting. Compared to the baseline values of 76.69±29.32 ng/ml, already on the 4th hour after the end of the angiographic examination, a strong increase in the biomarker was registered with peak levels of 128.18±99 ng/ml (p=0.002). At the 24th hour after the examination, increased values compared to the baseline (97.05±36.66 ng/ml, p= 0.001) remained, but there was no additional elevation (
Figure 1B).
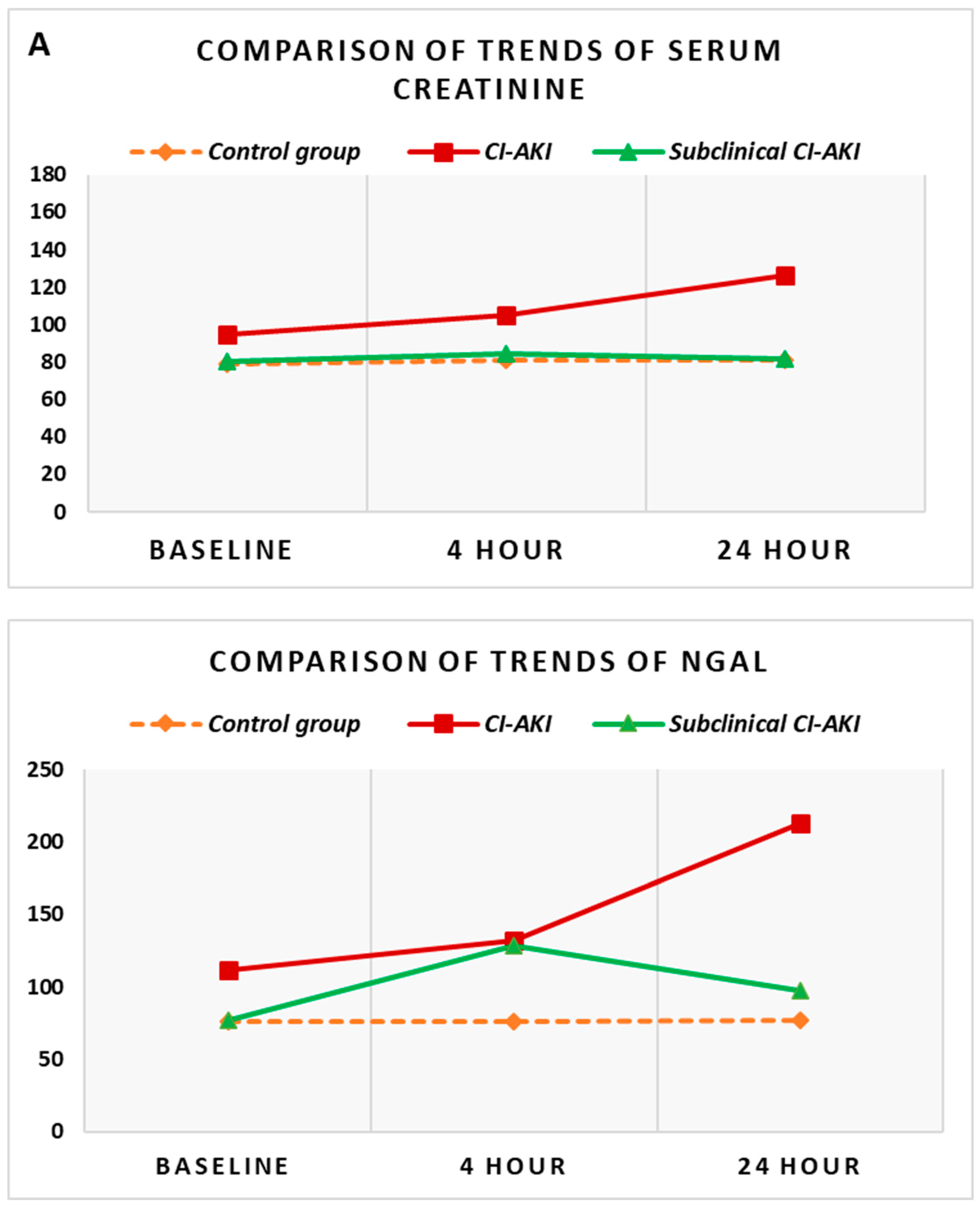
Besides we conducted an additional analysis focused on the comparison of each indicator in the same time interval in the different groups. Standard markers of renal function (serum creatinine and GFR) in patients who developed CI-AKI were significantly higher compared to the control group of patients. In the same comparison, the baseline levels of NGAL did not differ significantly between the two groups, but with the onset of acute kidney injury and the increase of NGAL, the levels reached at the 4th and 24th hours after the contrast administration were significantly higher compared to the controls (p<0.005 ) (
Figure 2B).
The comparative analysis of the group with subclinical CI-AKI was carried out against the other two groups—control group and group with CI-AKI. The comparison with
the control group demonstrated no significant difference between all reported values of serum creatinine and GFR. The increase in NGAL, however, which was observed in the group with subclinical CI-AKI, was significantly higher at the 4th hour compared to controls (p=0.024) (
Figure 2B). The comparison of the groups with CI-AKI and subclinical CI-AKI shows that while all the values of serum creatinine and GFR are significantly different between the two groups (p<0.05), the initial levels of NGAL and the subsequently monitored dynamic levels are extremely close and no statistically significant difference was found between them. The general presentation of these trends for the three groups simultaneously can be seen in
Figure 2.
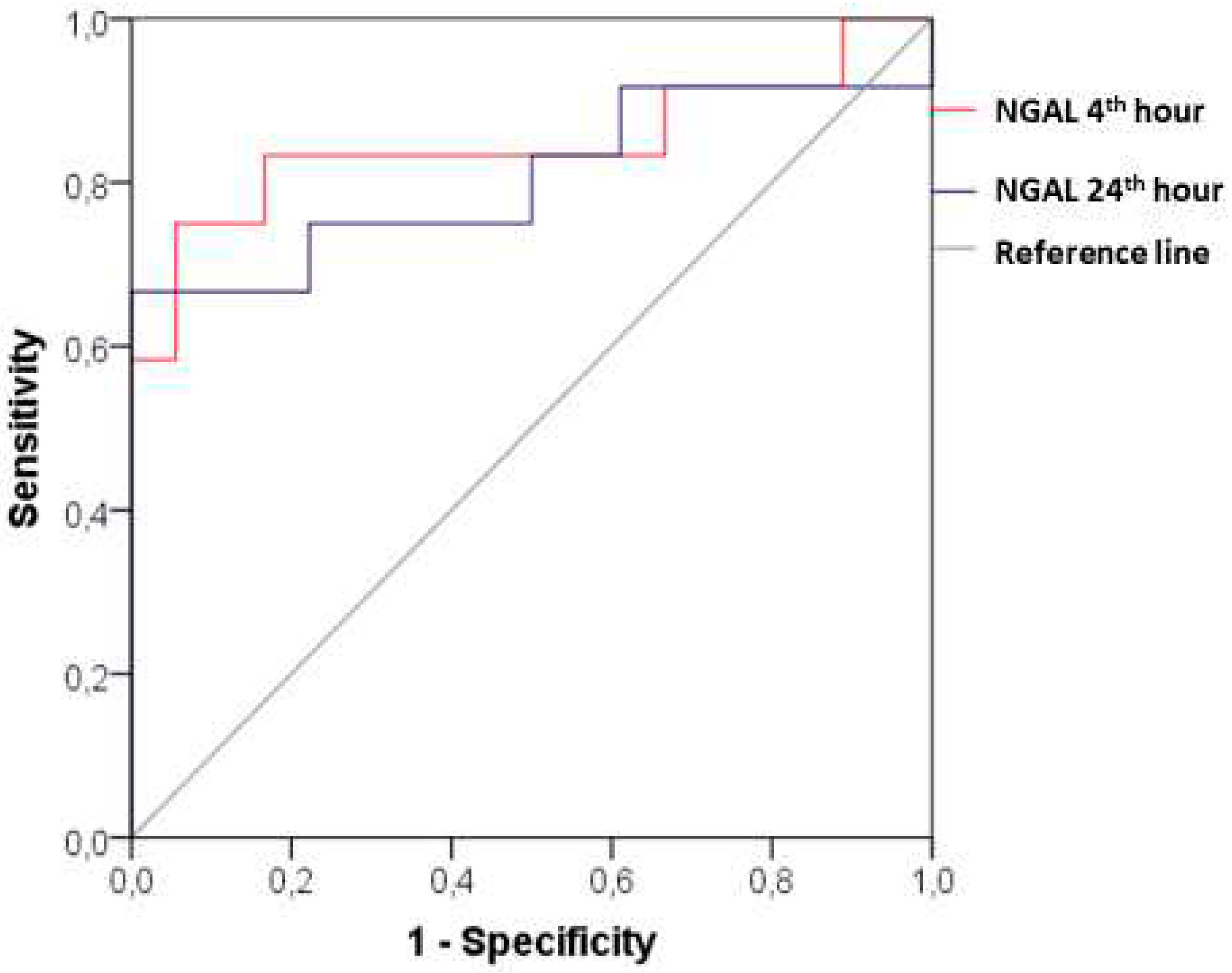
ROC analysis provides a clear insight into the diagnostic value of the new biomarker. In patients with CI-AKI, the plasma NGAL at the 4th hour after the contrast administration demonstrated AUC 0.847 (95% CI: 0.677- 1.000; p=0.001), sensitivity 83.33% and specificity 83.33% at a cut-off value of 90.20 ng/ml. The diagnostic power remains significant considering the changes at the 24th hour after the angiographic examination - АUC 0.806 (95% CI: 0.617-0.994; p=0.005) with sensitivity of 75%, specificity of 77.78% and cut-off value of NGAL 88.30 ng/ml (
Figure 3). In patients with a subclinical form of CI-AKI, the good diagnostic prediction of NGAL is preserved at the 4th hour after the angiographic examination - АUC 0.731 (95% CI: 0.539 – 0.924; p=0.024) with sensitivity 73.33% and specificity 72.22% at a cut-off value of 85.65 ng/ml (
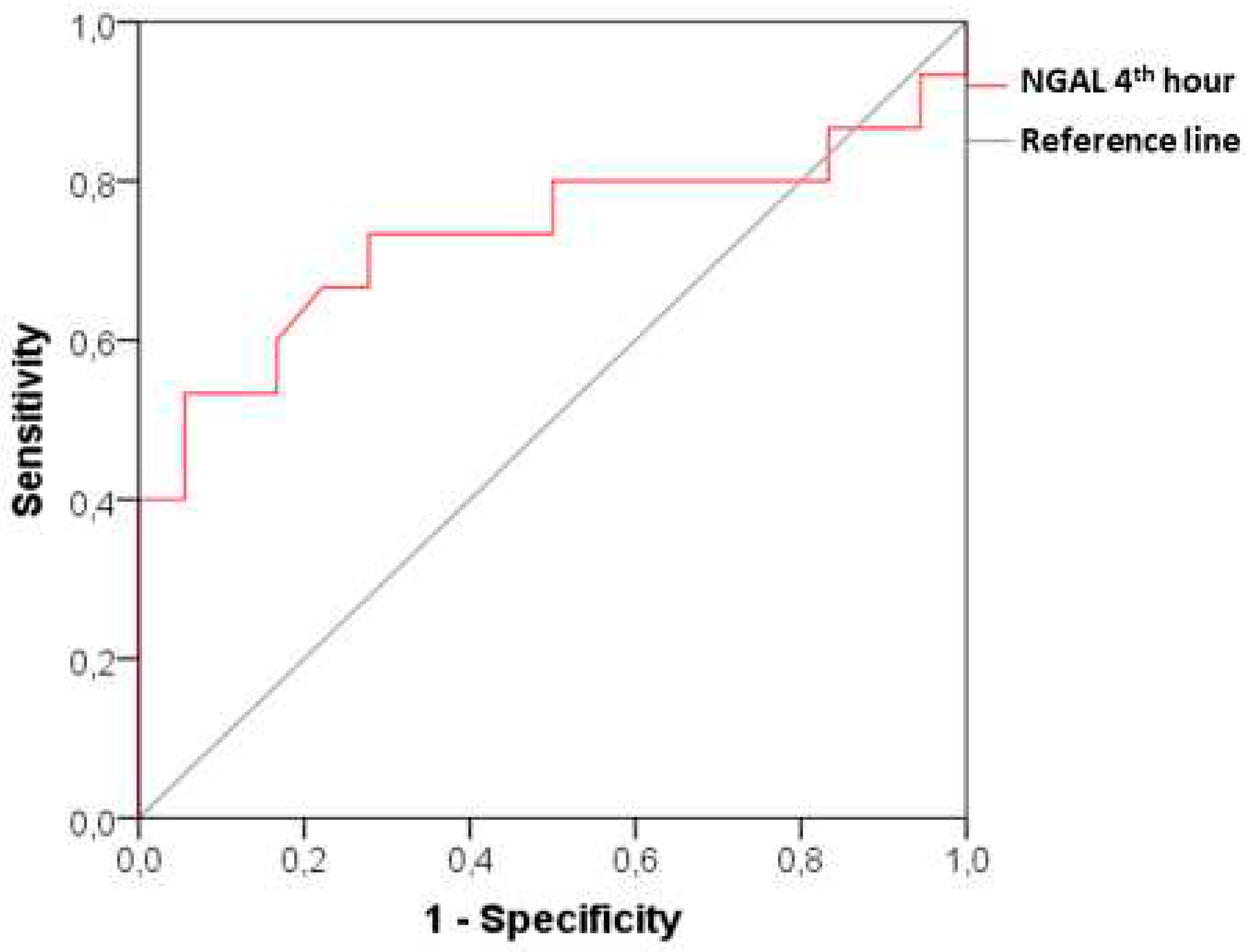
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
In our study, the follow-up of renal function with the standard biomarker serum creatinine and the new biomarker NGAL showed that in the patients of the CI-AKI group, all indicators changed significantly after the administration of a contrast media. Creatinine peak values are reached at the 24th hour, and the reported glomerular filtration rate in this hour range is correspondingly the lowest. Plasma NGAL demonstrated a significant increase at 4 hour and at 24 hour from baseline, but statistical analysis indicated that the majority of the biomarker increase occurred in the first few hours after contrast administration.
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (contrast-induced nephropathy as used in the past) continues to be a serious problem after diagnostic and therapeutic contrast-enhanced angiography, ranking third as a cause of hospital-acquired acute renal failure [
29] . As a result of the implementation of various preventive strategies in the last decade, a tendency to reduce the incidence of CIN has been reported [
30,
31]. On the other hand, a number of authors emphasize that intra-arterial (ia) administration of contrast media through a catheter during angiography with or without percutaneous coronary intervention is associated with a higher incidence of post-contrast AKI than intravenous (iv) administration [
32,
33] . While some literature data report CIN after coronary interventions in the general population between 11.3% and 14.5% [
34], other authors emphasize that the combination of more risk factors leads to a significant increase in its frequency - from 26.6% up to 36.9% [
2].
In our study, patients with a high risk profile (
arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, DM type 2 in >90% of patients) and a high ischemic burden with clinically manifested or proven coronary heart disease (
stable angina pectoris >85%, history of MI, previous PCI or ACB revascularization >48% of all patients) were enrolled. The frequency of CI-AKI was found to be 26.7%, which is close to the 24.1% reported in the literature in a cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [
35].
NGAL is a small protein that is normally expressed in healthy individuals in very small amounts in various types of cells in the body [
36]. Immediately after the occurrence of acute kidney injury, the production of NGAL is increased in the distal parts of the nephron, the thick ascending part of the Henley’s loop, the distal tubules and collecting ducts [
37,
38], which results in increased urinary and plasma NGAL levels due to increased secretion from the apical and basolateral surface of the nephron epithelium. Experimental studies have shown that plasma NGAL increases as a result of “backflow” of increased synthesis molecules to the systemic circulation [
39]. Some authors emphasize that AKI leads to a dramatic increase in RNA expression for NGAL in distant organs [
39], such as liver and lung. The overexpressed protein released into the circulation forms a distant systemic pool that is the source of the plasma levels of NGAL. In hope that the “renal troponin” may have been discovered, a number of authors focused on it in various clinical situations - contrast-induced nephropathy, critically ill patients in intensive care units, in patients after cardiac surgery, and others. Special attention is paid to cohorts of patients with chronic kidney disease, where some authors have reported specific biomarker kinetics and higher baseline NGAL concentrations [
28,
40,
41].
In this direction, several studies in the literature reported clinical use of NGAL among patients with coronary heart disease and baseline preserved renal function who underwent elective angiography [
18,
19,
20,
42,
43,
44]. As Bachorzewska-Gajewska [
19] demonstrated in one of the first studies, and a number of other authors [
18,
20,
45] subsequently confirmed that NGAL significantly increased in the first hours after contrast administration. In the study by Shaker et al. [
20] it was demonstrated that compared to the baseline values of plasma NGAL of 52.5 ± 13.8 ng / ml , at the 4th hour after angiographic examination, an increase to 88.5 ± 16.4 ng/ml was reported (P < 0.001) , and at the 24th hour the values were 63.6 ± 10.5 ng/ml (P < 0.001). The regression analysis proved a positive significant correlation between the levels of the new biomarker and serum creatinine in each of the studied time intervals. According to Padhy et al.
[18] serum NGAL is a biomarker with a “narrow diagnostic window” in which peak values can be reached within 4 hours after contrast angiography examination, remain significantly higher for up to 24 hours, but by 48 hours can be completely normalized. Liao et al. [
42] reported in their study among 240 patients that the diagnostic power of serum NGAL was extremely good – at 6 hours after contrast examination the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.81 (p=0.03) with a sensitivity of 97.64% and specificity 67.78% at a cut-off point of 96.35 ng/ml ; and at the 24th hour, respectively, AUC = 0.89 ( p< 0.01 ), sensitivity 96.63% and specificity 68.72% at an established reference level of 97.57 ng/ml. In summary, NGAL is emerging as an early biomarker for contrast-induced AKI with a significant increase within 24 hours after the procedure [
19,
20,
42,
44,
46] and significantly before rising of the standard serum creatinine which significantly different values are registered only on the second day [
19,
44].
The results of our study fully confirm dynamic changes in NGAL and prove its good diagnostic value as an early marker for the onset of CI-AKI, considering the data from the ROC analysis (
at 4 hours - АUC 0.847, cut-off point of plasma NGAL 90.20 ng/ ml , sensitivity 83.33%, specificity of 83.33% ). These results fully correlate with those cited in the literature (
AUC 0.81–1.00 at 4–6 h [
18,
42]
and AUC 0.89 at 24 hours [
42]) and presented in several meta-analyses focused on CIN [
21,
22,
23].
It should be noted, however, that the increase in serum creatinine within the first 24 hours after angiography is somewhat different from the trends described in some studies [
19,
28,
45]. This may be due to design differences across studies. In many study designs, it is assumed that the laboratory samples were obtained at different times, with creatinine being reported only at baseline and at the end of the observed period (within 48-72 hour after procedure) [
19,
28,
45]. In contrast, we examine both biomarkers from blood samples obtained simultaneously at the same time interval, allowing full parallel comparison of their dynamic changes. Furthermore, our selected cohort of patients with predominant diabetes mellitus type 2 (91.1%) was completely different from most studies [
18,
19,
42,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48] where the incidence of DM is between 14% and 34%. In this perspective the only study reporting the role of NGAL exclusively in diabetic patients is presented by Ashalatha et al. [
35] and its results showed that serum creatinine and NGAL increased significantly as early as the 4th hour, and the difference compared to the “non-CIN” group was observed at the 24th hour, but only for creatinine. The authors conclude that patients with diabetes mellitus and preserved renal function are more likely to suffer from subclinical renal impairment, considering them as much more susceptible to contrast damage and leading to early elevation of biomarkers. They assume that the dynamic changes of indicators may be different in diabetic patients and in individuals without DM [
35].
This direction of scientific reasoning once again emphasizes the importance of comprehensive time wise study of kidney dysfunction in a completely different aspect - the existence, diagnosis and prognosis of subclinical forms of damage. As already mentioned, modern understanding of AKI emphasize diagnostic approach based on the simultaneous measurement of functional and structural biomarkers [
16,
17] . Based on this concept, patients undergoing invasive procedures with contrast administration should also be screened for the development of renal injury or impaired function by the evaluation of both types of biomarkers for AKI [
49]. Although some authors propose the introduction of terms such as “
CI-AKI with structural damage” or “
CI-AKI with renal dysfunction”, this distinction remains only theoretically grounded [
49].
In the literature, there is no clear definition of subclinical CIN or CI-AKI, as well as a clearly defined frequency of this group of events. Initially, some authors [
35] only describe that among the group “without CIN” there are individuals with an increase in NGAL similar to that reported in CIN . On the other hand other studies [
40,
50] suggest a limit as an increase > 25% of the biomarker, or assume that for the diagnosis of subclinical AKI, the biomarker must increase 2 times compared to its baseline levels [
41,
51]. In the studies of Breglia et al.[
52] and Rozenfield et al [
53], an absolute value is introduced as a reference limit above which the biomarker is reported as positive. While some authors reported an incidence of subclinical AKI of 11.1% [
41], others reported a “biomarker (+)/creatinine (−)” cohort with an incidence of 32.6% [
50] to 44% [
53]. A meta-analysis [
24] of 10 prospective studies, among critically ill patients, found that based on the „NGAL (+)/serum creatinine (-)” result up to 40% more cases of AKI could be identified that would have been missed, if the standard creatinine-based AKI criteria are used. Our results are complementary with the sources reported in the literature regarding the frequency of this form of renal damage.
In our study, we accept subclinical CI-AKI to be defined as an increase in plasma NGAL >25%, which fully corresponds to the change in the biomarker registered in the group with the clinically manifested form of CI-AKI. In relation to the entire studied sample, this result was found in 33.3% of patients, which may exceed some of the cited sources [
41] , but covers the wide range reported by others [
53]. As already noted, the selection of a cohort of patients with diabetes mellitus may alter the sample profile, delivering higher risk of subclinical renal impairment [
35] . Monitoring of NGAL in such cases may help to detect AKI before the change in serum creatinine.
In the study by Alharazy et al. [
40] among 100 patients undergoing elective coronary angiography ± PCI, was investigated the diagnostic role of serum NGAL and cystatin C in the detection of CIN. The authors reported that this event (
defined as a >25% rise in serum creatinine by 48 hours ) occurred in 11% of patients ( n=11/100) and both biomarkers had good diagnostic performance at 24 hours after the contrast angiography. It is interesting to note that, a limit of 25% increase in serum NGAL, was registered in n=7/11 patients with CIN and in n=12/87 patients in the non-CIN group. An elevation of cystatin C > 25% was found in only 4 of the CIN patients and among one of the remaining cohort. The authors hypothesize that, in addition to diagnosing contrast-induced renal injury, the new biomarkers are likely to capture cases with subclinical AKI. The latter are only described as a finding, but no further analysis is conducted in this direction. On the other hand, an assumption is made that such patients are likely to be missed in the standard diagnostics of CIN.
We have managed to advance further in our study by inclusion of a group with subclinical CI-AKI, monitoring dynamic changes in biomarkers at all time intervals in parallel with the changes observed in a group with clinically manifested CI-AKI. It can be seen from the obtained results in the patients with subclinical CI-AKI, that serum creatinine (respectively GFR) has no significant changes compared to its initial levels through the entire observation period (48 hours after the end of angiography). In terms of dynamics, however, plasma NGAL increases significantly as early as the 4th hour after the contrast administration and maintains its high levels until the 24th hour. The diagnostic power of the new biomarker for early detection of renal damage is relatively good, as shown by the ROC analysis with AUC 0.731 (p=0.024), sensitivity 73.33% and specificity 72.22% at a cut-off value of 85.65 ng/ml.
The comparative analysis against the other two groups clearly shows the positioning of this cohort of patients in the whole sample. Compared to the control group, patients with subclinical CI-AKI were significantly distinguished only by the values of plasma NGAL, which increased early after the end of contrast angiography (at the 4th hour). Compared to the group with CI-AKI, a significant difference was found only in the dynamics of serum creatinine (respectively GFR). Based on these data, we can conclude that the group with subclinical CI-AKI occupies an intermediate place in the clinical continuum between patients without renal function impairment and patients with clinically manifested contrast-induced nephropathy. In other words, if solely the classic creatinine-based definition of AKI is applied in clinical practice, the only patients who will differ from the entire study cohort are those with CI-AKI. Patients in the control group and those with an “NGAL+” result, having close values (p = NS) of serum creatinine levels that do not change over time after the contrast study, will be misidentified as individuals without impaired renal function.
The first study designed to specifically investigate subclinical AKI is reported by the Akrawinthawong group et al. [
41] and was conducted among 63 patients with GFR<90 ml/min/1.73 m
2 , undergoing routine angiographic examination. CI-AKI is defined according to the AKIN criteria
(>0.3 mg/dl or > 50% increase in serum creatinine up to 48 hours ), while “subclinical AKI” is defined as increase in serum NGAL ≥ 2 times compared to baseline levels, without concurrent change in creatinine. According to the results, CI-AKI was diagnosed among n=8/63 (12.7%) of the examined patients, while in seven others (n=7/63; 11.1%) subclinical ACI was identified. A general examination of all patients with AKI (defined by AKIN and subclinical form) showed that 23.8% had certain renal dysfunction after the administration of contrast media, and in all of them the peak values of NGAL were significantly higher than at baseline levels. The study confirms the fact that the application of one of the new structural biomarkers captures almost twice as many cases of AKI. However the authors emphasize the need for more research in this direction.
Our study differs from the aforementioned one by of Akrawinthawong et al . [
41] in terms of the selected patient cohort, including patients with different levels of renal function (GFR is in a wide range from 15 to 90 ml/min), which is also reflected in the different baseline levels of NGAL cited by the authors (360.29±227.94 ng/ml at GFR 15-30 ml /min versus 114.02±57.42 ng/ml at GFR 60-90 ml/min). Considering that the existence of chronic kidney disease affects the level of NGAL [
28,
54] , as well as our preliminary data in this direction [
26], we turned our attention to a more strictly selected sample according to renal function, examining separately the characteristics of NGAL among patients with GFR above 60 ml/min.
Breglia et al .[
52] also reported the occurrence of CI-AKI and subclinical CI-AKI after intra- arterial administration of contrast material in patients with GFR > 60 ml/min, but applied a combination of structural biomarkers urinary NGAL, IGFBP7 (
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7) and TIMP-2 (
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2) , measured 4-8 hours post procedure. According to the study design, CI-AKI was defined according to KDIGO criteria (creatinine
> 0.3 mg/dl or >50% compared to baseline levels), and subclinical CI-AKI is defined as a positive result for the relevant biomarker (
TIMP-2 и IGFBP7> 0.3 (ng/ml)2/1000; NGAL > 90 μg /L ). Out of a total of 100 selected patients, with performed neurological invasive procedures, none of them was found to have CI-AKI according to the KDIGO criteria. At the same time, the studied biomarkers were positive in 13 patients ( NGAL (+) result was found in 5 patients, TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 (+) result in 10 patients respectively, and in three all biomarkers were positive). The critical message from this study is that while in a low-risk patient population (assessed
as such according to the Mehran score), no cases of CI-AKI defined by creatinine were observed, subclinical CI-AKI defined as elevation of biomarkers of the lesion, is found in > 10% of patients with contrast diagnostic/therapeutic procedures.
The importance of subclinical forms of AKI is noted by a number of authors. Haase ‘s meta-analysis demonstrated that the “NGAL (+)/serum creatinine (-)” patient cohort had an increased risk of prolonged ICU stay, initiation of renal replacement therapy, and increased mortality [
24]. According to other authors patients with positive new biomarkers (urinary KIM-1 and urinary NGAL) compared to patients with a negative result have increased risk of renal replacement therapy and in -hospital mortality [
55,
56]. A study of STEMI patients undergoing primary angioplasty reported that 44% of patients had “NGAL(+)/creatinine(−)” result (defined as NGAL values ≥100 ng/ml), and 14% of patients had “NGAL (+)/ creatinine (+)” result. Compared to the “NGAL (-)/ creatinine (-)” subgroup, NGAL positivity alone resulted in a significantly increased risk of adverse in-hospital events (46% vs. 64%, respectively; OR 2.1; 95% CI 1.1-4.5; p = 0.05) [
53] Other authors [
57] demonstrated that even baseline measurement of higher NGAL values could be associated with an increased frequency of major adverse events and overall mortality among patients from the third quartile (143.9 to 567.9 ng/mL) compared to a group from the first quartile (25.4 to 83.7 ng/mL). Recent studies in the field of subclinical CI-AKI demonstrate, in addition to a higher frequency of these events when applying NGAL-based definition (18%), but also persistence of subclinical damage for more than one month among half of these patients [
58] .
In summary, our presented data contribute to the current scientific literature in the diagnosis of subclinical forms of acute kidney injury after contrast angiography, demonstrating the characteristics of renal biomarkers in a relatively homogeneous cohort of patients in terms of high risk profile and baseline renal function. A number of the conducted studies included mixed cohorts of patients and focused primarily on the application of NGAL as a diagnostic marker for a clinically apparent form of CI-AKI. An advantage of our study is the investigation with equal focus of clinical and subclinical forms of AKI, applying the current ADQI recommendations and two different type of renal biomarkers.
Limitations of the study. It should be noted the relatively small sample size. Nonetheless both in the field of contrast nephropathy and in a number of other emerging fields related to imaging methods, relatively small cohorts with less than 100 patients have been reported [
20,
41] . The relatively narrow follow-up interval of the patients up to 48 hours after the contrast examination does not allow us to establish whether some of the patients with subclinical forms of kidney damage did not demonstrate a delayed increase in serum creatinine. On the other hand, the definition we apply for CI-AKI is in accordance with the one adopted in the literature [
6,
9]. Considering that NGAL is described in a number of sources as a marker with a “narrow diagnostic window” [
18] in the first hours after exposure to the damaging agent, we fully justified the biomarker follow-up in our study to be as early as possible after the contrast administration procedure.