1. Introduction
Acute heart failure (AHF) is a clinical syndrome whose overall incidence is increasing due to the aging of the population. The incidence rate in Europe is around 5/1,000 person-years in the adult population, affecting 1-2% of the adults [
1,
2]. Mortality can be as high as 67% at 5 years after diagnosis [
3]. Moreover, it is known that after diagnosis, patients with heart failure are hospitalized on average once a year [
4]. Multidisciplinary programs had been implemented to tackle this high prevalence [
5,
6]. However, the optimal follow-up frequency is unknown. For this reason, tools are needed to refine patient prognosis.
The venous excess ultrasonography (VExUS) score has been proposed as a score to evaluate systemic congestion and predict Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Its use has been adopted especially in heart failure patients, but to date there is no formal validation. Our study aims to evaluate different ultrasound parameters (including the VExUS score) in the prediction of clinically important outcomes (i.e. heart failure related death, heart failure related readmission).
2. Materials and Methods
This is a prospective study performed in a tertiary and a secondary hospital. This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and approved by our local Ethics Committee. We obtained informed consent from each patient.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
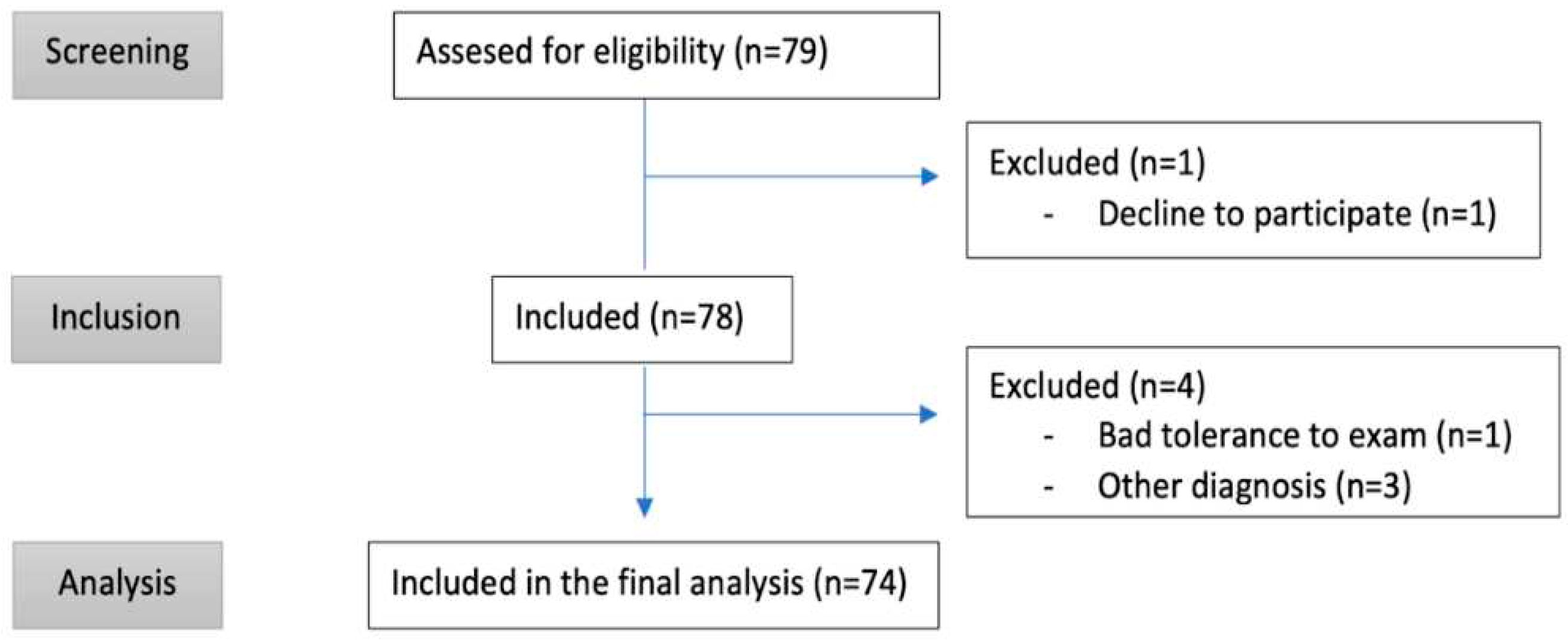
Patients whose main hospital admission diagnosis was acute heart failure (AHF) and a NT-proBNP level above 500 pg/mL were included. Patients under 18 years of age, with hemodynamic instability, who declined to participate or who had received more than 24 hours of diuretic treatment were excluded. Case inclusion was performed by four investigating physicians, different from the physician responsible for the patient. If an alternative pathology was diagnosed, the patient was excluded from the study. 74 patients who met the following inclusion criteria were prospectively studied (
Figure 1).
2.2. Initial Assessment
Demographic data (age, sex, weight), comorbidities, risk factors for AHF (i.e. cardiopulmonary diseases), physical examination (weight, blood pressure, oxygen saturation), heart rate and laboratory tests (creatinine, urea, hemoglobin, leukocytes, NT-proBNP among others) were recorded at admission, discharge and follow-up visit. Early follow-up visit was scheduled in the outpatient clinic within the first fifteen days after discharge.
The EVEREST classification score (10), as a marker of the clinical course of congestion during hospitalization, was calculated for each patient at admission, discharge and consultation; the same was done with the NYHA dyspnea assessment scale. We defined worsening renal function as an increase of 0.3 mg/dL.
2.3. Collecting Ultrasound Data
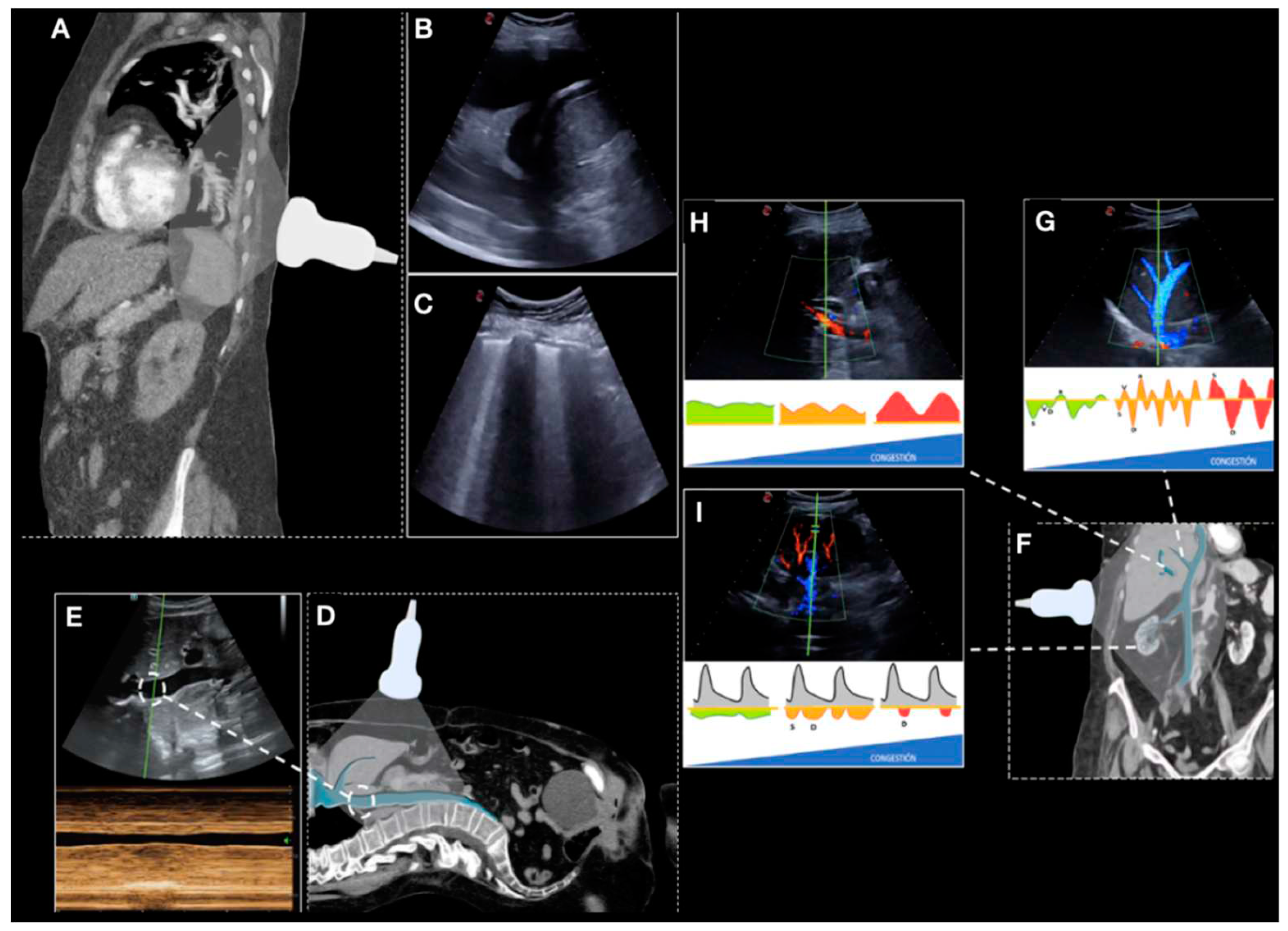
Multiorgan ultrasound was performed in the first 24 hours after admission, as well as on the day of discharge and in the follow-up within the first fifteen days after discharge (
Figure 2). The different ultrasound parameters that could be associated with volume overload were registered:
Number of areas with pulmonary B-lines and pleural effusion (scored through the Lung Score, a lung involvement score that evaluates 6 areas per lung with a maximum score of 36) [
7].
Diameter and collapsibility of the inferior vena cava (IVC). As in previous reported studies, we set the cut-off diameter at 2 cm [
8].
Doppler ultrasound of hepatic, portal, renal and femoral veins [
9].
Then, the VExUS score was obtained as described from previous reports [
10]. In addition, based on a previous study from our research group [
9], we calculated a simplified score from the previous categories (VExUS 0 = no congestion; VExUS 1 = mild congestion, VExUS 2 = moderate congestion; VExUS 3 = severe congestion) to two (0 = absence to moderate congestion, previous VExUS 0 to 2; 1 = severe congestion, previous VExUS 3).
Echocardiographic findings were also registered [
9] (left ventricular diastolic and systolic diameters, interventricular septum and posterior wall), left ventricular ejection fraction, left and right atrial area, transmitral filling pattern, TAPSE, tricuspid regurgitation (TR) velocity, pulmonary artery diameter, right ventricular outflow acceleration time, pulmonary regurgitation velocity, presence of moderate or severe left valvular heart disease, and probability of pulmonary hypertension according to the European Society of Cardiology guidelines [
11].
A Mindray M7 and M9 diagnostic ultrasound machine equipped with a phased, curvilinear, and linear transducer (Mindray España, Madrid, Spain) and a Kosmos portable ultrasound machine (EchoNous, Redmond, WA, USA) were used in the study.
2.4. Objective and Definitions
Our study aims to determine the prognostic role of different ultrasound parameters and scores (including the popular VExUS systemic congestion score); on the prediction of heart failure death and readmissions related to a decompensated heart failure episode.
3. Results
From November 2021 to August 2022, a total of 79 patients were evaluated and met the inclusion criteria (summarized in Figure and
Table 1), and 74 patients were included in the final analysis.
The mean age was 79.5 years (Standard Deviation - SD 12.5) and 51.4% were women. A total of 78.4% had an underlying cardiovascular disease and 43.2% had a previous pulmonary disease. 10 patients (13.5%) died during hospitalization, 5 (6.8%) within 1 month of discharge and 4 (5.4%) within 2 months. In total, 19 patients (25.7%) died, 12 deaths (16.2%) attributed to heart failure. 26 patients (35.1%) were admitted in the first 3 months after discharge (15, 20.3% during the first month). 22 patients (29.7%) had a heart failure related readmission (
Table 1, second column). Regarding to the echocardiographic findings on admission (
Table 1, third column), 96% of patients had some degree of tricuspid regurgitation. Based on this, the probability of pulmonary hypertension was assessed; it was low in 14 patients (18.9%), intermediate in 11 patients (14.9%) and high in 49 patients (66.2%). Left ventricular function was normal in 41 patients (55.4%), mildly reduced in 8 (10.8%) and severely reduced in 25 (33.8%). Right ventricular function, assessed by TAPSE, was severely reduced (TAPSE less than or equal to 17 mm) in 31 patients (41.9%).
Most patients were in NYHA III on admission (62%) and improved to NYHA II upon discharge (37.8%), and NYHA I (37.8%) at follow-up visit to the clinic (
Table 2). The median EVEREST score at admission was 8 (SD 3.1), at discharge was 1 (SD 1.17) and at follow-up it slightly increased to 2 (SD 2.43).
Regarding laboratory findings (
Table 2), mean NT-proBNP was 10278.5 pg/l (SD 12740) on admission, 6156 pg/l (SD 7889) at discharge and 5438 pg/l (SD 5712) at follow-up. Mean creatinine was 1.58 mg/dL (SD 0.8) at admission, 1.47 mg/dL (0.94) at discharge and 1.52 at follow-up. 55 patients (74.3%) had impaired creatinine at admission, 59 patients (79.7%) at discharge and 59 patients (79.7%) at follow-up. 44 patients (59%) had worsening renal function at discharge and 52 patients (70%) at follow-up.
Among the dynamic changes on the ultrasound exams (
Table 3), were remarkable the mean VCI diameter, which reduced from 2.25 cm (SD 0.53) to 1.81 cm (SD 0.42) from admission to discharge, and remained similar at early follow-up (1.85 cm, SD 0.53). The absence of collapsibility was present in 71 patients at admission (95.9%) and decreased at discharge (41 patients, 55.4%) and follow-up (38 patients, 51.4%). The dominant hepatic vein pattern at admission was systolic inversion, present in 35 patients (47.3%), improving in 26 patients (35.1%) during hospitalization. Portal vein pulsatility at admission was > 50% in 27 patients (36.5%) and predominantly continuous (50 patients, 67.5%) at discharge. Regarding the intrarenal veins, the most observed pattern at admission was biphasic (30 patients, 40.5%) and continuous at discharge (40 patients, 51.4%) and follow-up (31 patients, 41.9%). The dominant VExUS score on admission was 3 (24 patients, 32.4%). Remarkably at the same moment, 21 patients (28.4%) had a VExUS of 0, which increased to 56.8% at discharge, but decreased to 39.2% at follow-up. There were significant differences in all ultrasound parameters except for the collapsibility index between admission and discharge. However, this was not so significant between discharge and follow-up for the portal Doppler and VExUS score.
We collected significant (p < 0.01) moderate (r = 0.3-0-5) to strong (r > 0.5) correlations in
Table 4. As we can see, the intrarenal Doppler assessment is likely to be the most useful marker, it maintains the best correlation on admission, discharge, and follow-up.
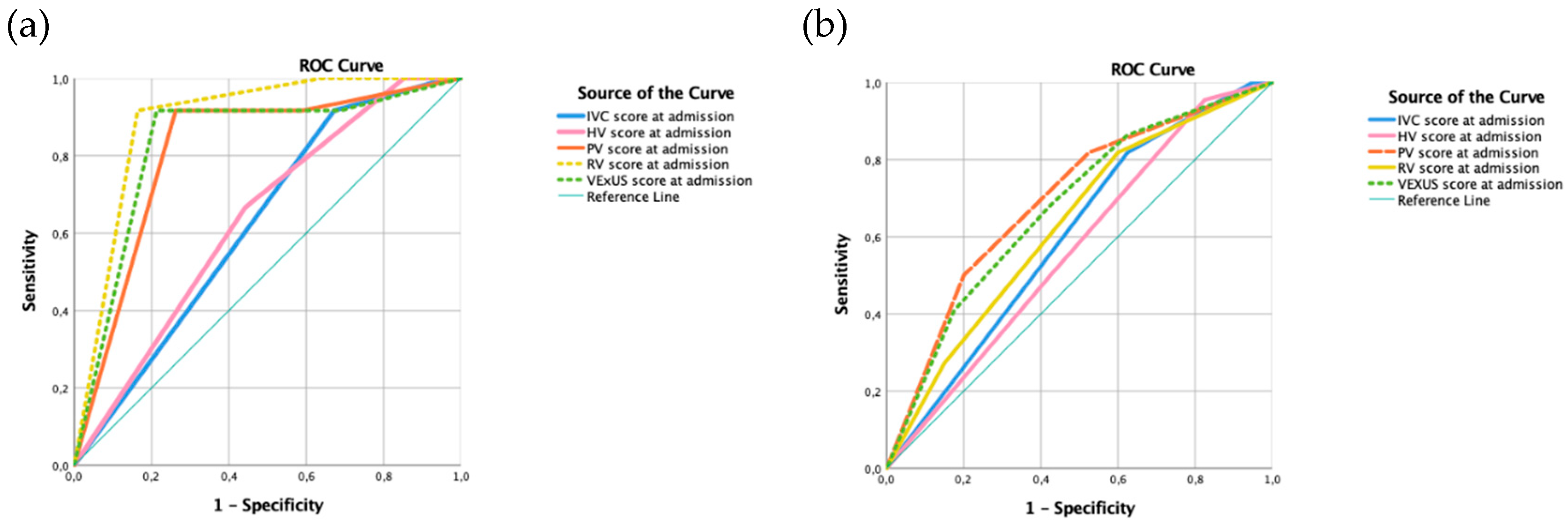
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (
Figure 3 and
Supplemental Material) was calculated for predicting mortality (
Figure 3a) and readmission (
Figure 3b) related to heart failure, based on the initial ultrasound exam.
The presence of an intrarenal monophasic pattern (Area under the curve - AUC 0.923, sensitivity - Sn 90%, specificity – Sp 81%, positive predictive value - PPV 43%, negative predictive value - NPV 98%) predicted death during admission. A VExUS score of 3 performed similar (AUC 0.885, sensitivity 80%, specificity 75%, PPV 33%, NPV 96%). A valid alternative could be the detection of a portal pulsatility > 50% (AUC 0.749, Sn 80%, Sp 69%, PPV 30%, NPV 96%).
To predict HF related death, the VExUS of 3 had an AUC of 0.892 (Sn 92% and Sp 79%, PPV 46% and NPV 98%), like the Simplified Porta Score (AUC 0.882, Sn 92%, Sp 74%, PPV 41%, NVP 98%) but less complex to calculate (
Supplemental Material).
All ultrasound parameters were less accurate to predict HF related readmission. The best parameters were an IVC above 2 cm (AUC 0.758, Sn 93.l% and Sp 58.3) and the presence of an intrarenal discontinuous monophasic pattern (AUC 0. 834, sensitivity 0.917, specificity 67.4%) in the follow-up visit (appendix A). However, it is interesting to find that the portal vein (AUC 0.696, p=0.11) followed by VExUS (AUC 0.676, p=0.23) at admission could be also of use (fig 3b).
4. Discussion
Mortality and readmission rates for decompensated acute heart failure (AHF) is overall increasing and risk stratification might be challenging, with a 5 year mortality rate of over 60% [
3] and 1 re-admission per year [
4]. Given that it currently affects 1-2% [
1,
2] and the prevalence is increasing, to accurately stratify high-risk patients is of vital importance to optimize efforts an allocate resources.
Previous studies have already pointed out the role of ultrasound in accurately determining prognosis. Regarding the IVC, Cubo-Romano et al reported in 80 patients hospitalized due to AHF that an IVC greater than 1.9 cm at admission had higher mortality rates at 90 days (25.4 vs. 3.4%; p=0.009) and at 180 days (29.3 vs. 3.4 %, p=0.003) [
8]. However, in the study of Beauvien-Souligny they showed that the correlation with the IVC was poor [
10], this could partly be explained due to the selected post-surgical population they recruited. Similar to our results, Goonwardena et al. followed a total of 75 patients admitted due to AHF and observed that the best predictors of readmission were the IVC diameter of 2 cm (Sn of 81% and Sp of 72%) and the NT-proBNP (cutoff point of 2327 with a Sn of 82% and Sp of 56%) [
12]. Moreover, Khandwalla et al. observed that each 0.5 cm increase in IVC diameter was associated with a 38% increase in the risk of readmission (RR 1.38, p<0.01) [
13]. Like our results, the AUC of the IVC at admission showed a trend towards significance in the prediction of readmission and HF-associated death, probably due to the low sample size. We want to highlight its usefulness in the follow-up visit after discharge, with a high NPV for mortality (Sn 100%, Sp 51%, PPV 38%, NPV 100%) and early readmission (Sn 93%, Sp 60%, PPV 41%, NPV 97%).
Considering systemic congestion and its repercussion on the organs affected by it, Bouabda-llaoui et al. reported that portal pulsatility was associated with mortality in a cohort of 95 patients [
14]. Like our results, measuring the portal vein at admission could be a good parameter for predicting death or early readmission, as well as serve as a monitoring marker during follow-up. Therefore, our study emphasizes the potential role of the portal vein, with the advantage of its easy acquisition and reproducibility.
The data regarding intrarenal venous assessment are probably the most interesting. Husain-Syed prospectively evaluated 205 patients with RV failure undergoing cardiac catheterization and assessed congestion patterns and calculated the renal venous stasis index (RVSI), found it to be prognostic [
15]. Yoshihisa prospectively evaluated 314 patients and assessed both intrarenal arterial and venous components, observing that right atrial pressure was higher in monophasic than in non-monophasic, and that the cardiac event rate was higher in the low velocity time integral (VTI) and monophasic groups [
16]. Like our study, we show an excellent AUC, and owing its high NPV could serve as an screening marker to identify high risk mortality and readmission patients.
Beaubien-Souligny et al. [
10] designed a venous congestion score (VExUS) in postoperative cardiac patients using the pulsed Doppler pattern of a hepatic vein, the portal vein and a renal interlobular vein [
10], which had an association with the development of AKI. This system of congestion quantification has become widespread in the evaluation of AHF without data to support its use to guide therapy or as a prognostic estimate.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that assess the role of VExUS score in the prognosis of AHF patients. For obvious reasons, we have focused on clinical outcomes rather than trying to define AKI in this population [
17,
18]. From our data we can state that the presence of a VExUS score of 3 on admission could predict death during admission, HF-related death, and early readmission, but similar to other simpler ultrasound evaluations.
Another strength is that our study is one of the first reports that explore the frequency that ultrasound should be performed in this population. We have analyzed the ultrasound exam at admission, discharge, and follow-up, and found significant differences in the parameters from admission to discharge, but less between the discharge and follow-up. This would support that serial ultrasound scans are not necessary and that the most cost-effective approach would be performing only an exam on admission and not repeating it during hospitalization.
On the admission ultrasound, portal and renal assessment would be an adequate predictor of mortality. Although the presence of a VExUS score of 3 may be also adequate, it does not contribute much more than the intrarenal or the portal veins, carrying a greater complexity and time-consuming in its evaluation. Consequently, if on the admission ultrasound we do not find a severe intrarenal or portal patterns of congestion, we can probably classify this patient as a lower risk group of complications. During follow-up, the most reliable marker could be the size of the VCI, being low risk those below 2 cm.
It is important to acknowledge that our study has different limitations. First, in the tertiary hospital, there was an established heart failure program and in the secondary hospital, the follow-up was carried out by the internal medicine physician in charge, with a direct impact in the management. Second, patients living in long term care facilities with reduced mobility were less likely to have followed-up appointments, and therefore were less likely to be included. Thirdly, as this is a pilot study, only four expert sonographers were chosen to perform the exam, and, therefore, the results might not be reproducible. Future studies should investigate if the skill can be mastered by a greater number of novice sonographers. And finally, the small sample size and number of involved centers, might also affect reproducibility. Further studies on the prognostic implications of venous congestion ultrasound are needed to support the findings of this study.
Although, these limitations are important, we believe that integrating ultrasound in our current practice is appropriate as it addresses more physiologically the assessment of the volume status in AHF patients.
5. Conclusions
The most cost-effective ultrasound scans are those on admission and at follow-up. Intrarenal venous Doppler assessment, VExUS score and the presence of a pulsatility above 50% on admission similarly predicts mortality. An inferior vena cava greater than 2 cm and an intrarenal monophasic pattern accurately predicts readmission risk. VExUS probably adds unnecessary complexity to the assessment and prognosis of AHF patients. Early and multidisciplinary follow-up visit remains necessary to improve prognosis of this highly prevalent disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, ROC analysis from all ultrasound parameters.
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed to this work. Conception and design: MTA, YTC. Analysis and interpretation: MTA, GGCS, YTC. Data collection: MTA, AMM, RAG, EHM, MCM. Writing the article: MTA, YTC. Critical revision of the article: MTA, AMM, DT, GGCS, VCM, RAG, BSS, EHM, MCM, YTC. Final approval of the article: MTA, AMM, DT, GGCS, VCM, RAG, YTC, BSS, EHM, MCM. Statistical analysis: YTC, MTA. Overall responsibility: MTA, YTC.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro (Protocolo MIR/HPDH_2021_02 and date of approval:13/07/2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brouwers FP, de Boer RA, van der Harst P, Voors AA, Gansevoort RT, Bakker SJ, et al. Incidence and epidemiology of new onset heart failure with preserved vs. reduced ejection fraction in a community-based cohort: 11-year follow-up of PREVEND. Eur Heart J. 1 de mayo de 2013;34(19):1424-31. [CrossRef]
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 21 de septiembre de 2021;42(36):3599-726. [CrossRef]
- Motiejūnaitė J, Akiyama E, Cohen-Solal A, Maggioni AP, Mueller C, Choi DJ, et al. The association of long-term outcome and biological sex in patients with acute heart failure from different geographic regions. Eur Heart J. 1 de abril de 2020;41(13):1357-64. [CrossRef]
- Barasa A, Schaufelberger M, Lappas G, Swedberg K, Dellborg M, Rosengren A. Heart failure in young adults: 20-year trends in hospitalization, aetiology, and case fatality in Sweden. Eur Heart J. 1 de enero de 2014;35(1):25-32. [CrossRef]
- Jonkman NH, Westland H, Groenwold RHH, Ågren S, Anguita M, Blue L, et al. What Are Effective Program Characteristics of Self-Management Interventions in Patients With Heart Failure? An Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis. J Card Fail. noviembre de 2016;22(11):861-71. [CrossRef]
- Van Spall HGC, Rahman T, Mytton O, Ramasundarahettige C, Ibrahim Q, Kabali C, et al. Comparative effectiveness of transitional care services in patients discharged from the hospital with heart failure: a systematic review and network meta-analysis: Comparative effectiveness of transitional care services in patients hospitalized with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. noviembre de 2017;19(11):1427-43. [CrossRef]
- Tung-Chen Y, Ossaba-Vélez S, Acosta Velásquez KS, Parra-Gordo ML, Díez-Tascón A, Villén-Villegas T, et al. The Impact of Different Lung Ultrasound Protocols in the Assessment of Lung Lesions in COVID-19 Patients: Is There an Ideal Lung Ultrasound Protocol? J Ultrasound [Internet]. 2 de diciembre de 2021 [citado 2 de diciembre de 2021]; Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40477-021-00610-x. [CrossRef]
- Cubo-Romano P, Torres-Macho J, Soni NJ, Reyes LF, Rodríguez-Almodóvar A, Fernández-Alonso JM, et al. Admission inferior vena cava measurements are associated with mortality after hospitalization for acute decompensated heart failure. J Hosp Med. noviembre de 2016;11(11):778-84. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Arrese M, García de Casasola-Sánchez G, Méndez-Bailón M, Montero-Hernández E, Cobo-Marcos M, Rivas-Lasarte M, et al. Usefulness of Serial Multiorgan Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Acute Heart Failure: Results from a Prospective Observational Cohort [Internet]. MEDICINE & PHARMACOLOGY; 2021 dic [citado 14 de enero de 2022]. Disponible en: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202112.0113/v1.
- Beaubien-Souligny W, Rola P, Haycock K, Bouchard J, Lamarche Y, Spiegel R, et al. Quantifying systemic congestion with Point-Of-Care ultrasound: development of the venous excess ultrasound grading system. Ultrasound J. diciembre de 2020;12(1):16. [CrossRef]
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 1 de enero de 2016;37(1):67-119. [CrossRef]
- Goonewardena SN, Blair JEA, Manuchehry A, Brennan JM, Keller M, Reeves R, et al. Use of hand carried ultrasound, B-type natriuretic peptide, and clinical assessment in identifying abnormal left ventricular filling pressures in patients referred for right heart catheterization. J Card Fail. enero de 2010;16(1):69-75. [CrossRef]
- Khandwalla RM, Birkeland KT, Zimmer R, Henry TD, Nazarian R, Sudan M, et al. Usefulness of Serial Measurements of Inferior Vena Cava Diameter by Vscan TM to Identify Patients With Heart Failure at High Risk of Hospitalization. Am J Cardiol. mayo de 2017;119(10):1631-6. [CrossRef]
- Bouabdallaoui N, Beaubien-Souligny W, Oussaïd E, Henri C, Racine N, Denault AY, et al. Assessing Splanchnic Compartment Using Portal Venous Doppler and Impact of Adding It to the EVEREST Score for Risk Assessment in Heart Failure. CJC Open. septiembre de 2020;2(5):311-20. [CrossRef]
- Husain-Syed F, Birk H, Ronco C, Schörmann T, Tello K, Richter MJ, et al. Doppler-Derived Renal Venous Stasis Index in the Prognosis of Right Heart Failure. J Am Heart Assoc [Internet]. 5 de noviembre de 2019 [citado 24 de noviembre de 2021];8(21). Disponible en: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JAHA.119.013584. [CrossRef]
- Yoshihisa A, Watanabe K, Sato Y, Ishibashi S, Matsuda M, Yamadera Y, et al. Intrarenal Doppler ultrasonography reflects hemodynamics and predicts prognosis in patients with heart failure. Sci Rep. 17 de diciembre de 2020;10(1):22257. [CrossRef]
- Brisco MA, Zile MR, Hanberg JS, Wilson FP, Parikh CR, Coca SG, et al. Relevance of Changes in Serum Creatinine During a Heart Failure Trial of Decongestive Strategies: Insights From the DOSE Trial. J Card Fail. octubre de 2016;22(10):753-60. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad T, Jackson K, Rao VS, Tang WHW, Brisco-Bacik MA, Chen HH, et al. Worsening Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure Undergoing Aggressive Diuresis Is Not Associated With Tubular Injury. Circulation. 8 de mayo de 2018;137(19):2016-28. [CrossRef]
- Wachsberg RH, Needleman L, Wilson DJ. Portal vein pulsatility in normal and cirrhotic adults without cardiac disease. J Clin Ultrasound JCU. enero de 1995;23(1):3-15. [CrossRef]
- Fadel BM, Husain A, Alassoussi N, Dahdouh Z, Mohty D. Spectral Doppler of the Hepatic Veins in Pulmonary Hypertension. Echocardiography. enero de 2015;32(1):170-3. [CrossRef]
- Fadel BM, Mohty D, Husain A, Alassas K, Echahidi N, Dahdouh Z, et al. Spectral Doppler of the Hepatic Veins in Rate, Rhythm, and Conduction Disorders. Echocardiography. enero de 2016;33(1):136-40. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).