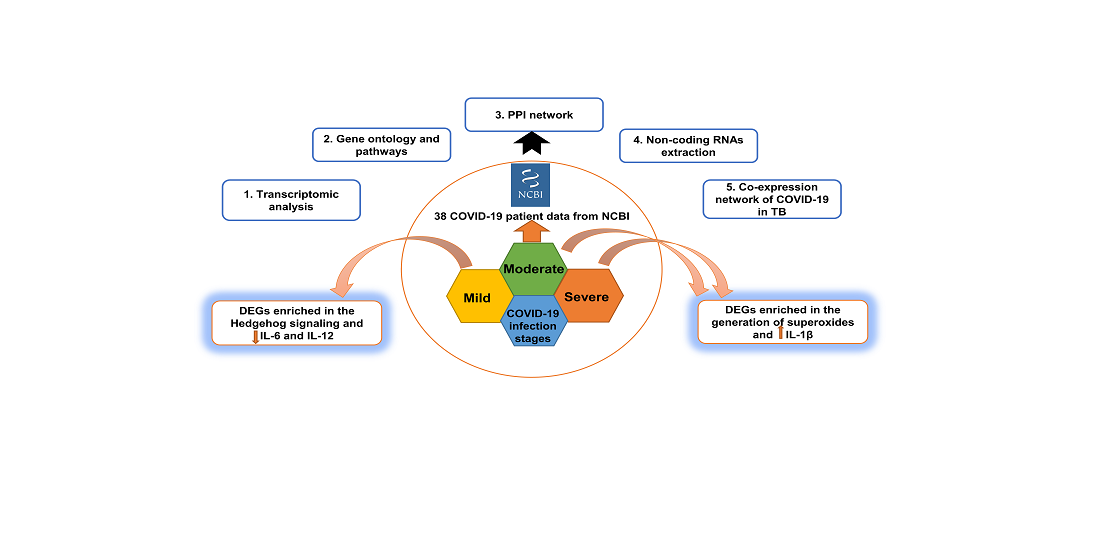
The pandemic of COVID-19 ravaged most countries and made the healthcare system go for a toss. The impact of the disease is different in each patient and it progresses differently. Based on the severity, the COVID-19 infection is stratified into three main categories- mild, moderate, and severe. In this study, we performed a transcriptomic study of different stages and studied the progression of the disease. The study was based on an Indian population of 28 COVID-19 patients, which were classified into different groups. Our analysis has shown that as the disease progresses, the genes involved in the degranulation of the neutrophils and galactose metabolism increase. Furthermore, we identified the hub proteins in each stage. TB is one of the comorbidities of COVID-19 and a comparative study was done to identify the preserved module of genes in both. Enrichment analysis showed that the members of this module are significantly involved in translation and ribosome synthesis.