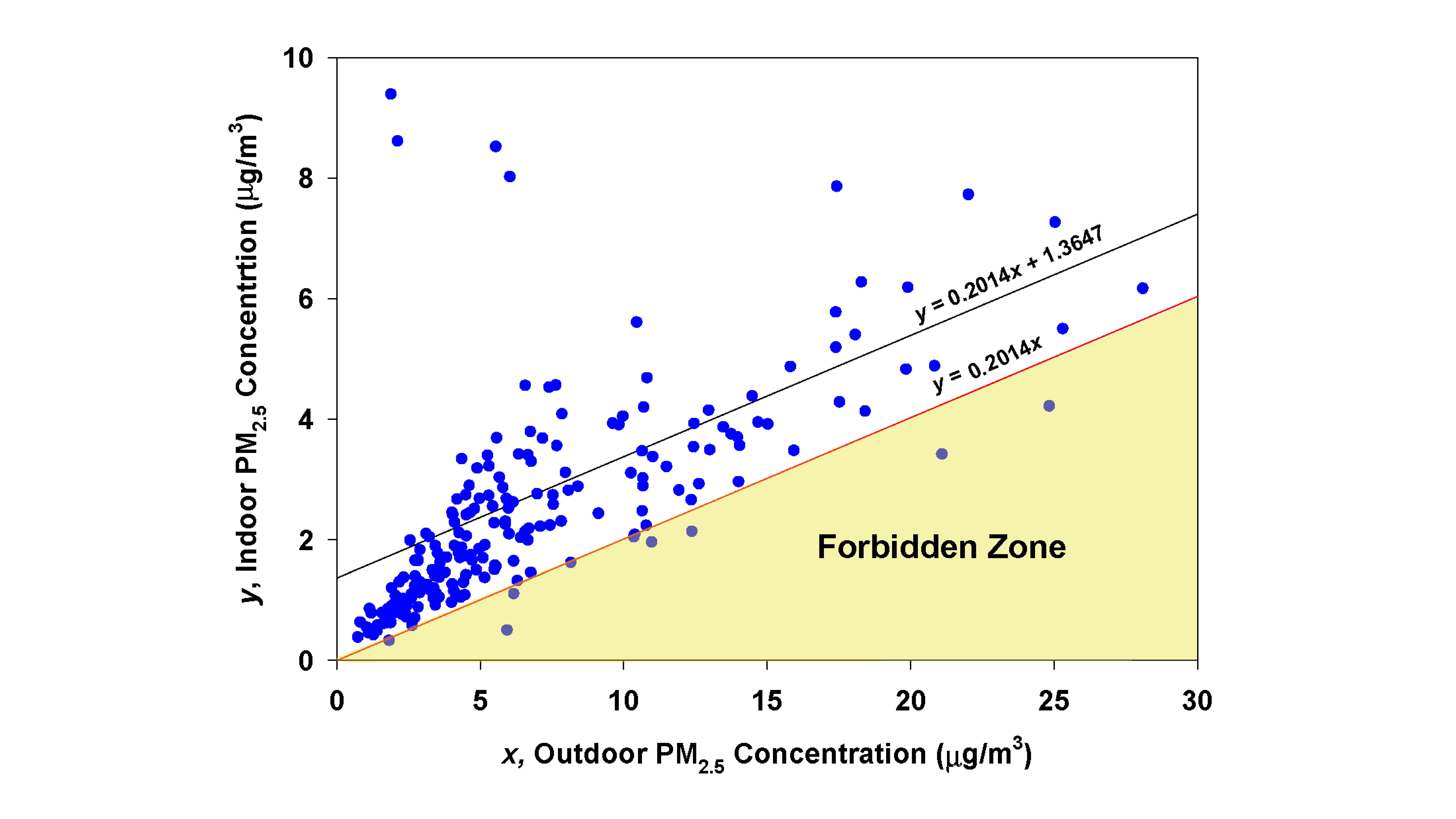
Low-cost monitors make it possible now for the first time to collect long-term (months to years) measurements of potential indoor exposure to fine particles. Indoor exposure is due to two sources: particles infiltrating from outdoors and those generated by indoor activities. Calculating the relative contribution of each source requires identifying an infiltration factor. We develop a method of identifying periods when the infiltration factor is not constant, and searching for periods when it is relatively constant. From an initial regression of indoor on outdoor particle concentrations, a Forbidden Zone can be defined with an upper boundary below which no observations should appear. If many observations appear in the Forbidden Zone, they falsify the assumption of a single constant infiltration factor. This is a useful quality assurance feature, since investigators may then search for subsets of the data in which few observations appear in the Forbidden Zone. The usefulness of this approach is illustrated using examples drawn from the PurpleAir network of optical particle monitors. An improved algorithm is applied with reduced bias, improved precision, and a lower limit of detection than either of the two proprietary algorithms offered by the manufacturer of the sensors used in PurpleAir monitors.