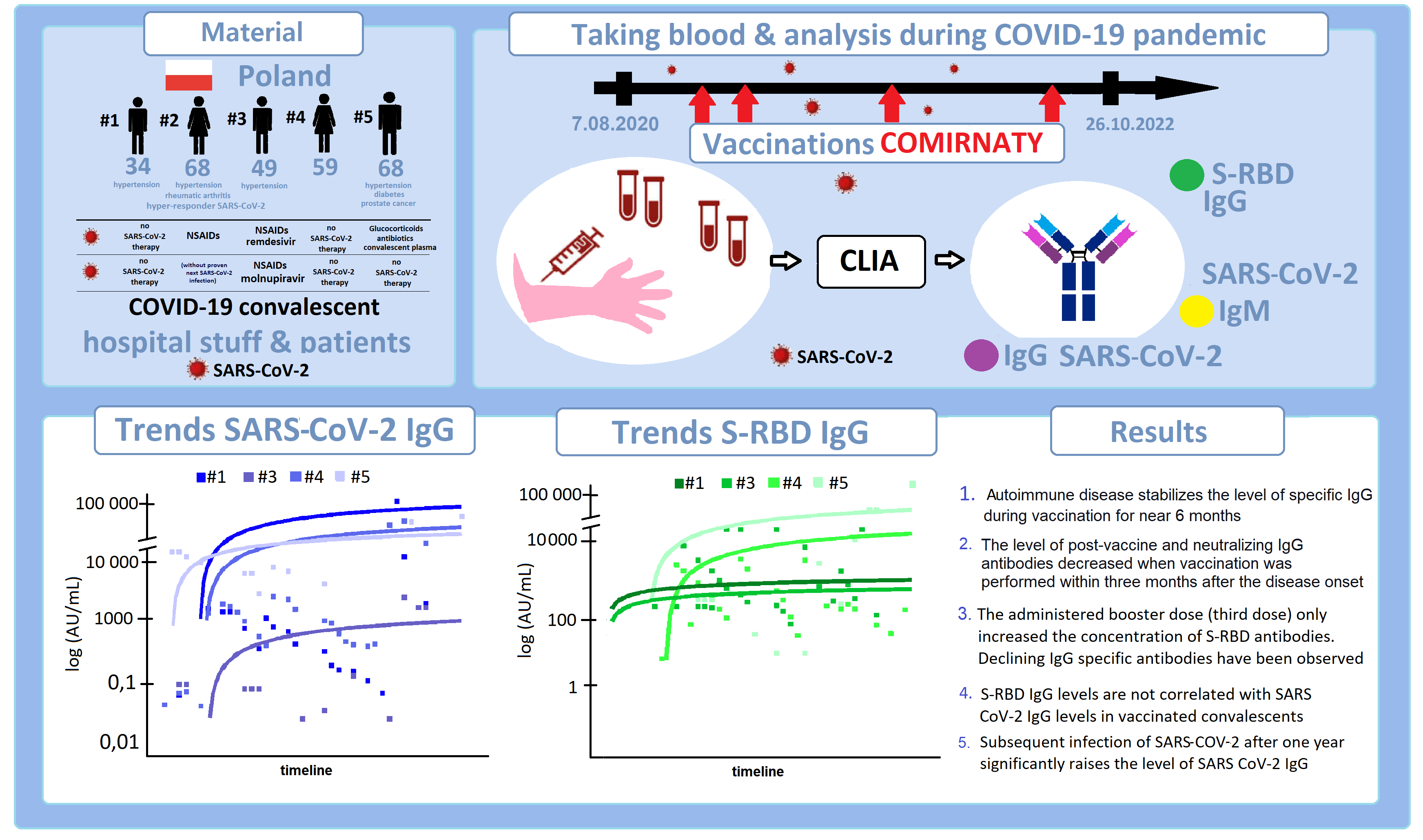
The humoral response of the COVID-19 vaccine varies from person to person. It largely depends on prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, obtaining an adequate immune response, and leaving a trace of changing antibody concentration over time. We retrospectively analyzed five clinical cases from selected patients and employees of the oncology hospital. All mild COVID-19 convalescents received the BNT162b2-Comirnaty mRNA vaccine three or four times. The levels of SARS-CoV-2 IgM- and IgG-specific antibodies, as well as S-RBD antibodies, were analyzed for two years. The concentration of antibodies was assessed in the laboratory using the chemiluminescent immunoassay CLIA, MAGLUMI. Results: (1) Active autoimmune disease stabilized the level of IgG-specific antibodies after systemic mRNA vaccination for at least six months. (2) Post-vaccination IgG and S-RBD levels decreased when vaccination was performed within three months of onset. (3) The booster dose administered only increased the S-RBD antibody levels. Declining IgG-specific antibodies were observed. (4) The S-RBD IgG levels were not correlated with the SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels in the vaccinated convalescents. (5) Subsequent reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination three times released a more significant specific antibody response. Based on the collected data, we suggest that monitoring S-RBD antibodies is sensitive but not equivalent to a specific humoral response for SARS-CoV-2 IgG. We suggested that administering at least three doses of the mRNA vaccine should serve as the basis for immunization. The three-month interval may be the best alternative to an immunization schedule for non-immunocompromised people.