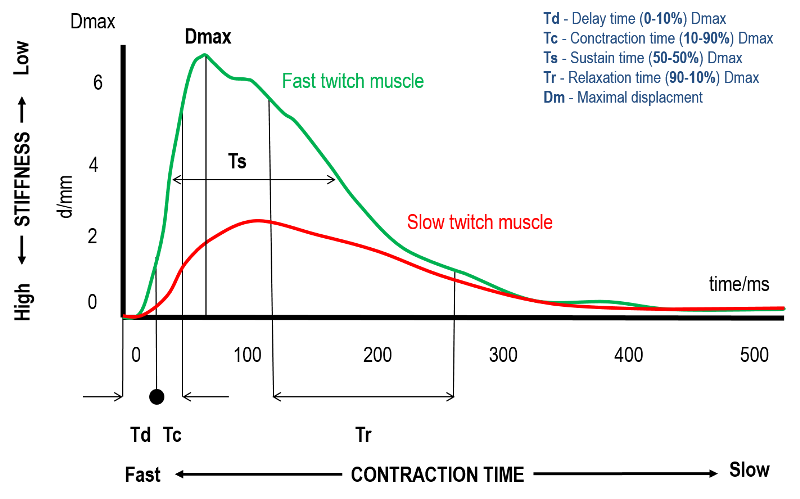
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to determine the normative values of muscles’ contractile properties, lateral symmetry, and the impact of aging on muscle contractility in gymnastics. Materials and Methods: A survey of 81 athletes from different disciplines was undertaken: MAG (n = 26), WAG (n = 28), and RG (n = 27). The athletes’ average age was 15.41 ± 5.03 years. We try to establish the normative values for contraction time (muscle pairs) in gymnastics for Slovenian athletes for ten skeletal muscles. Results: Athletes’ age affects contractility in a negative way. Differences between the duration of contractility and age were found in all disciplines: m. BF (r = 0.48, p < 0.001), m. TB (r = 0.37, p < 0.013), m. ES (r = 0.17, p < 0.025), m. VL (r = 0.36, p < 0.00) and m. VM (r = 0.40, p < 0.000) at a statistical significance of p < 0.05. Conclusions: A comparison between the left and right sides shows little asymmetry in WAG and that the occurrence of injuries is in the middle range. In RG we see a bigger deviation, which could trigger the emergence of pain or injury in m. BF (13%) and m. GL (14.5%), but in MAG the deviation is greater in m. BB (12%), m. BF (11%) and m. GM (13%).