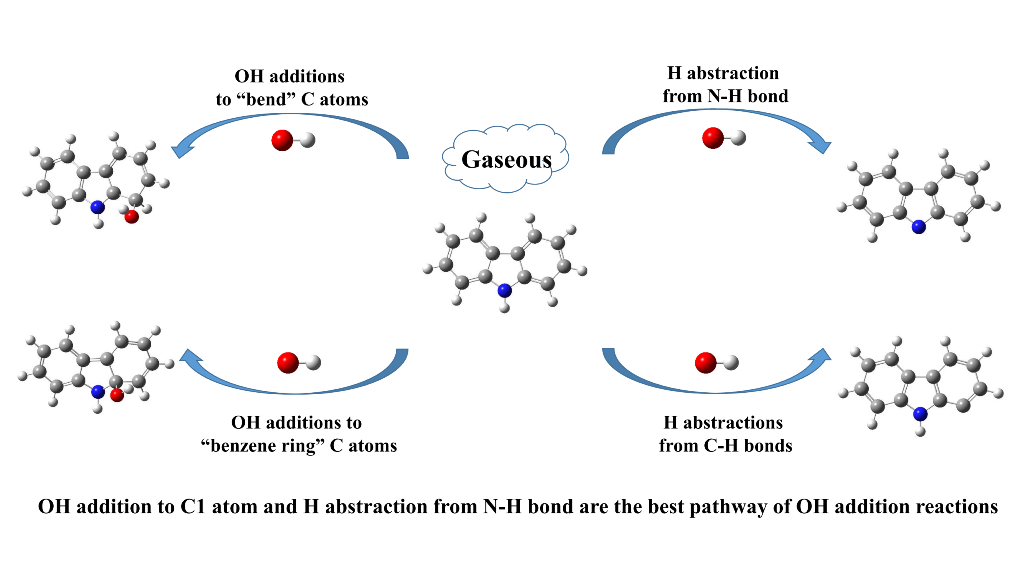
Carbazole is one of the typical heterocyclic aromatic compounds (NSO-HETs) observed in pol-luted urban atmosphere, which has become a serious environmental concern. The most im-portant atmospheric loss process of carbazole is the reaction with OH radical. The present work investigated the mechanism of OH-initiated atmospheric oxidation degradation of carbazole by using density functional theory (DFT) calculations at the M06-2X/6-311++G(3df,2p)//M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) level. The rate constants were determined by the Rice-Ramsperger-Kassel-Marcus (RRKM) theory. The lifetime of carbazole determined by OH was compared with other typical NSO-HETs. The theoretical results show that the degradation of carbazole initiated by OH radical includes four types of reactions: OH additions to “bend” C atoms, OH additions to “benzene ring” C atoms, H abstractions from C-H bonds and the H ab-straction from N-H bond. The OH addition to C1 atom and the H abstraction from N-H bond are energetically favorable. The main oxidation products are hydroxycarbazole, dialdehyde, carba-zolequinone, carbazole-ol, hydroxy-carbazole-one and hydroperoxyl-carbazole-one. The calcu-lated overall rate constant of carbazole oxidation by OH radical is 6.52 × 10−12 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 and the atmospheric lifetime is 43.92 h under the condition of 298 K and 1 atm. The lifetime of carbazole determined by OH radical is similar with that of dibenzothiophene oxidation but longer than those of pyrrole, indole, dibenzofuran and fluorene. This work provides a better understanding of the reactivity of carbazole in the atmospheric environment, the formation of secondary organic aerosols, and the chemical degradation and removal of carbazole in the at-mospheric environment.