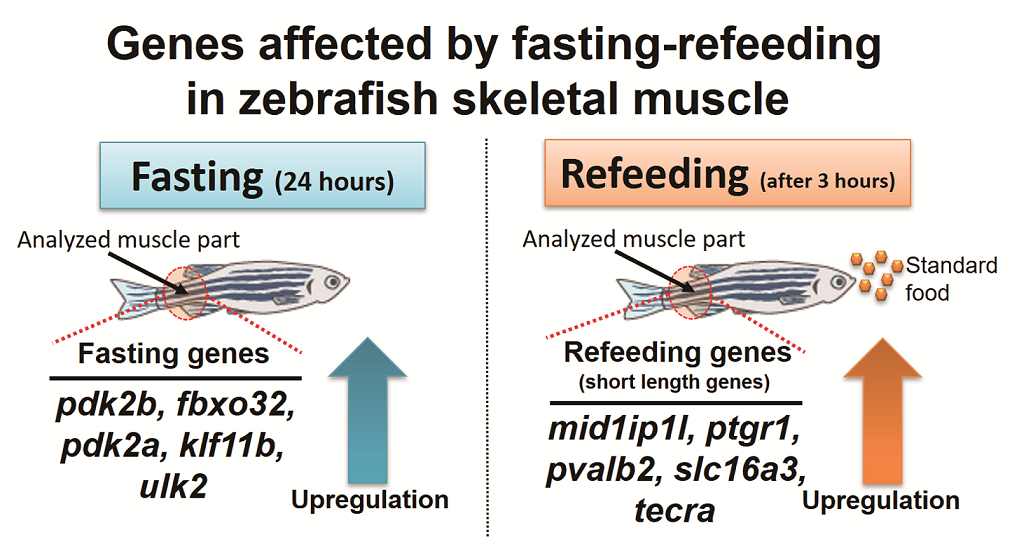
Recently, fasting has been spotlighted from a healthcare perspective. However, the de-tailed biological mechanisms and significance by which the effects of fasting confer health benefits are not yet clear. Due to certain advantages of zebrafish, as a vertebrate model widely utilized in biological studies, we used mRNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis to examine comprehensive gene expression changes in skeletal muscle tissues during fasting-refeeding. Our results produced a novel set of nutrition-related genes under a fasting-refeeding protocol. We found five dramatically upregulated genes in each fasting (for 24 hours) and refeeding (after 3 hours), exhibiting a rapid response to the provided conditional changes. The assessment of the gene length revealed, the gene set whose expression was elevated only after 3 hours of refeeding had a shorter length, suggesting that nutrition-related gene function is associated with gene length. Taken together, our results from bioinformatics analyses provide new insights into biological mechanisms induced by fasting-refeeding conditions within zebrafish skeletal muscle.