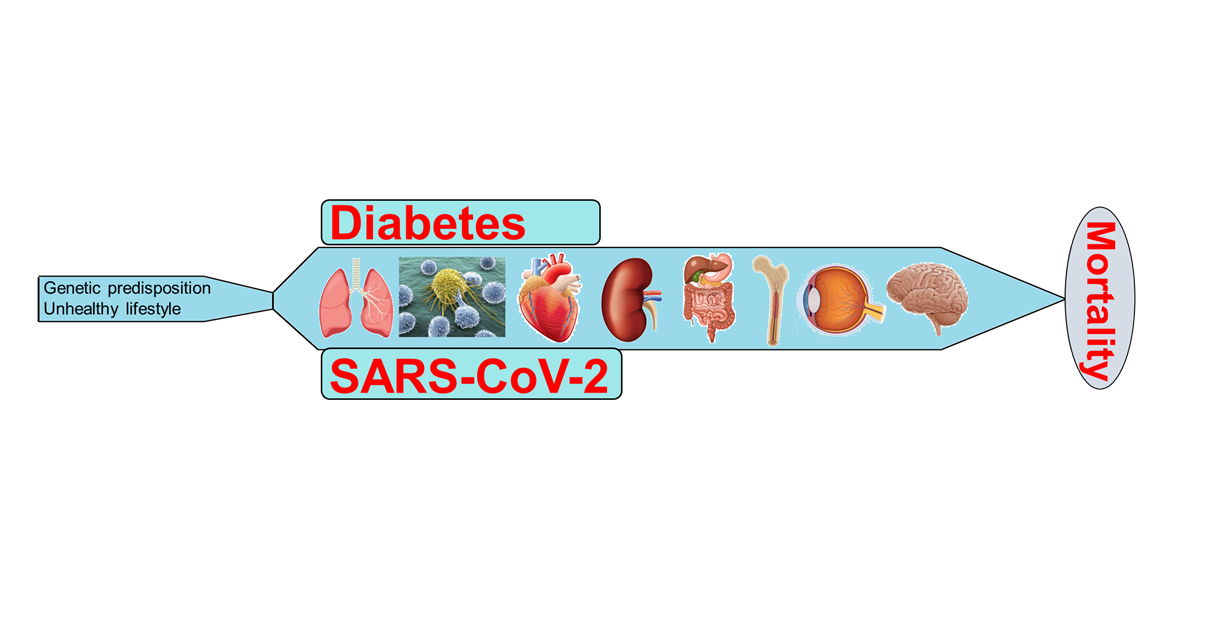
Since the discovery of the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak, a vast majority of studies have been carried out that confirmed the worst outcome of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in people with preexisting health conditions, including diabetes. Both diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 have their independent ability to induce the pathogenesis of multi-system organ dysfunction, while the co-existence of these two culprits can accelerate the pathophysiology and magnify the severity of the diseases. However, the exact pathophysiology of multi-system organ failure in diabetic patients after SARS-CoV-2 infection is still obscure. This review summarized the organ-specific possible molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 and diabetes-induced pathophysiology of several diseases, including the lungs, heart, kidney, brain, eyes, gastrointestinal system, and bones and subsequent manifestation of multi-system organ failure.