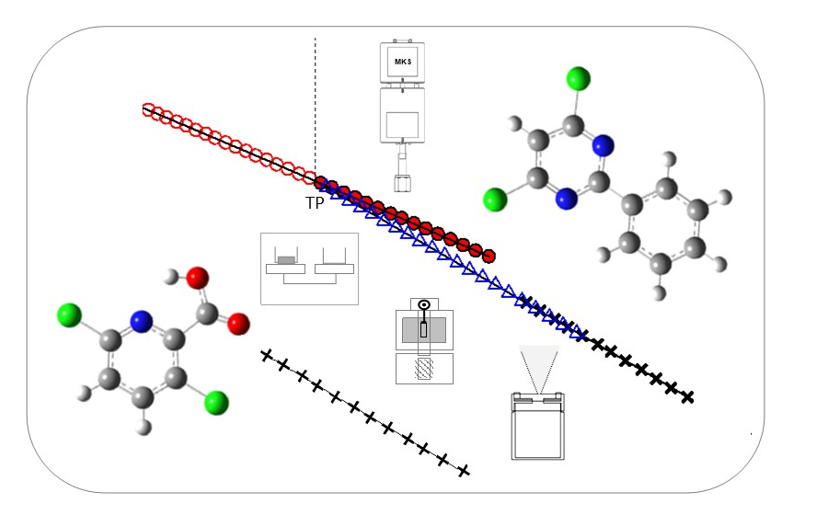
The present work reports an experimental thermodynamic study of two nitrogen heterocyclic organic compounds, fenclorim and clopyralid, that have been used as herbicides. The sublimation vapor pressures of fenclorim (4,6-dichloro-2-phenylpyrimidine) and of clopyralid (3,6-dichloro-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid) were measured, at different temperatures, using a Knudsen mass-loss effusion technique. The vapor pressures of both crystalline and liquid (including supercooled liquid) phases of fenclorim were also determined using a static method based on capacitance diaphragm manometers. The experimental results enabled accurate determination of the standard molar enthalpies, entropies and Gibbs energies of sublimation for both compounds and of vaporization for fenclorim, allowing a phase diagram representation of the (p,T) results, in the neighborhood of the triple point of this compound. The temperatures and molar enthalpies of fusion of the two compounds studied were determined using differential scanning calorimetry. The standard isobaric molar heat capacities of the two crystalline compounds were determined at 298.15 K, using drop calorimetry. The gas phase thermodynamic properties of the two compounds were estimated through ab initio calculations, at the G3(MP2)//B3LYP level, and their thermodynamic stability was evaluated in the gaseous and crystalline phases, considering the calculated values of the standard Gibbs energies of formation, at 298.15 K.