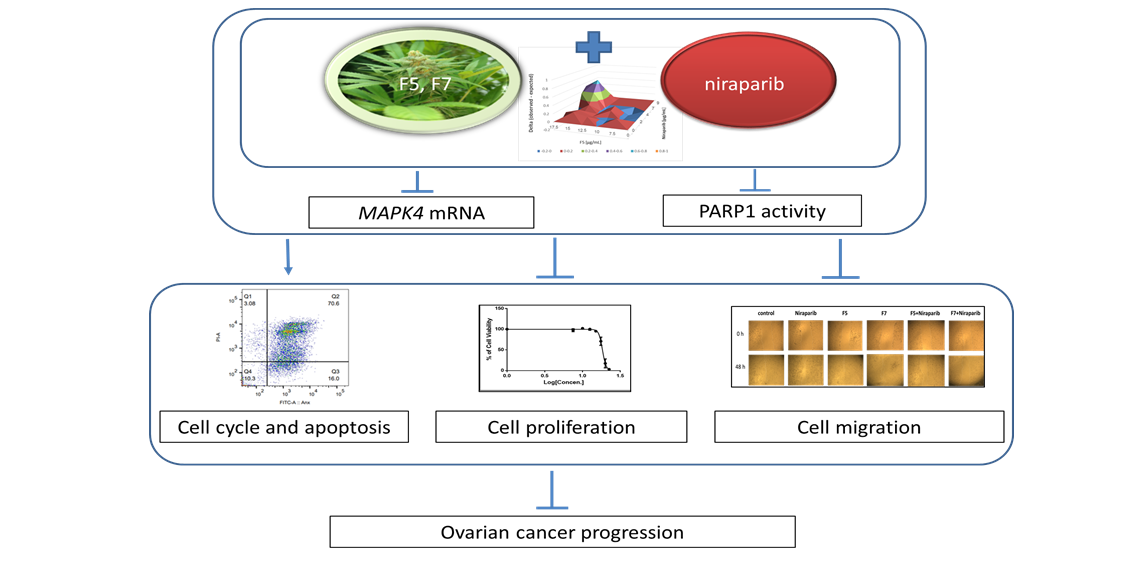
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy. Cannabis sativa is being used to treat different medical conditions. We sought to examine the effectiveness of combinations of cannabis compounds against OC. Cytotoxic activity was determined by XTT assay on HTB75 and HTB161 cell lines. Apoptosis and cell cycle were determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Gene expression was determined by quantitative PCR. The two most active fractions, F5 and F7, from a high Δ9–tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) cannabis strain extract and their standard mix (SM) showed cytotoxic activity against OC cells. The most effective phytocannabinoid combination was THC+cannabichromene (CBC)+cannabigerol (CBG). F5, F7 and SM affected cell cycle, led to cell apoptosis and to a marked reduction in cell migration. Moreover, these fractions act in synergy with niraparib, and were ~50 fold more cytotoxic to OC cells than to normal keratenocytes. Niraparib+F7 treatment was effective on OC patient's cells. F7 and the niraparin+fraction (F5 and F7) treatments reduced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 4 (MAPK4) gene expression; this reduction may act in synergy with the niraparib inhibition of Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) activity. Combinations of cannabis compounds and niraparib should be examined for efficacy in pre-clinical studies and clinical trials.