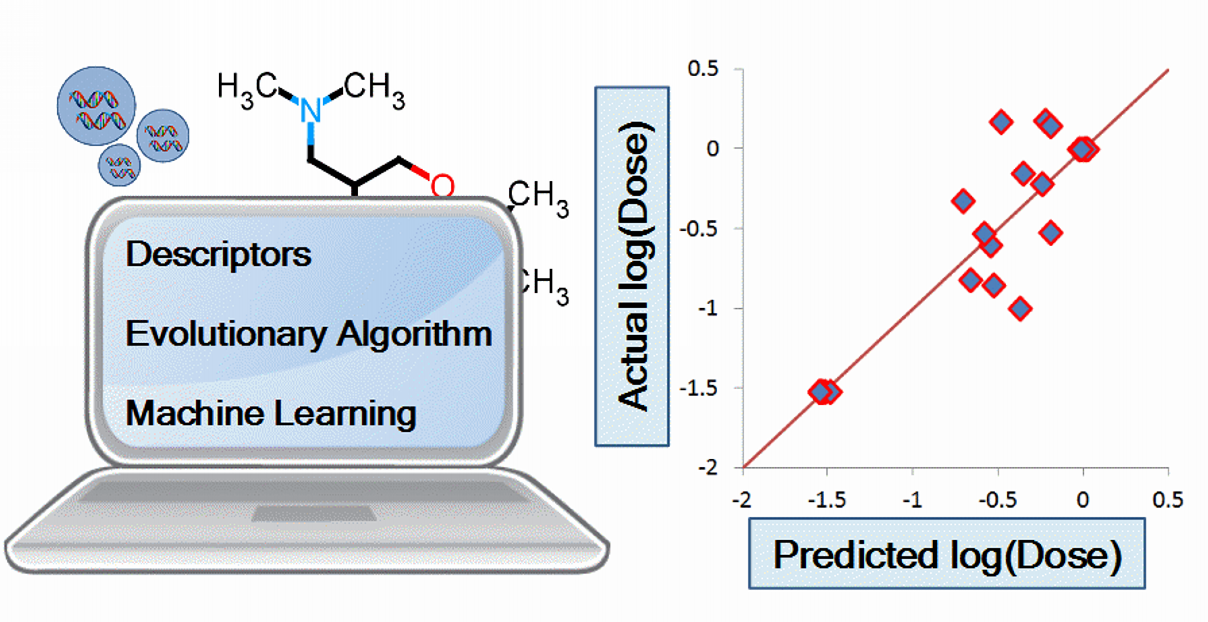
In silico prediction of the in vivo efficacy of siRNA ionizable-lipid nanoparticles is desirable yet never achieved before. This study aims to computationally predict siRNA nanoparticles in vivo efficacy, which saves time and resources. A data set containing 120 entries was prepared by combining molecular descriptors of the ionizable lipids together with two nanoparticles formulation characteristics. Input descriptor combinations were selected by an evolutionary algorithm. Artificial neural networks, support vector machines and partial least squares regression were used for QSAR modeling. Depending on how the data set is split, two training sets and two external validation sets were prepared. Training and validation sets contained 90 and 30 entries respectively. The results showed the successful predictions of validation set log(dose) with R2val = 0.86 – 0.89 and 0.75 – 80 for validation sets one and two respectively. Artificial neural networks resulted in the best R2val for both validation sets. For predictions that have high bias, improvement of R2val from 0.47 to 0.96 was achieved by selecting the training set lipids lying within the applicability domain. In conclusion, in vivo performance of siRNA nanoparticles was successfully predicted by combining cheminformatics with machine learning techniques.