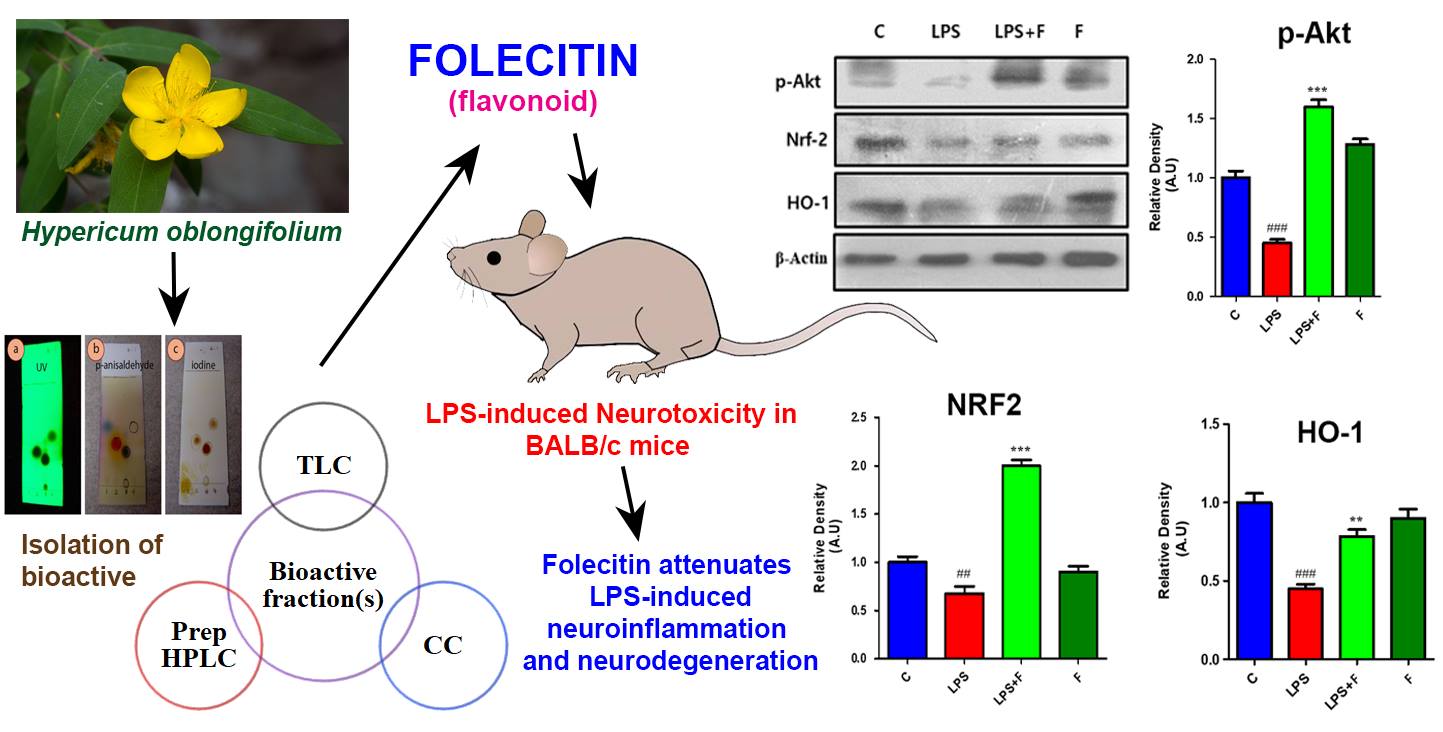
Neurological disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease, are commonly associated with persistent neuro-inflammation, and there is an urgent need to discover new therapeutic agents that may target the various pathways involved in neurodegeneration. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic potential of folecitin, a flavonoid isolated from Hypericum oblongifolium, against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress associated with neurodegeneration, amyloidogenic Aβ production pathway, and memory dysfunction in mice. LPS was administered i.p. at 250 µg/kg/day for 3 weeks, followed by the administration of folecitin at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day for the last two weeks. A Western blot technique was used to assess the expression of different proteins involved in oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and neuronal synapse. Results indicated that folecitin significantly reduced LPS-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration, including the expression of BAX, Caspase-3, and PARP-1 proteins, inhibited BACE1, and the amyloidogenic Aβ production pathway. Folecitin improved both pre- and post-neuronal synapse, as well as memory dysfunction. Furthermore, folecitin significantly activated endogenous antioxidant proteins such as Nrf-2 and HO-1 via stimulating the phosphorylation of Akt proteins. These findings suggest that folecitin may be a suitable lead to design new drugs for neurotoxin-triggered neurodegenerative disorders.