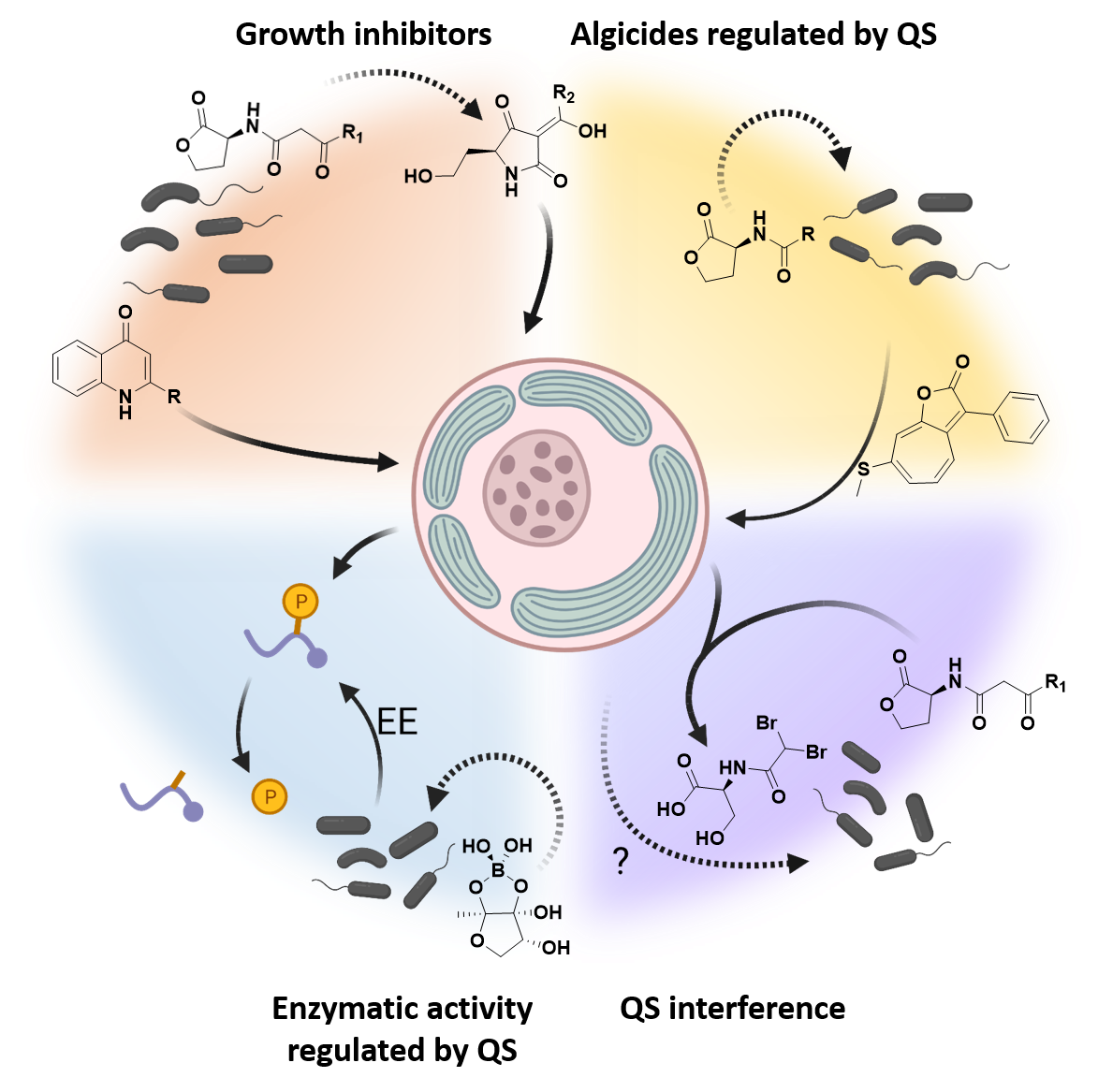
Quorum sensing (QS) describes a process by which bacteria can sense the local cell density of their own species, thus enabling them to coordinate gene expression and physiological processes on a community-wide scale. Small molecules called autoinducers or QS signals, which act as intraspecies signals, mediate quorum sensing. As our knowledge of QS has progressed, so too has our understanding of the structural diversity of QS signals, along with the diversity of bacteria conducting QS and the range of ecosystems in which QS takes place. It is now also clear that QS signals are more than just intraspecies signals. QS signals mediate interactions between species of prokaryotes, and between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In recent years, our understanding of QS signals as mediators of algae–bacteria interactions has advanced such that we are beginning to develop a mechanistic understanding of their effects. This review will summarize the recent efforts to understand how different classes of QS signals contribute to the interactions between planktonic microalgae and bacteria in our oceans, primarily N-acyl-homoserine lactones, their degradation products tetramic acids, and 2-alkyl-4-quinolones. In particular, this review will discuss the ways in which QS signals alter microalgae growth and metabolism, namely as direct effectors of photosynthesis, regulators of the cell cycle, and as modulators of other algicidal mechanisms. Furthermore, the contribution of QS signals to nutrient acquisition is discussed, and finally how microalgae can modulate these small molecules to dampen their effects.