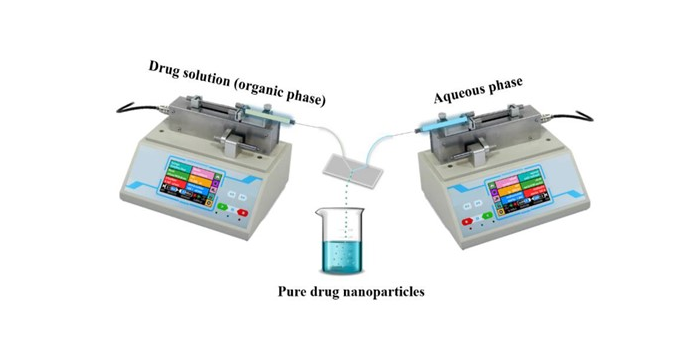
Nanoprecipitation by liquid anti-solvent precipitation is one of the most versatile methods to produce pure drug nanoparticles (PDNPs) owing to the ability to optimize the properties of the product. Nevertheless, nanoprecipitation shows broad particle size distribution and low physical stability, leading to high batch-to-batch variability and challenging the bench-to-bedside translation. Microfluidics has emerged as a powerful tool to produce PDNPs in a simple, reproducible, and cost-effective manner with excellent control over NP size. In this work, we designed and fabricated T- and Y-shaped Si-made microfluidics device and used it to produce pure NPs of three kinase inhibitors of different lipophilicity and water-solubility, namely imatinib, dasatinib and tofacitinib, without the use of colloidal stabilizers. PDNPs display sizes in the 90-350 nm range (dynamic light scattering) and a rounded shape (high-resolution scanning electron microscopy). Analysis by X-rays diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry confirmed that this method results in highly amorphous NPs. In addition, we show that the flow rate of solvent, the anti-solvent, and the channel geometry of the device play a key role in the size of the generated NPs.