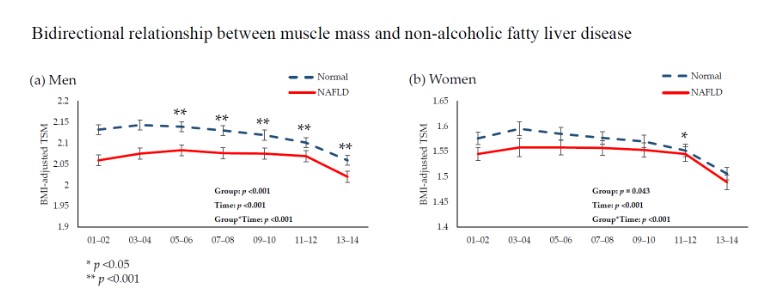
Although sarcopenia is known to be a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), whether NAFLD is a risk factor for the development of sarcopenia is not clear. We investigated bidirectional relationships between NAFLD and low skeletal muscle mass index (LSMI) using three different datasets. Participants were classified into LSMI and normal groups. LSMI was defined as a body mass index (BMI)-adjusted appendicular skeletal muscle mass <0.789 in men and <0.512 in women or as the sex-specific lowest quintile of BMI-adjusted total skeletal muscle mass. NAFLD was determined according to NAFLD liver fat score or abdominal ultrasonography. The NAFLD groups showed a higher hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for LSMI than the normal groups (HRs=1.213, 95% CIs=1.050–1.402). The LSMI groups also showed a higher HRs with 95% CIs for NAFLD than normal groups (HRs=1.564, 95% CIs=1.378–1.775). Participants with NAFLD had consistently less skeletal muscle mass over 12 years of follow-up. In conclusion, LSMI and NAFLD showed a bidirectional relationship. Maintaining muscle mass should be emphasized in the management of NAFLD.