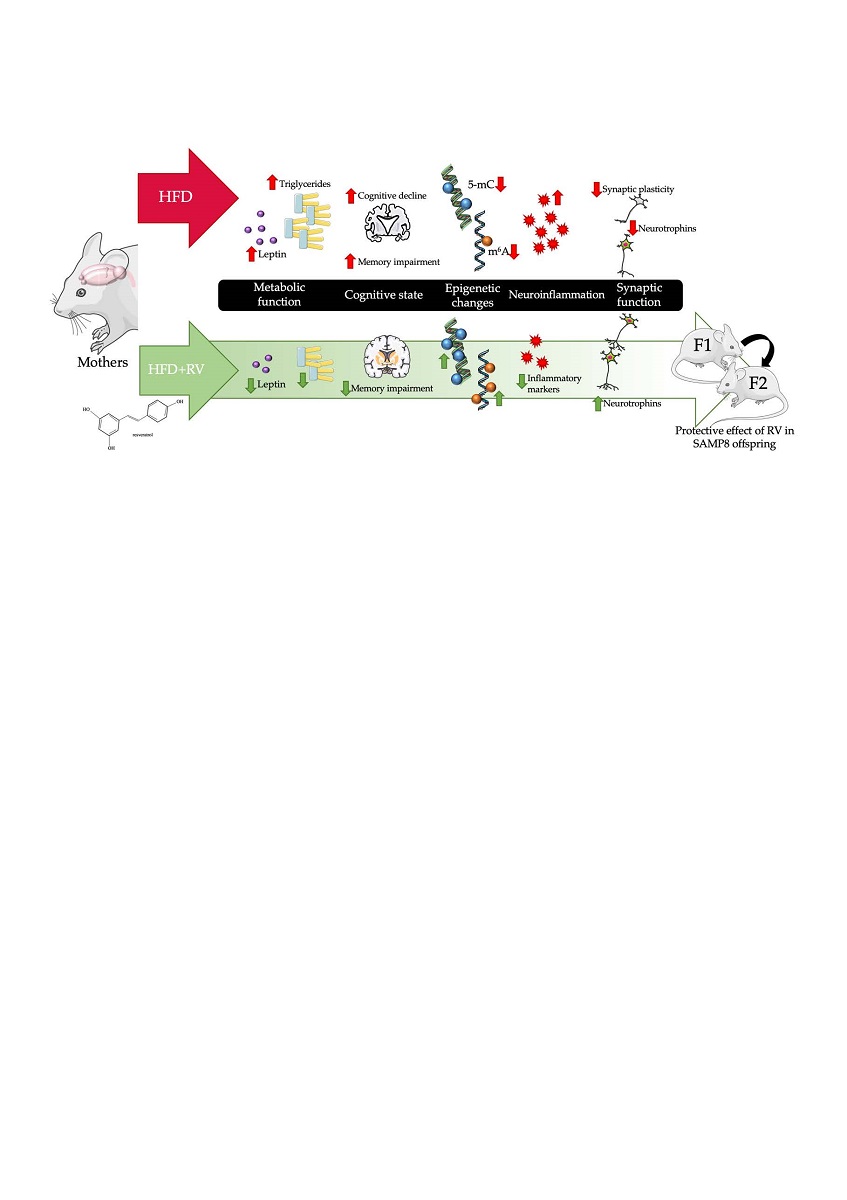
Environmental factors as maternal high-fat diet (HFD) intake can increase the risk of age-related cognitive decline in adult offspring. The epigenetic mechanisms are a possible link between diet effect and neurodegeneration across generations. Here, we found a significant decrease in triglyceride levels in a high-fat diet with resveratrol HFD+RV group and the offspring. Firstly, we obtained better cognitive performance in HFD+RV groups and their offspring. Molecularly, a significant increase in 5-mC levels, as well as increased gene expression of Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a in HFD+RV F1 group, were found. Furthermore, a significantly increased of m6A levels in HFD+RV F1 were found, and there were changes in gene expression of its enzymes (Mettl3 and Fto). Moreover, we found a decrease in gene expression levels of pro-inflammatory markers such as Il1-β, Il-6, Tnf-α, Cxcl-10, Mcp-1 and Tgf-β1 in HFD+RV and HFD+RV F1 groups. Moreover, there was increased gene expression of neurotrophins such as Ngf and Nt3 and its receptors TrkA and TrkB. Likewise, an increase in protein levels of BDNF and p-Akt in HFD+RV F1 was found. These results suggest that maternal RV supplementation under HFD intake prevents cognitive decline in SAMP8 adult offspring, promoting a reduction in triglycerides and leptin plasma levels, changes in the pro-inflammatory profile, restoring the epigenetic landscape as well as synaptic plasticity.