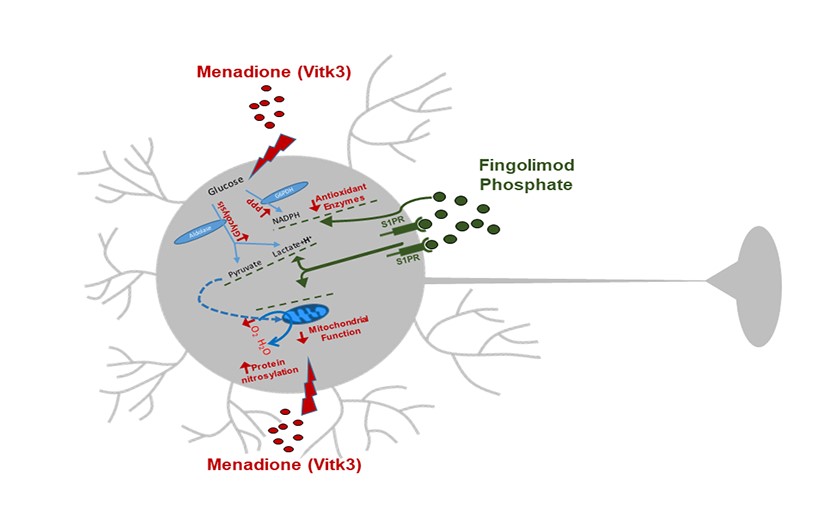
Imbalance in the oxidative status in neurons, along with mitochondrial damage, are common characteristics in some neurodegenerative diseases. The maintenance in energy production is crucial to face and recover from the oxidative damage and the coexistence of different sources of energy production, such as mitochondrial and glycolytic ATP, allows faster adaptative mechanisms to situations of high energy demand and may help in the maintenance of neuronal function in stress situations. Fingolimod phosphate is a drug with neuroprotective and antioxidant actions, used in the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. This work has been performed in a model of oxidative damage on neuronal cell cultures exposed to menadione, in presence or absence of fingolimod phosphate. We have studied the mitochondrial function and several pathways related with glucose metabolism, including oxidative, glycolytic and pentose phosphate in neuronal cells cultures. Our results showed a beneficial effect on neuronal survival probably based in the recovery of all, oxidative balance, glycolysis and pentose phosphate, promoted by fingolimod phosphate. These effects are mediated, at least in part by the interaction with its specific receptor. These actions would make this drug a potential tool to the treatment of neurodegenerative processes, either to slow progression or alleviate symptoms.