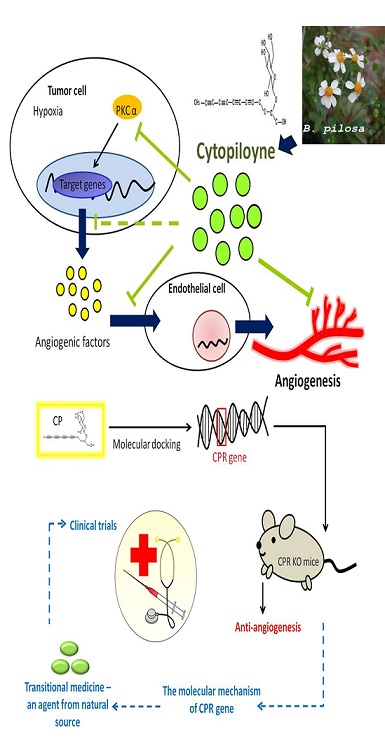
Simply Summary: Translation of new cancer treatments between pets and human were noticed in comparative oncological investigation. The current study aims at evaluating a polyacetylenic glucoside purified from an edible herb, Bidens pilosa, to present its anti-angiogenic effects. We innovatively find this polyacetylenic glucoside, cytopiloyne, shows anti-angiogenic effect on different in vitro assays and various in vivo animal models under hypoxia. Based on results of this study, cytopiloyne will be a prospective herb angiogenesis inhibitor candidate to control animal or human cancer formation as adjuvant therapy. Abstract: Anti-angiogenesis is a pivotal combination treatment approach in cancer therapy but rare using on companion animals. This study aimed at evaluating the anti-angiogenic effect of a B. pilosa sourced polyacetylenic glucoside, cytopiloyne, on various in vitro assays and in vivo models. We provide evidences showing that CP has anti-angiogenic activities. Firstly, CP inhibited sponge/ Matrigel plug angiogenesis from tumor cells and decreased the survival of tumor cells on hypoxic conditions. Besides, CP declined PKCα protein expression which a protein leads to the growth and spread of tumors under hypoxia. Secondly, inhibitory effects of CP on endothelial angiogenesis were confirmed by chick chorioallantoic membrane assay, tube formation of SVEC4-10 cells and Matrigel plug assay. A dose-dependent CP treatment inhibited 4T1 cells proliferation under hypoxia and migration. It also suppresses VEGF transcription under hypoxia. Finally, we found that CP decreased PDIA4, a novel regulator of cancer growth, expression in endothelial cells. This effect was confirmed by PDIA4 knockout mice with reduced angiogenesis in Matrigel plug assay. Taken together, these results suggest that CP might act as a promising anti-angiogenic herbal agent candidate to be used in animal hypervascularized cancer of veterinary medicine or in combination to control human cancer as adjuvant therapy.