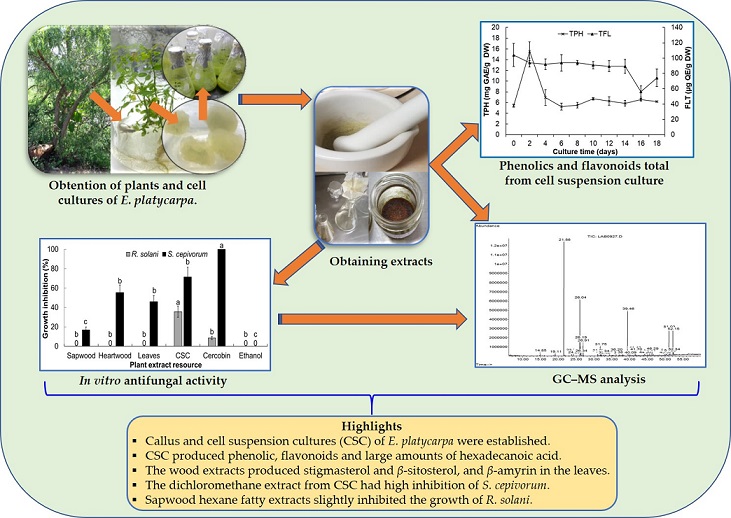
Eysenhardtia platycarpa (Fabaceae) is a medicinal plant used in México and it lacks biotechnological studies for its use. The aim of this work was to establish a cell suspension cultures (CSC) of E. platycarpa, determine the phytochemical profile, and evaluate its antifungal activity. Friable callus and CSC were established with 2 mg/L 1-naphthaleneacetic acid plus 0.1 mg/L kinetin. The highest total phenolics of CSC was 15.6 mg GAE/g dry weight and the total flavonoids content ranged from 56.2 to 104.1 µg QE/g dry weight. CG‒MS analysis showed that the dichloromethane extracts of CSC, sapwood and heartwood have a high amount of hexadecanoic acid (22.3 ‒ 35.3 %) and steroids (13.5 ‒ 14.7%). Heartwood and sapwood defatted hexane extracts have the highest amount of stigmasterol (≈ 23.4%) and β-sitosterol (≈ 43%), and leaf extracts presented β-amyrin (16.3%). Methanolic leaves extracts showed mostly sugars and some polyols, mainly D-pinitol (74.3%). Dichloromethane and fatty hexane extracts of CSC exhibited the percentages inhibition higher for Sclerotium cepivorum with 71.5 and 62.0%, respectively. The maximum inhibition for Rhizoctonia solani was with fatty hexane extracts of the sapwood (51.4%). Our study suggest that CSC extracts could be used as a possible complementary alternative to synthetic fungicides.