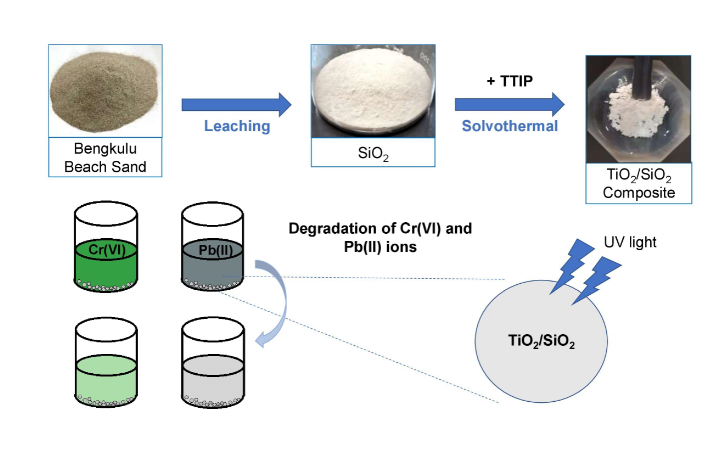
Heavy metals are non-biodegradable and have a high toxicity effect to living things which makes their presence in the environment extremely dangerous. The method of handling heavy metals waste by photocatalysis techniques using TiO2/SiO2 composite showed a good performance in reducing harmful pollutants. In this study, SiO2 from Bengkulu beach sand was used as a support material for TiO2 photocatalyst to reduce Cr(VI) and Pb(II) concentrations. SiO2 was obtained through leaching techniques using NaOH as a solvent. The TiO2/SiO2 composite photocatalyst were synthesized using a solvothermal method at 130 °C and then characterized using XRD, FTIR, SEM and PSA. Based on the XRD diffractogram, the synthesized TiO2 showed the anatase structure while the SiO2 showed the amorphous structure. Ti-O-Si bond is defined in the IR spectra, which indicates that the relationship between TiO2 and SiO2 is a chemical interaction. The results of SEM and PSA characterizations show agglomerated spherical (round) particles with a mean particle size of 616.9 nm. The TiO2/SiO2 composite of 7:1 ratio showed the highest photocatalytic activity after 180 minutes of UV irradiation, with a concentration-decrease percentage of 93.77% and 93.55% for for Cr(VI) and Pb(II), respectively.