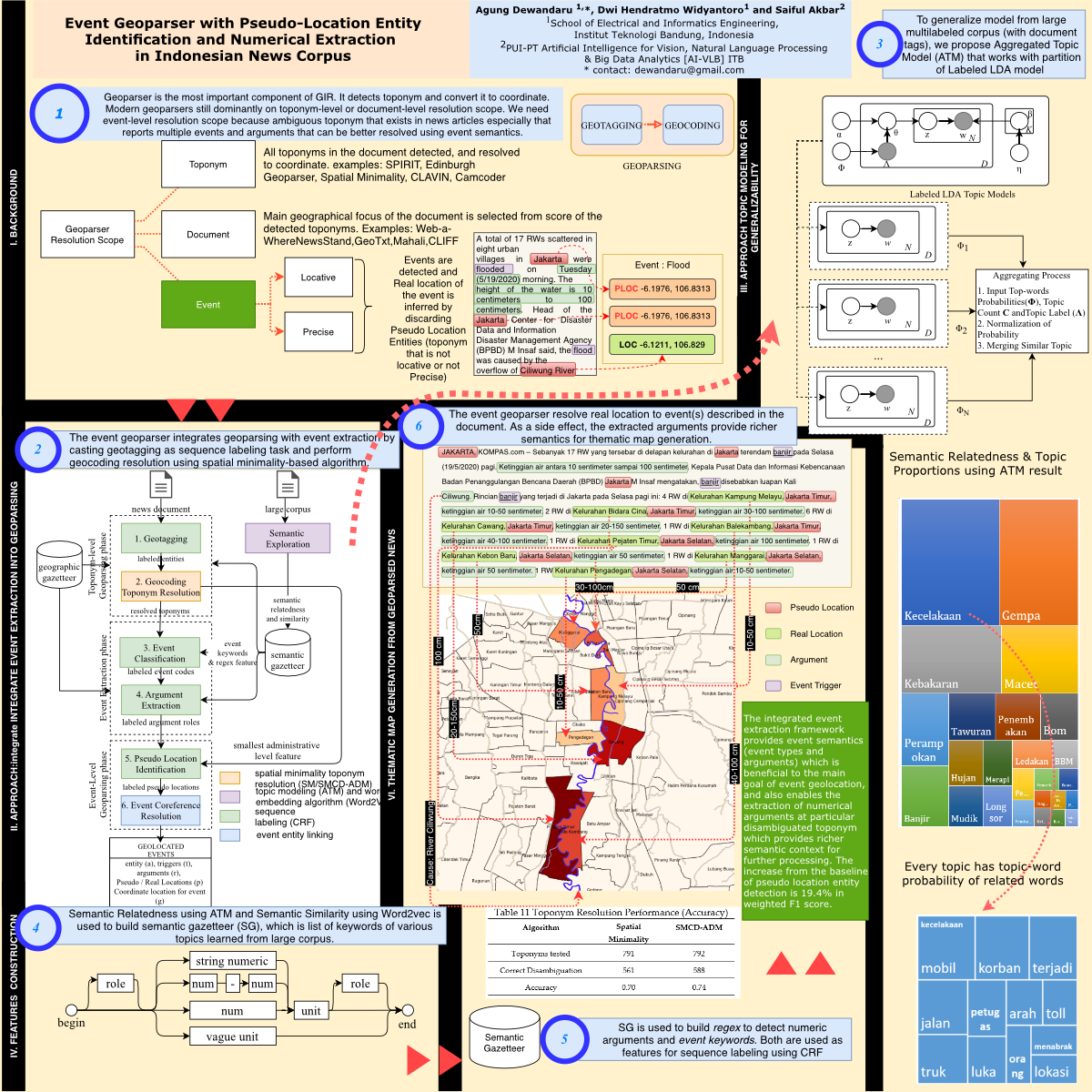
One of the most important component of a Geographic Information Retrieval (GIR) is the geoparser, which performs toponym recognition, disambiguation, and geographic coordinate resolution from unstructured text domain. However, news articles which report several events across many place references mentioned in the document is not yet adequately modeled by regular geoparser types where the scope of resolution is either on toponym-level or document-level. The capacity to detect multiple events, geolocate its true locations and coordinates along with their numerical arguments are still missing from modern geoparsers, much less in Indonesian news corpora domain. We propose a novel type event geoparser which integrates an ACE-based event extraction model and provides precise event-level scope resolution. The geoparser casts the geotagging and event extraction as sequence labeling and uses Conditional Random Field with keywords feature obtained using Aggregated Topic Model as a semantic exploration from large corpus, which eventually increases the generalizability of the model. The geoparser also use Smallest Administrative Level feature along with Spatial Minimality-derived algorithm to improve the identification of Pseudo-location entities, resulting 19.4% increase for weighted F1 score. As a side effect of event extraction, the geoparser also extracts various numerical arguments and able to generate thematic choropleth map from a single news story.