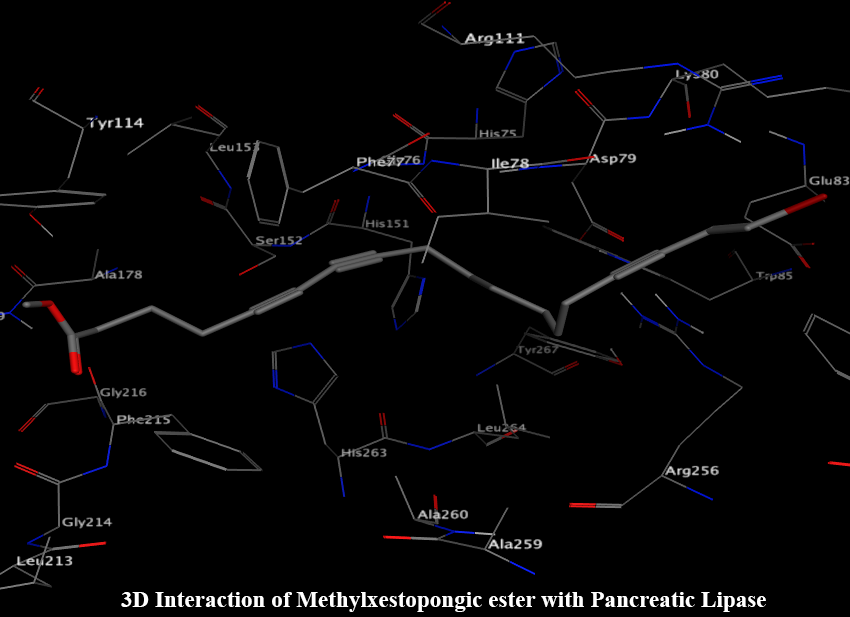
Metabolic enzymes are often targeted for drug development programs of metabolic diseases such as diabetes and its complications. Many secondary metabolites isolated from natural products have shown therapeutic action against these enzymes. However, some commercially available synthetic drugs have shown unfriendly impacts with various side effects. Thus, this research has focused on a comprehensive study of secondary metabolites showing better inhibitory activities towards metabolic enzymes such as α-amylase, α-glucosidase, aldose reductase, and lipase. Further receptor-based virtual screening was performed against the various secondary metabolites database designed in-silico. Using Gold combined with subsequent post-docking analyses, the score was obtained as methyl xestospongic ester (Gold score 65.83), 2,″4″-O-diacetylquercitrin (Gold score 65.15), kaempferol-3-O-neohesperidoside (Gold score 53.37) and isosalvianolic acid C methyl ester (Gold score 53.44) for lipase, aldol reductase, α-amylase, and α-glucosidase, respectively. Besides, vitexin and isovitexin for α-amylase; N-trans-Caffeoyl-tyramin for α-glucosidase; purpurolide F and schaftoside for lipase; acteoside and orientin for aldose reductase could be potential drugs for respective enzymes based on in-silico analyses, supported by experimental IC50 values reported. They could bind to the competitive sites of the various targets of metabolic enzymes, and finally, toxicity analysis using ProTox-II was also performed.