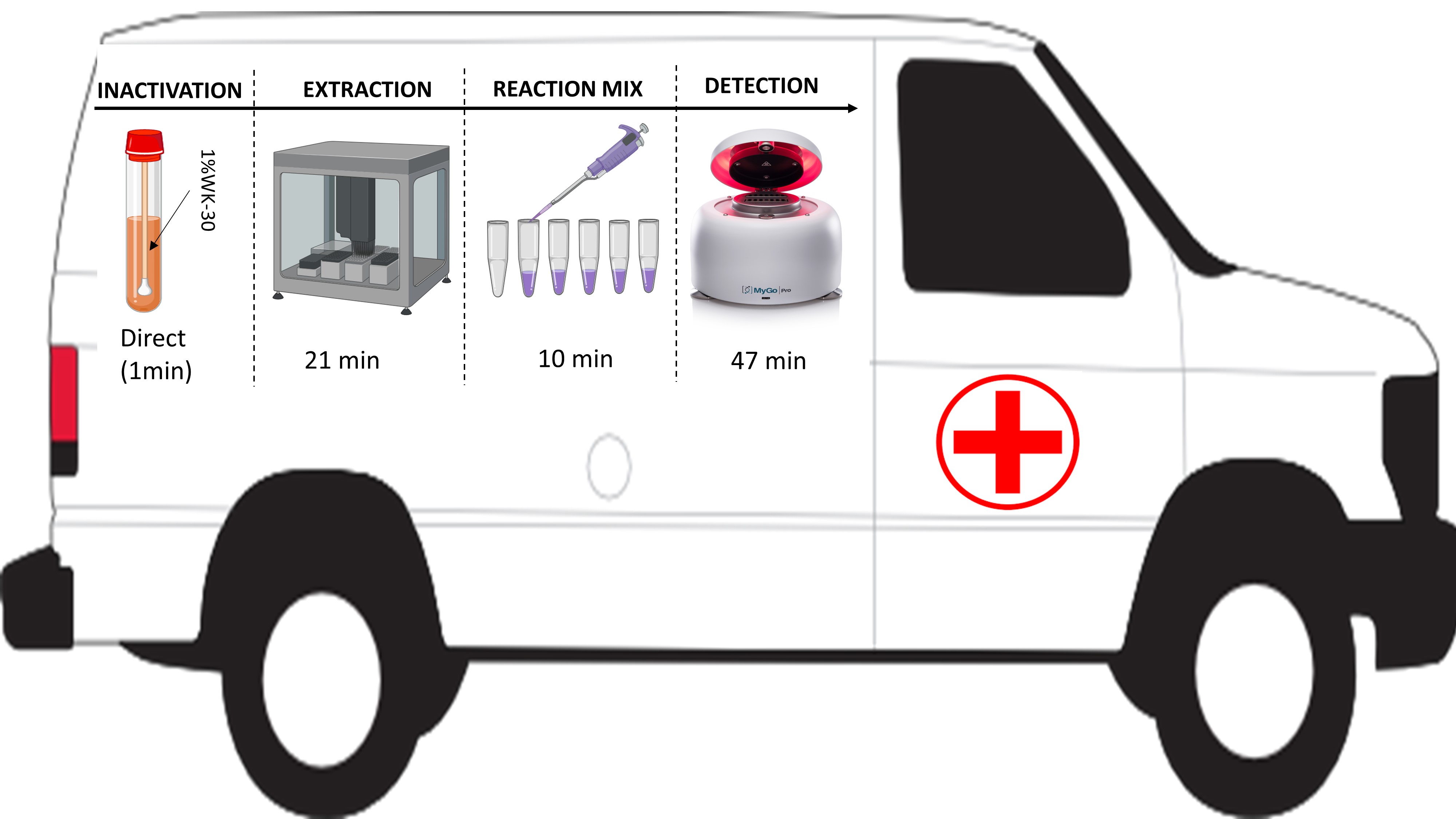
Outbreaks of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been recorded in different countries across the globe. The virus is highly contagious, hence early detection, isolation, and quarantine of infected patients will play an important role in containing the viral spread. Diagnosis in a mobile lab can aid to find infected patients in time. Here, we develop a field-deployable diagnostic workflow that can reliably detect COVID-19. Instruments used in this workflow could easily fit in a mobile cabin hospital and also be installed in the community. Different steps from sample inactivation to detection were optimized to find the fastest steps and portable instruments in detection of COVID-19. Each step was compared to that of the normal laboratory diagnosis set-up. From the results, our proposed workflow (80 min) was two times faster compared to that of the normal laboratory workflow (183 min) and a maximum of 32 samples could be detected at each run. Additionally, we showed that using 1% Rewocid WK-30 could inactivate the novel coronavirus directly without affecting the overall detection results. Comparison of our workflow using an in-house assay to that of a commercially acquired assay produced highly reliable results. From the 250 hospital samples tested, there was a high concordance 247/250 (98.8%) between the two assays. The in-house assay sensitivity and specificity were 116/116 (100%) and 131/134 (97.8%) compared to that of the commercial assay. Based on these results, we believe that our workflow is fast, reliable, adaptable and most importantly, field deployable.