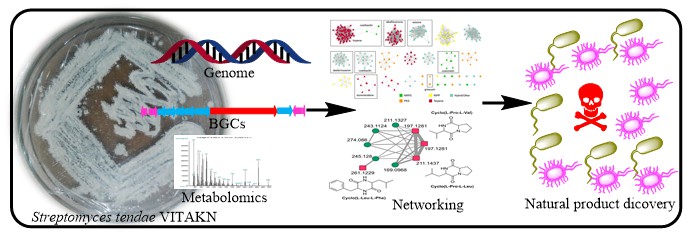
Streptomyces, being one of the most promising genera due to its ability to synthesize a variety of bioactive secondary metabolites of pharmaceutical interest, here studied in relation to its genomic and metabolomic potential. Coinciding with the increase in sequenced data, mining of bacterial genomes for biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) has become a routine component of natural product discovery. Herein, we describe the isolation and characterization of a Streptomyces tendae VITAKN with quorum sensing inhibitory activity (QSI) that was isolated from southern coastal parts of India. The nearly complete genome consists of 8,621,231bp with a GC content of 72.2%. Utilizing the BiG-SCAPE-CORASON platform, a sequence similarity network predicted from this strain was evaluated through sequence similarity analysis with the MIBiG database and existing 3,365 BGCs predicted by antiSMASH analysis of publicly available complete Streptomyces genomes. Crude extract analyzed on LC-HRMS/MS and Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) online workflow using dereplication resulted in the identification of cyclic dipeptides (2,5-diketopiperazines, DKPs) in the extract, which are known to possess QSI activity. Our results highlight the potential use of genomic mining coupled with LC-HRMS/MS and bionformatic tools (GNPS) as a potent approach for metabolome studies in discovering novel QSI lead compounds. This study also provides the biosynthetic diversity of these BGCs and an assessment of the predicted chemical space yet to be discovered.