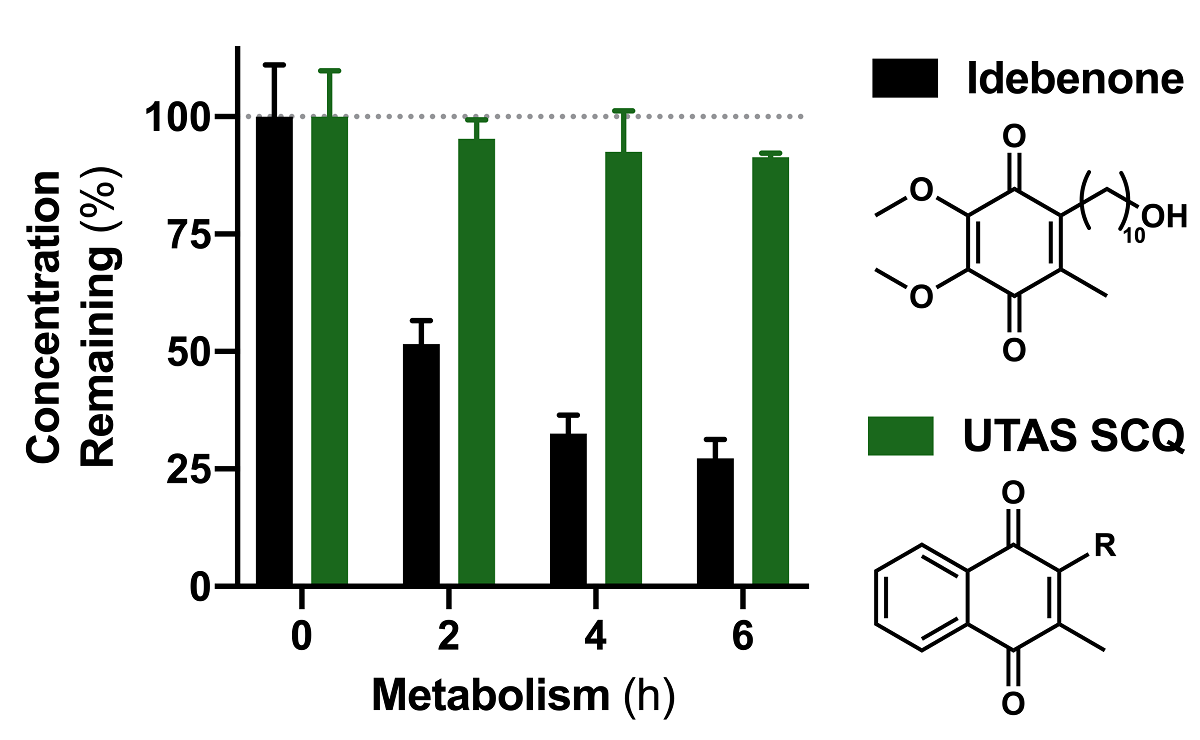
Short chain quinones (SCQs) have been identified as potential drug candidates against mitochondrial dysfunction, which is largely dependent on their reversible redox characteristics of the active quinone core. We recently synthesized a SCQ library of > 148 naphthoquinone derivatives and identified 16 compounds with enhanced cytoprotection compared to the clinically used benzoquinone idebenone. One of the major drawbacks of idebenone is its high metabolic conversion in the liver, which significantly restricts is therapeutic activity. Therefore, this study assessed the metabolic stability of the 16 identified naphthoquinone derivatives 1-16 using hepatocarcinoma cells in combination with an optimized reverse-phase liquid chromatography (RP-LC) method. Most of the derivatives showed significantly better stability than idebenone over 6 hours (p < 0.001). By extending the side-chain of SCQs, increased stability for some compounds was observed. Metabolic conversion from the derivative 3 to 5 and reduced idebenone metabolism in the presence of 5 were also observed. These results highlight the therapeutic potential of naphthoquinone-based SCQs and provide essential insights for future drug design, prodrug therapy and polytherapy, respectively.