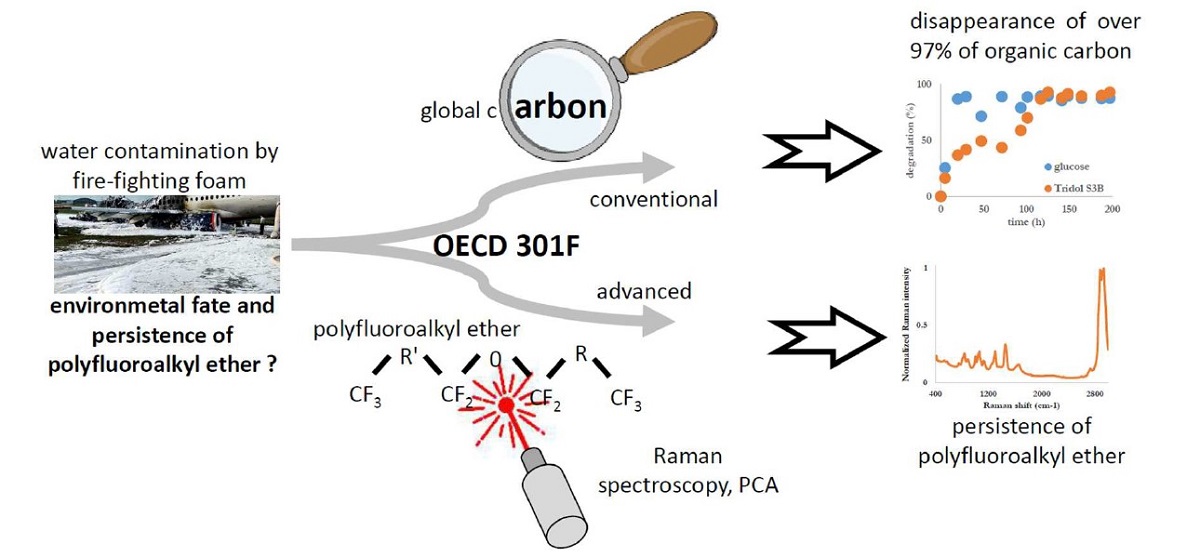
Surfactants based on polyfluoroalky ethers are commonly used in fire-fighting foams on airport platforms, including for training sessions. Because of their persistence into the environment, their toxicity and their bioaccumulation, abnormal amounts can be found in ground and surface water following operations of airport platforms. As many other anthropogenic organic compounds, some concerns raised about their biodegradation. That is why the OECD 301 F protocol was implemented to appreciate the oxygen consumption during the biodegradation of a commercial fire-fighting foam. However, a Raman spectroscopic monitoring of the process was also attached to this experimental procedure to evaluate to what extent a polyfluoroalkyl ether disappeared from the environmental matrix. The relevance of our approach is to use chemometrics, including the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and the Partial Least Square (PLS), in order to monitor the kinetics of the biodegradation reaction of one fire-fighting foam, Tridol S3B, containing a polyfluoroalkyl ether. This study provided a better appreciation of the partial biodegradation of some polyfluoroalkyl ethers by coupling Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics. This will ultimately facilitates the design of a future purification and remediation devices for the airport platforms.