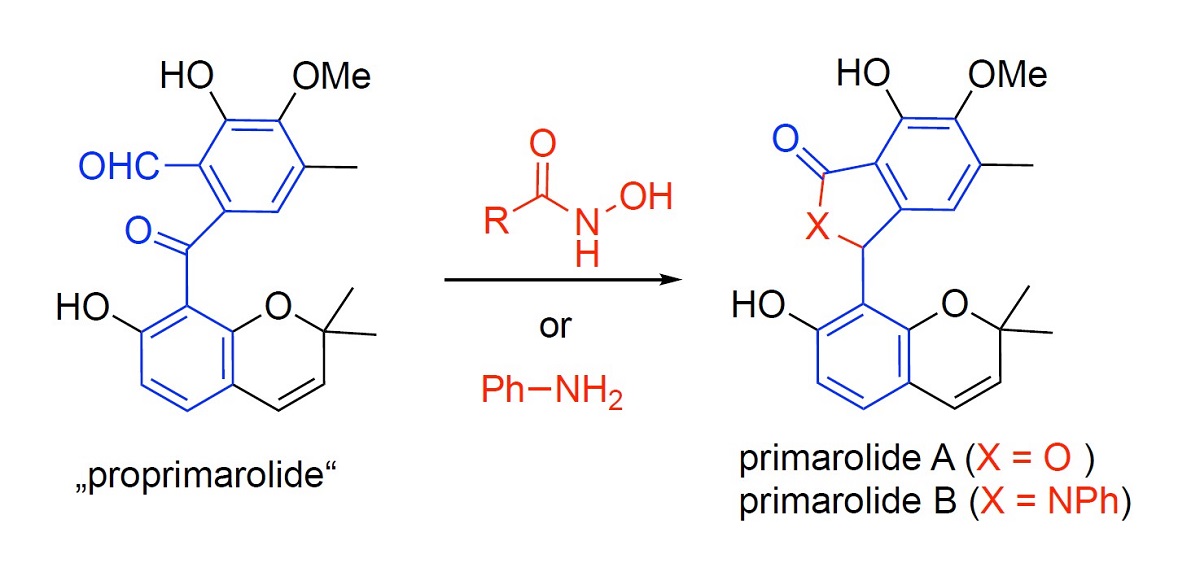
The structures of recently discovered primarolides A and B suggest their non-enzymatic formation from a common 2-formylbenzophenone precursor. This hypothesis is based on the experimentally proven facile conversion of pestalone (also a 2-formyl-benzophenone) either into the isomeric lactone pestalalactone or the structurally related isoindolinone pestalachloride A. In a related fashion, the racemic isoindolinone natural product mariline A is supposed to biosynthetically originate from the corresponding keto-aldehyde and an aniline, as experimentally supported by model studies. Due to the close structural relationship with known systems, it appears highly probable that primarolides A and B were generated under the fermentation conditions from a massarinin-related 2-formylbenzophenone (proprimarolide) by reaction either with aniline or a nucleophilic catalyst, respectively. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), used as an additive during the fermentation, is supposed to act both as a source of aniline and as a nucleophilic catalyst.