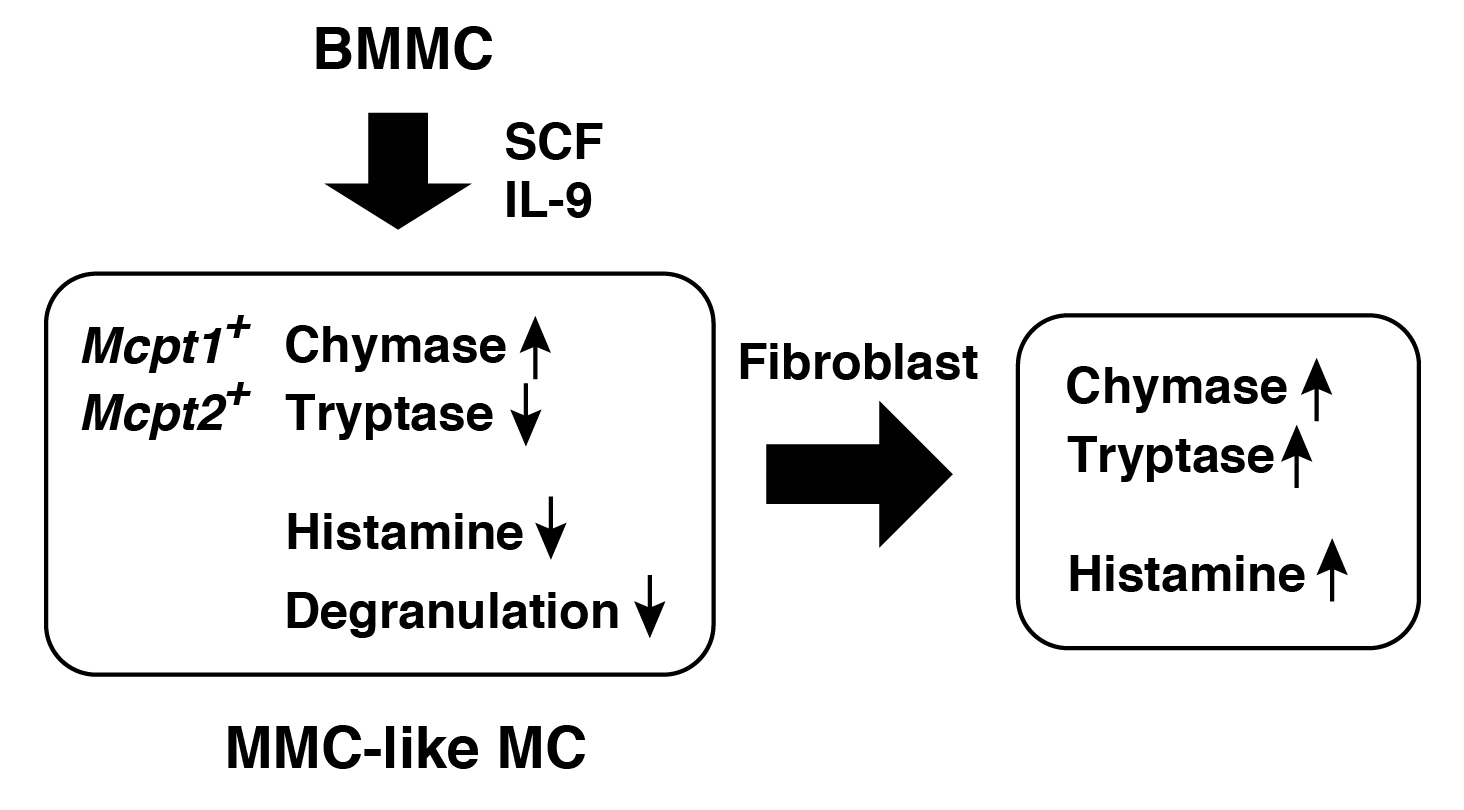
Accumulating evidence suggests that mast cells should play critical roles in disruption and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis, although it remains unknown how they affect local microenvironment. Interleukin-9 (IL-9) was found to play critical roles in intestinal mast cell accumulation induced in various pathological conditions, such as parasite infection and oral allergen-induced anaphylaxis. Newly recruited intestinal mast cells trigger inflammatory responses and damage epithelial integrity through release of a wide variety of mediators including mast cell proteases. We established a novel culture model (mucosal mast cell-like cultured mast cells, MMC-like MCs), in which murine IL-3-dependent bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells (BMMCs) were further cultured in the presence of stem cell factor and IL-9. In MMC-like MCs, drastic up-regulation of Mcpt1 and Mcpt2 was found. Although histamine storage and tryptase activity were significantly downregulated in the presence of SCF and IL-9, it was entirely reversed when mast cells were co-cultured with a murine fibroblastic cell line, Swiss 3T3. MMC-like MCs underwent degranulation upon IgE-mediated antigen stimulation, which was found to less sensitive to lower concentrations of IgE in comparison with BMMCs. This model might be useful for investigation of the spatiotemporal changes of newly recruited intestinal mast cells.