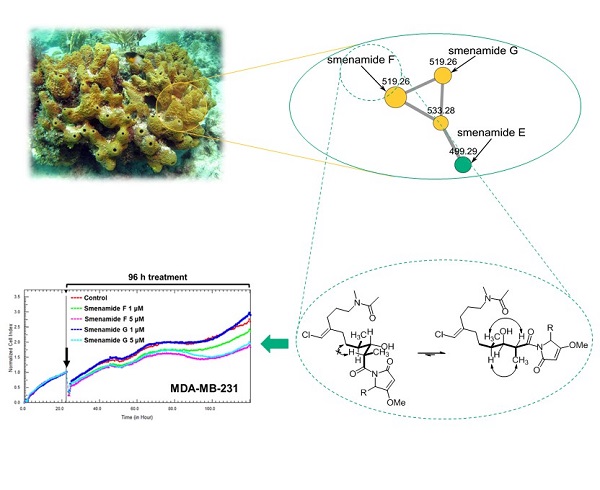
Caribbean sponges of the genus Smenospongia are a prolific source of chlorinated secondary metabolites. The use of molecular networking as a powerful dereplication tool revealed the presence in the metabolome of S. aurea of two new members of the smenamide family, namely smenamide F (1) and G (2). The structure of smenamide F (1) and G (2) was determined by spectroscopic analysis (NMR, MS, ECD). The relative and the absolute configuration at C-13, C-15, and C-16 was determined on the basis of the conformational rigidity of a 1,3-disubstituted alkyl chain system (i.e. the C-12/C-18 segment of compound 1). Smenamide F (1) and G (2) were shown to exert a selective moderate antiproliferative activity against cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231, while being inactive against MG-63.