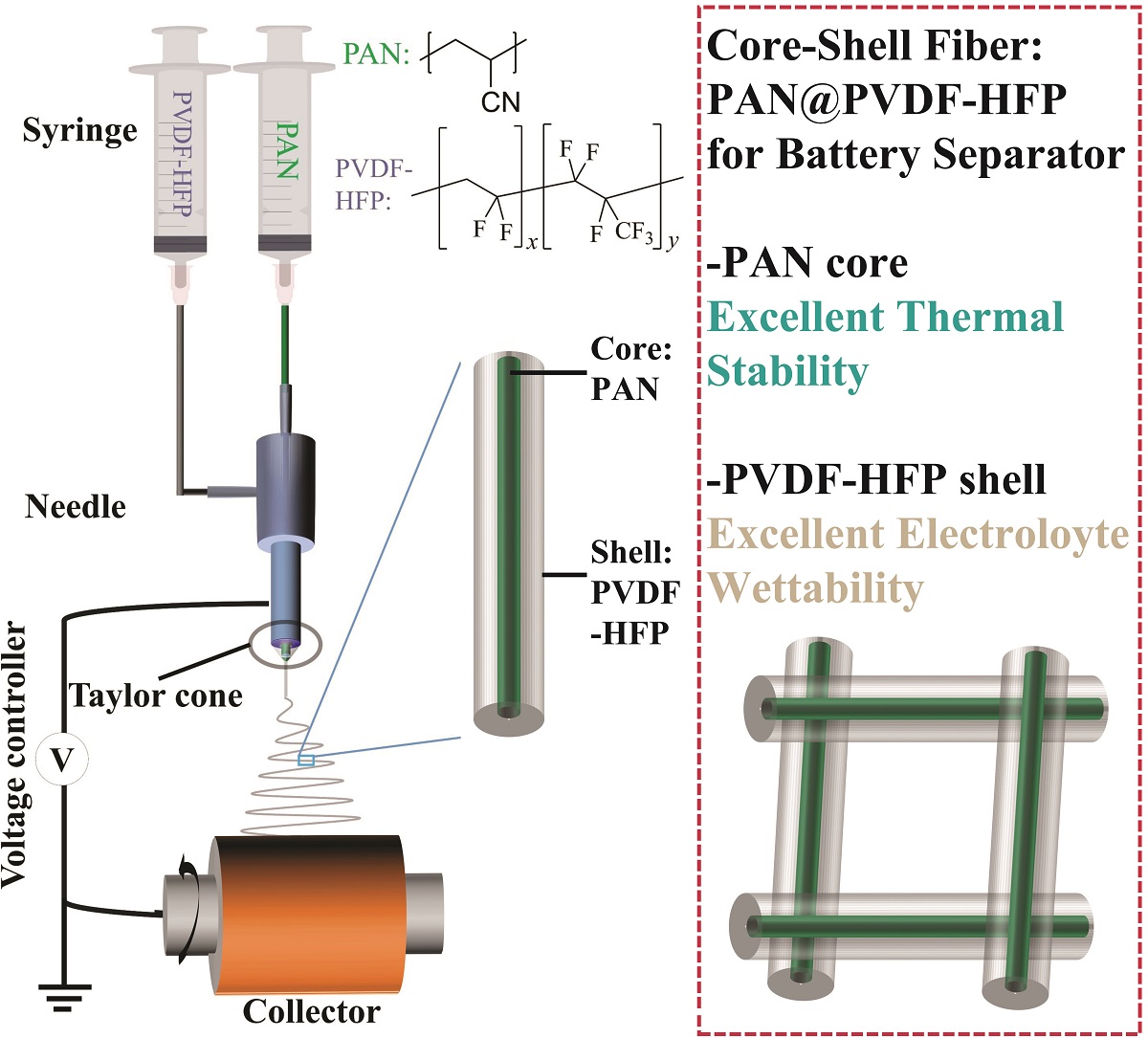
Though the energy density of lithium-ion batteries continues to increase, safety issues related with the internal short-circuit and the resulting combustion of highly flammable electrolyte impede the further development of lithium-ion batteries. It has been well-accepted that a thermal stable separator is important to postpone the entire battery short-circuit and thermal-runaway. Traditional methods to improve the thermal stability of separators includes surface modification and/or developing alternate material systems for separators which may always affect the battery performance negatively. Herein, a thermostable and shrink-free separator with little compromise in battery performance is prepared by coaxial electrospinning and tested. The separator consists of core-shell fiber networks where poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) layer serves as shell and polyacrylonitrile (PAN) as the core. This core-shell fiber network exhibits little or even no shrinking/melting at elevated temperature over 250 °C. Meanwhile, it shows excellent electrolyte wettability and can take large amount of liquid electrolyte three times more than that of conventional Celgard 2400 separator. In addition, the half-cell using LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 as cathode and the aforementioned electrospun core-shell fiber network as separator demonstrates superior electrochemical behavior, stably cycling for 200 cycles at 1 C with a reversible capacity of 130 mAh g-1 and little capacity decay.