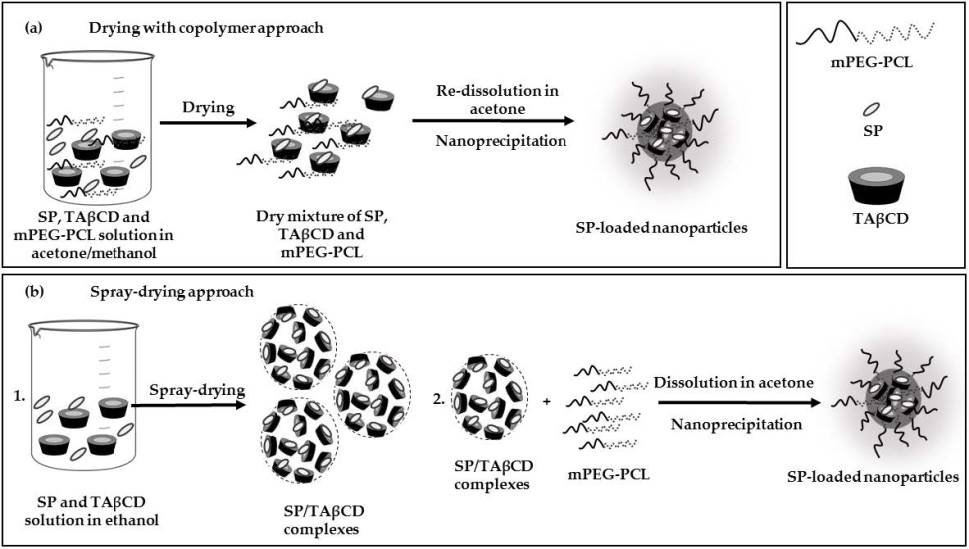
In this work, we investigated for the first time the complexation of sepiapterin (SP), the natural precursor of the natural essential cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin, that displays mild water-solubility and short biological half-life, with the hydrophobic triacetyl-β-cyclodextrin (TAβCD) to improve its encapsulation within methoxy-poly(ethylene-glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (mPEG-PCL) nanoparticles. First, TAβCD-SP complexes were produced by spray-drying of TAβCD/SP binary solutions by utilizing the Nano Spray Dryer B-90 HP. Then, dry powders were characterized by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and transmission and scanning electron microscopy (SEM and TEM, respectively) and compared to the complex components and physical mixtures (PMs). Next, SP was encapsulated within methoxy-poly(ethylene-glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (mPEG-PCL) nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation of a SP/TAβCD complex/mPEG-PCL solution. In addition to complex nanoencapsulation, we assessed encapsulation of pure SP by nanoprecipitation with an intermediate step, which comprised the co-drying of SP, TAβCD and mPEG-PCL copolymer solution in organic solvent; this step aimed to promote the formation of molecular interactions between SP, TAβCD and the PCL blocks in the copolymer. SP-loaded mPEG-PCL nanoparticles were characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and SEM. Nanoparticles with size of 74-75 nm and small polydispersity index (PDI <0.1) were obtained when SP-TAβCD equimolar spray-dried complex was used for nanoencapsulation, and SEM analysis indicated the absence of free SP crystals. Moreover, the encapsulation efficiency (%EE) and drug loading (DL) were 85% and 2.6%, respectively, as opposed to those achieved with pure SP encapsulation (14% and 0.6%, respectively). Overall, our results confirm that spray-drying of SP/TAβCD solutions at the appropriate molar ratio leads to the hydrophobization of the relatively hydrophilic SP molecule, enabling its encapsulation within mPEG-PCL nanoparticles.