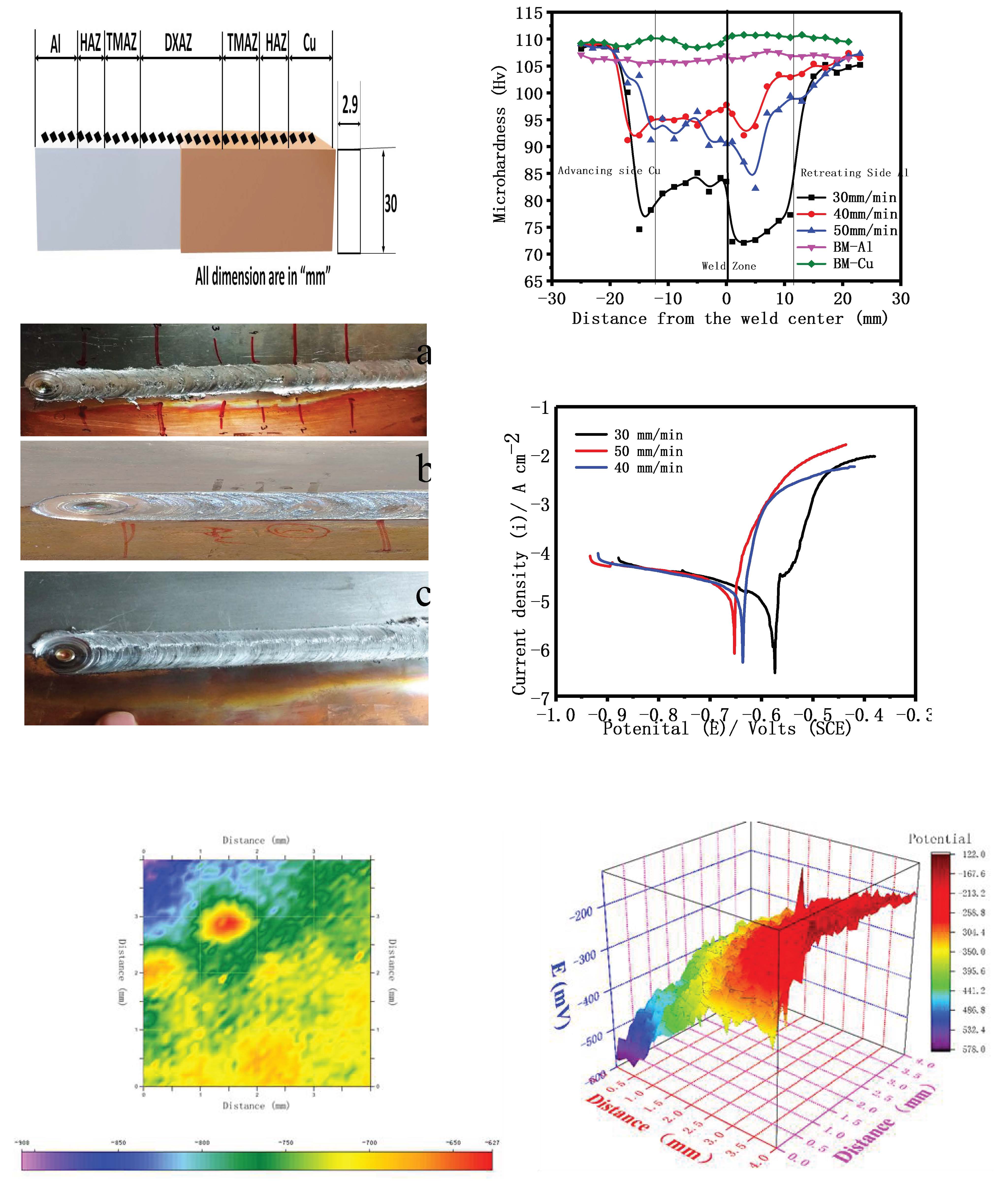
The aim of this work is to assess the influence of Friction Stir Welding (FSW), process parameters, optimized tool traveling speed, and corrosion resistance of the 0.95 Mg-Al-alloy and pure copper weldment. Samples of aluminum-copper with and without deformation were characterized to investigate the metallurgical effects created during the welding deformation process. Effect of process parameters on microstructure and corrosion rate have been investigated for all the samples. All the electrochemical and polarization tests were done in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Scanning Kelvin Probe (SKP) was done to detect the localized corrosion on the surface. Optical micrography observation indicated that the primary α-Al phase, which was formed during solidification can effectively limit the growth of Cu9Al4 phase. Finer acicular α-Al precipitates were observed in CuAl matrix during joining process that tends to coarser with the increase in tools travel speed. The electrochemical and polarization results showed that among all the tool travelling speed the specimen joined at tool travelling speed of 40 mm/min shows the best non-corrosive property.