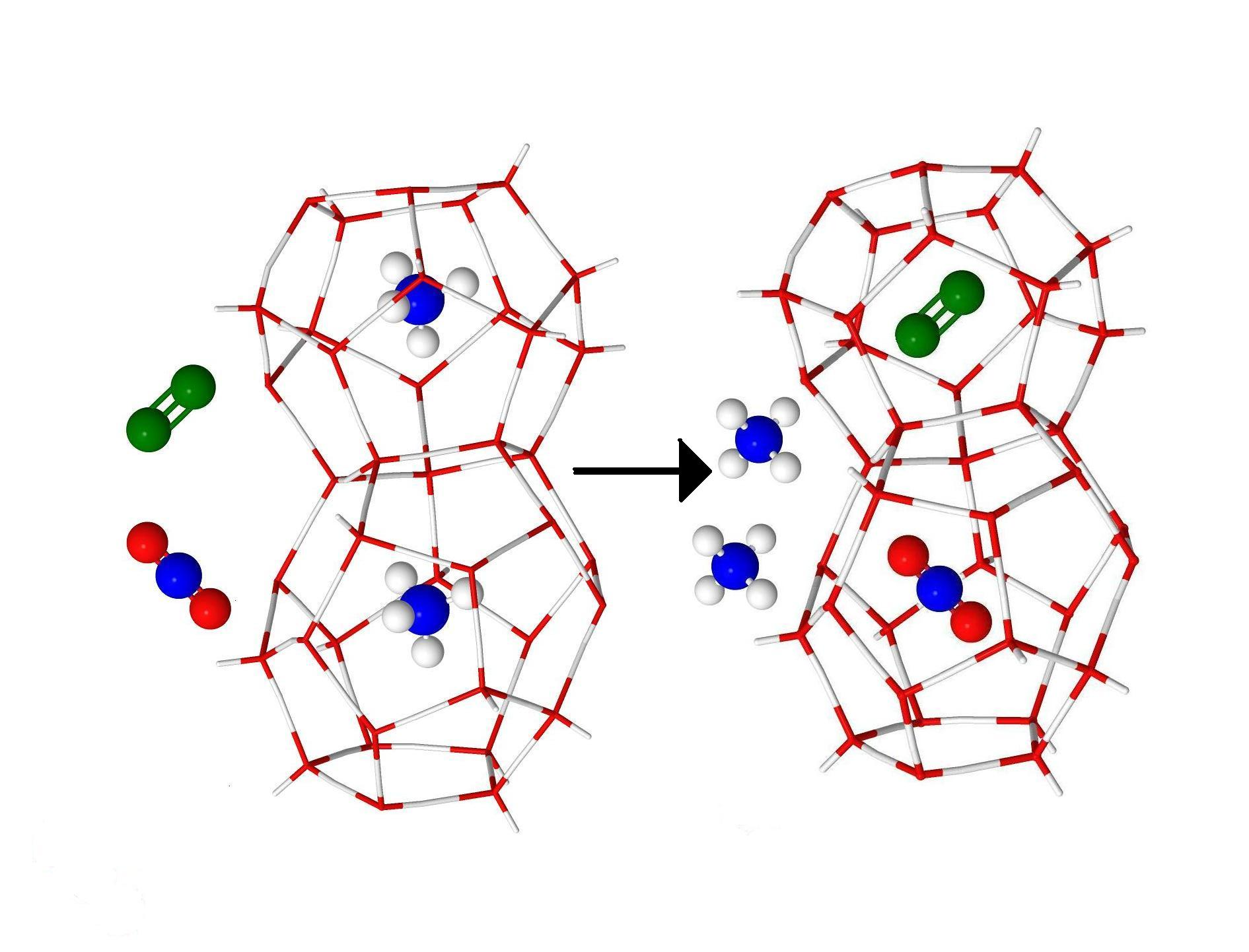
In this contribution, a method based on a solid solution theory of clathrate hydrate for multiple cage occupancy, host lattice relaxation and guest-guest interactions has been presented to estimate hydrate formation conditions of binary and ternary gas mixtures. We have performed molecular modeling of structure, guest distribution, and hydrate formation conditions for the CO2 + CH4, and CO2 + CH4 + N2 gas hydrates. In all considered systems with and without N2, at high and medium content of CO2 in the gas phase we have found that CO2 is more favorable to occupy clathrate hydrate cavities than CH4 or N2. Addition of N2 to the gas phase increases ratio concentration CO2 in compressing with concentration CH4 in clathrate hydrates and makes gas replacement more effective. The mole fractions of CO2 in CO2 + CH4 + N2 gas hydrate rapidly increases with the growth of its content in the gas phase. And the formation pressure of CO2 + CH4 + N2 gas hydrate rises in comparison with the formation pressure of CO2 + CH4 gas hydrate. Obtained results agree with the known experimental data for simple CH4, CO2 gas hydrates and mixed CO2 + CH4 gas hydrate.