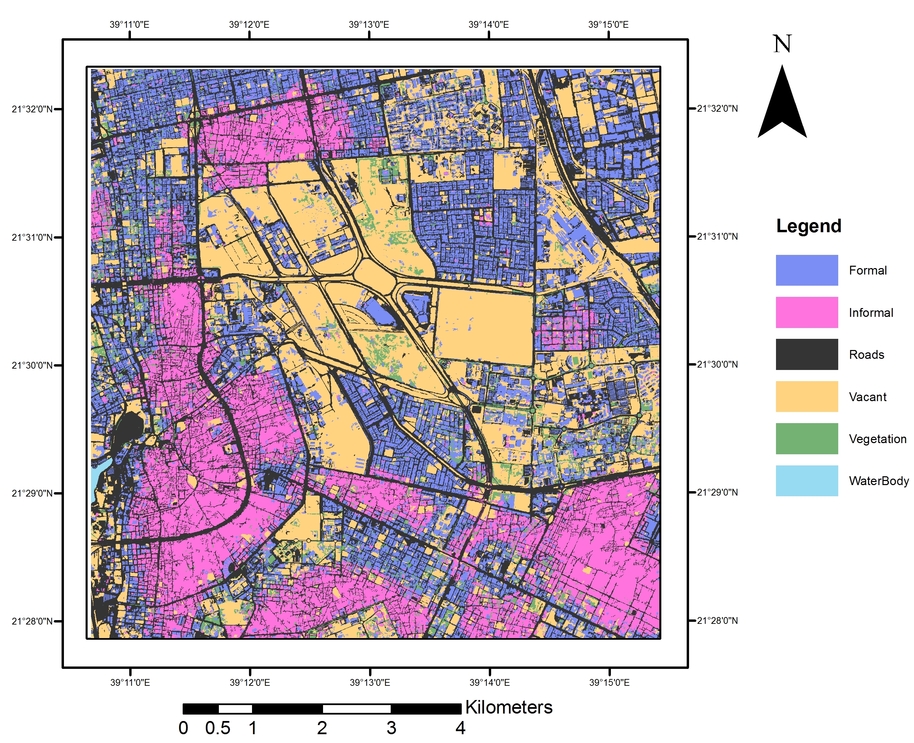
The identification of informal settlements in urban areas is an important step in developing and implementing pro-poor urban policies. Understanding when, where and who lives inside informal settlements is critical to efforts to improve their resilience. This study aims to analyse the capability of machine-learning (ML) methods to map informal areas in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, using very-high-resolution (VHR) imagery and terrain data. Fourteen indicators of settlement characteristics were derived and mapped using an object-based ML approach and VHR imagery. These indicators were categorised according to three different spatial levels: environ, settlement and object. The most useful indicators for prediction were found to be density and texture measures, (with random forest (RF) relative importance measures of over 25% and 23% respectively). The success of this approach was evaluated using a small, fully independent validation dataset. Informal areas were mapped with an overall accuracy of 91%. Object-based ML as a hybrid approach performed better (8%) than object-based image analysis alone due to its ability to encompass all available geospatial levels.