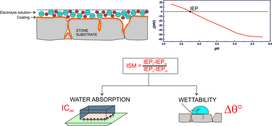
Protective coatings, in recent years also from nanocomposite formulations, are commonly applied onto architectural stone and stone artefacts, mainly to prevent absorption into the porous stone structure of condensed water and dissolved atmospheric pollutants. While standard protocols are available to assess a coating’s performance, understanding the response of the coating-stone system is a complex task, due to the interplay of various factors determining the overall behaviour. Characterization techniques allowing to correlate the extent and nature of surface modification upon treatment with the most relevant physical properties (i.e water absorption and surface wettability) are thus of great interest. Electrokinetic analysis based on streaming current measurements, thanks to its sensitivity towards even minor changes in the surface chemical composition, may fulfil such requirement. Indeed, by involving the interaction with a testing aqueous electrolyte solution, this technique allows to probe not only the outer surface but also the outermost layer of the pore network, which plays a crucial role in the interaction of the stone with condensed atmospheric water. In this work a correlation was found between the extent of surface modification, as determined by streaming current measurements, surface wettability and capillary water absorption of 6 coating-lithotype combinations (3 lithotypes and 2 nanocomposites).