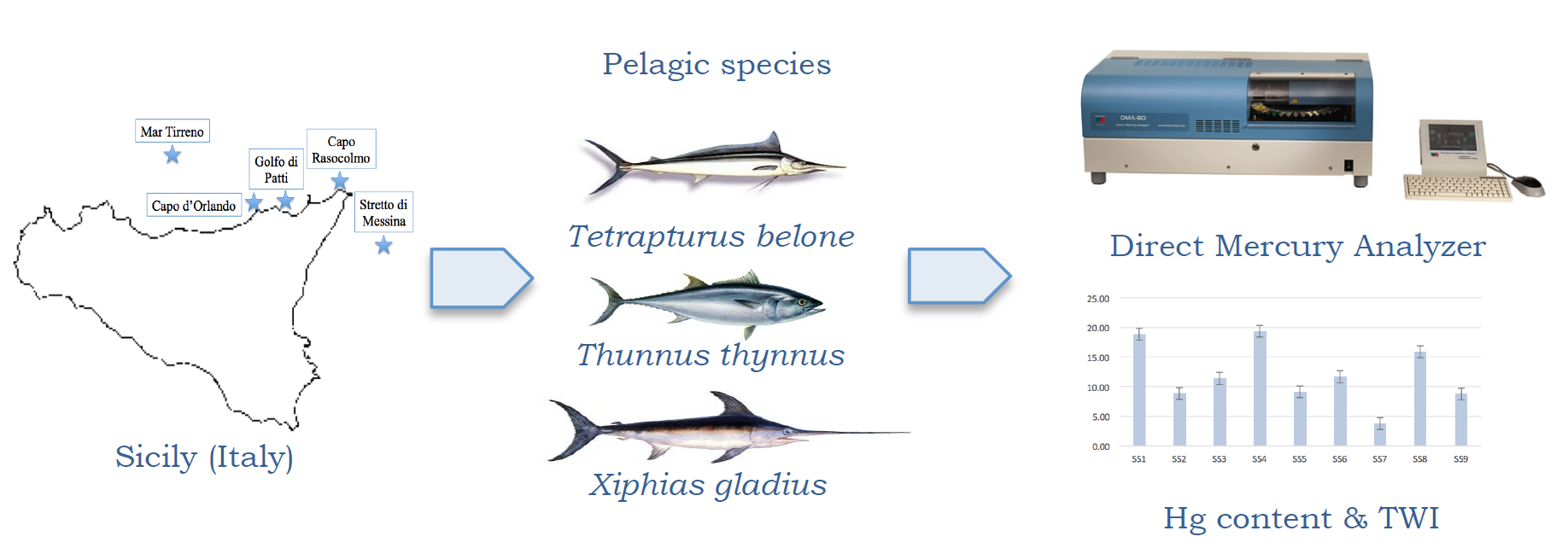
Mercury (Hg) fish and seafood contamination is a global concern and needs worldwide sea investigations in order to protect consumers. The aim of this study was to investigate the Hg concentration by means of a rapid and simple analytical technique with direct Mercury Analyzer (DMA-80) in pelagic fish species, Tetrapturus belone (spearfish), Thunnus thynnus (tuna) and Xiphias gladius (swordfish) caught in the Mediterranean Sea. Hg contents were evaluated also in Salmo salar (salmon) as pelagic fish not belonging to the Mediterranean area. The results obtained were variable ranging between 0,015-2,562 mg kg-1 for T. thynnus specie, 0,477-3,182 mg kg-1 for X. gladius, 0,434-1,730 mg kg-1 for T. belone and 0,004-0,019 mg kg-1 for S. salar, respectively. The total Hg tolerable weekly intake (TWI) and % tolerable weekly intake (TWI%) values according to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) were calculated. The results highlighted that the pelagic species caught in the Mediterranean Sea should be constantly monitored due to their high Hg contents as well as their TWI and TWI% with respect to S. salar samples.