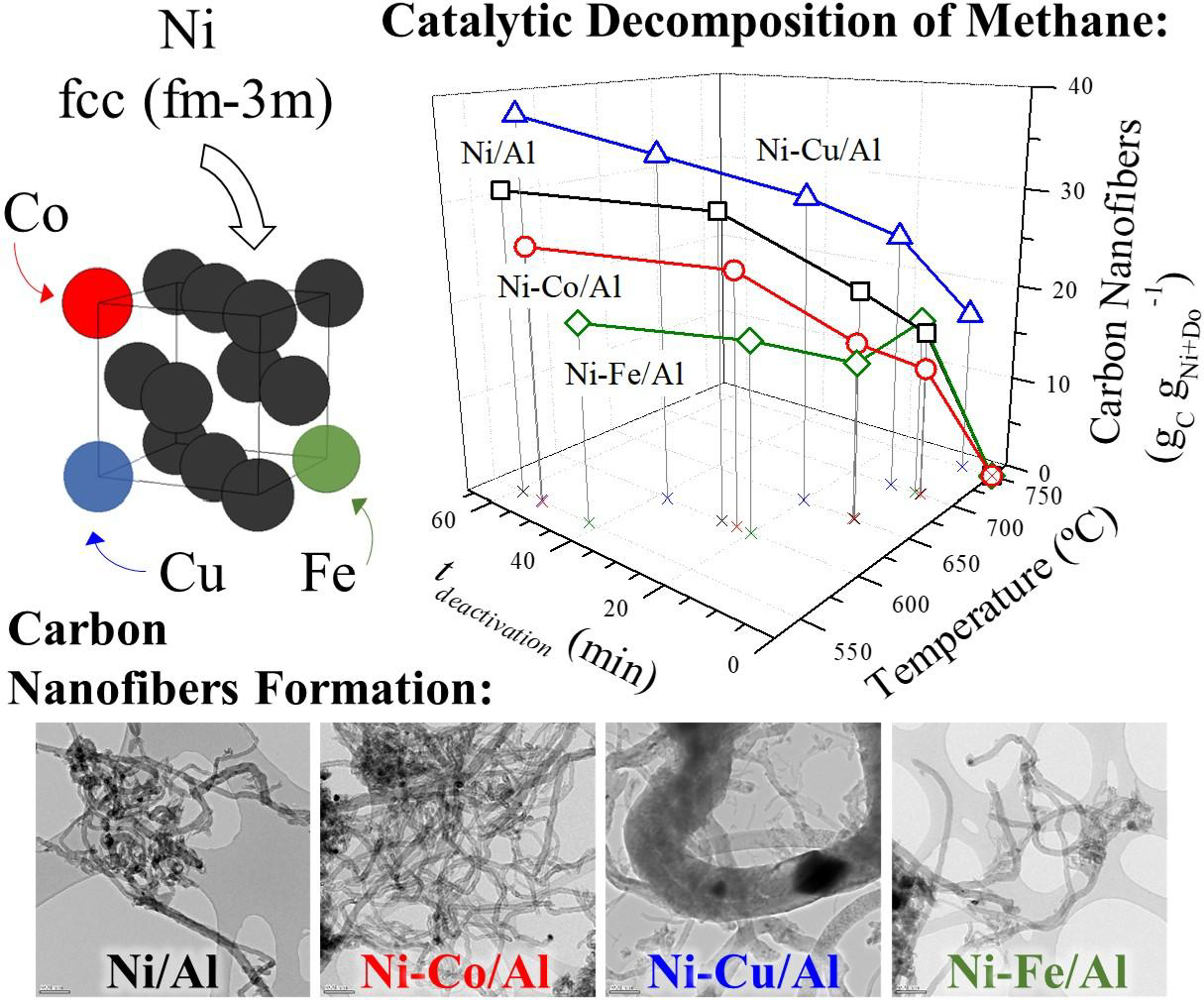
The catalytic decomposition of methane (CDM) process produces hydrogen in a single stage and avoids the CO2 emission thanks to the formation of high added value carbon nanofilaments as by-product. In this work, Ni monometallic and Ni-Co, Ni-Cu and Ni-Fe bimetallic catalysts are tested in the CDM reaction for the obtention of fishbone carbon nanofibers (CNF). Catalysts, in which Al2O3 is used as textural promoter in their formulation, are based on Ni as main active phase for the carbon formation and on Co, Cu or Fe as dopants in order to obtain alloys with an improved catalytic behaviour. Characterization of bimetallic catalysts showed the formation of particles of Ni alloys with a bimodal size distribution. For the doping content studied (5 mol. %), only Cu formed an alloy with a lattice constant high enough to be able to favor the carbon diffusion through the catalytic particle against surface diffusion, resulting in higher carbon formations, longer activity times and activity at 750 °C, where Ni, Ni-Co and Ni-Fe catalysts were inactive. On the other hand, Fe also improved the undoped catalyst performance presenting a higher carbon formation at 700 °C and the obtention of narrow carbon nanofilaments from active Ni3Fe crystallites.