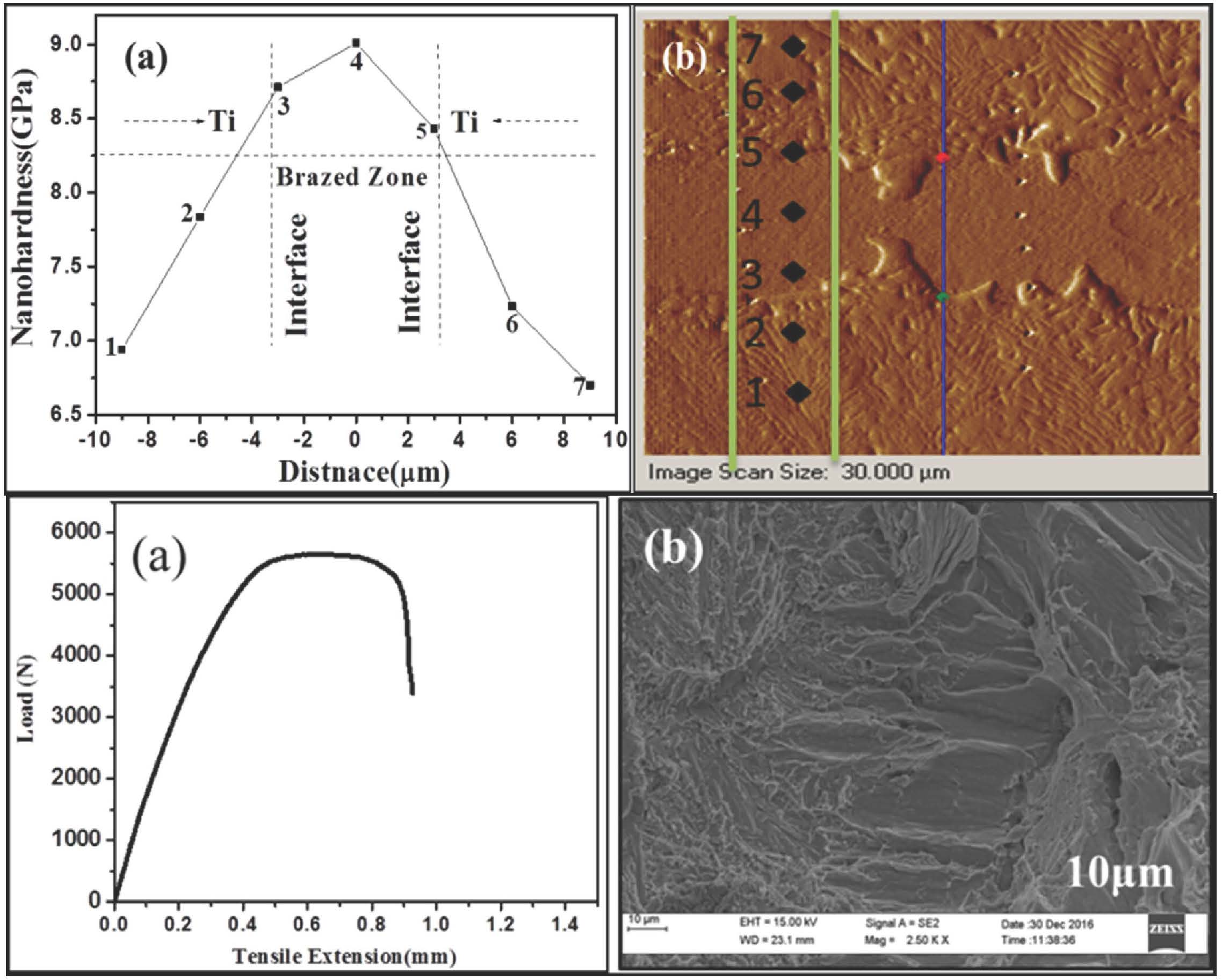
The developed microstructure features a long with mechanical properties in vacuum brazing of commercially pure Ti-alloy using Ti20Zr20Cu60-x-Nix (x=10, 20, 30, 40 and 50) metallic filler. Brazing temperatures and holding times employed in this study were 1240-1279 K (967-1006oC) for a period of 10 min, respectively. The mechanical properties of brazed joints were evaluated by nanoindention at a constant peak load of 5000 μN and tensile tests. The number of intermetallic phase, such as NiTi2, Ti2Cu, (Ti, Zr)2Cu, (Ti, Zr)2Ni, β(Ti, Zr), α-Ti and NiTi. The solid solution matrix have been identified at 1279 K out of these different regions the NiTi2 rich region had the highest nanohardness of 17 GPa, It is interesting to note that among five different glasses, the Ti20Zr20Cu10Ni50 has the highest yield strength of 17 GPa, which is mainly due to NiTi2 phase. Based on the tensile test results all cracks propagate along the brittle intermetallic compounds like NiTi2 in the reaction layer the reduction of the strength of the joints and fracture behaviour upon propagation of the crack, which shows the morphological cleavage including facets characteristics.