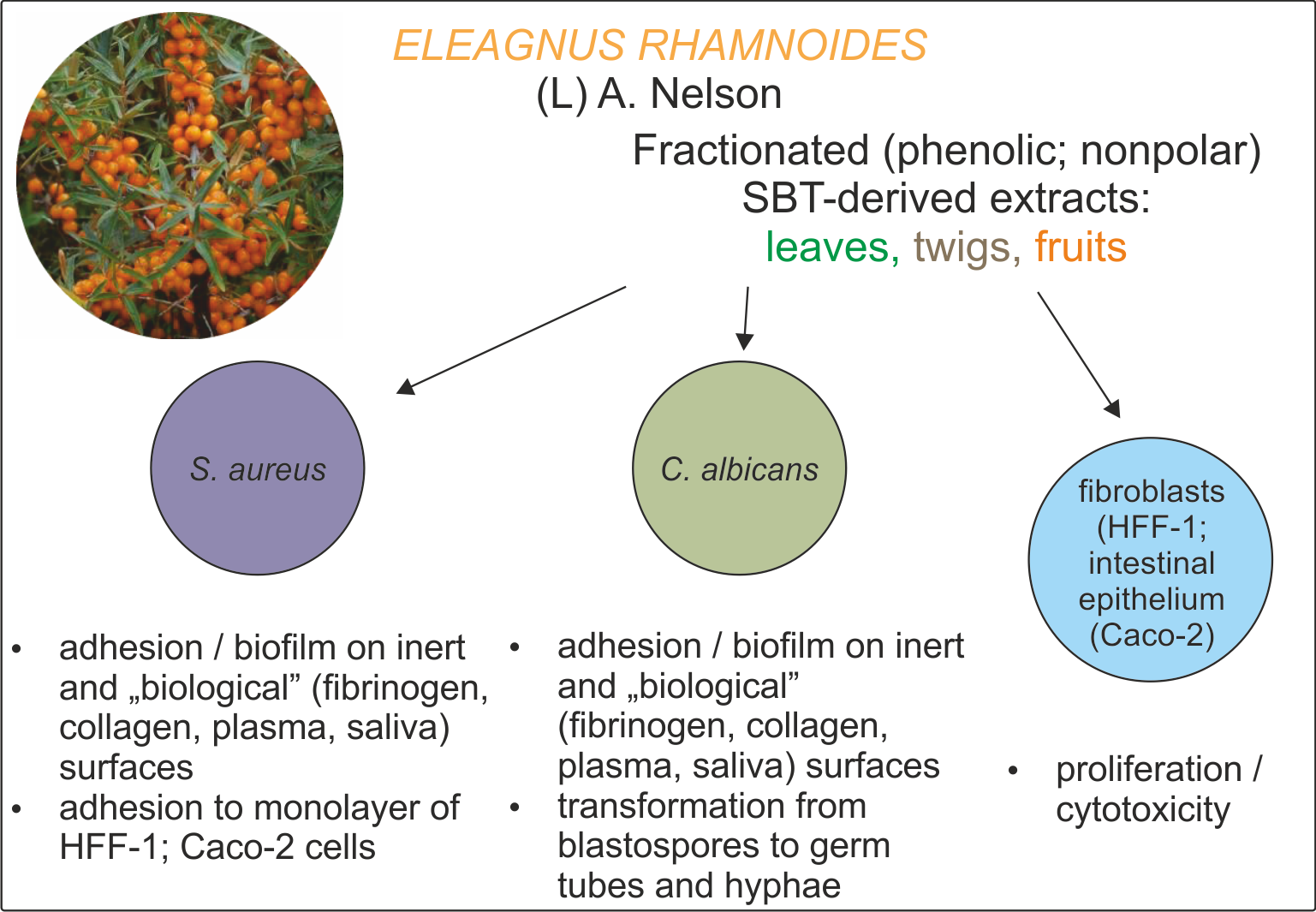
Butanol extracts from leaves, twigs and fruits of Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson (sea buckthorn, SBT) were fractionated into phenolic and non-polar lipid components. Their chemical composition was analyzed using the Thermo Ultimate 3000RS chromatographic system, equipped with a diode array detector, a corona-charged aerosol detector, and coupled with a (Q-TOF) mass spectrometer. Assuming that an effect on natural microbiotaand host epithelial cells needs to be assessed, regardless of the purpose of using SBT formulations in vivo, the MIC/MBC/MFC of the fractions and reference phytocompounds were screened involving 17 species of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Candida species. The impact of the fractions (subMIC) on the important in vivo persistence properties of S. aureus and C. albicans strains was evaluated. Tests for adhesion and biofilm formation on an abiotic surface and the surfaces conditioned with fibrinogen, collagen, plasma or artificial saliva showed the inhibitory activity of the fractions. The effects on FITC-labeled staphylococci adhesion to fibroblasts (HFF-1) and epithelial cells (Caco-2), and on fungal morphogenesis, indicated that SBT extracts have high anti-virulence potential. Cytotoxicity tests (MTT-reduction) on the standard fibroblast cell line showed variable biological safety of the fractions depending on their composition and concentration.