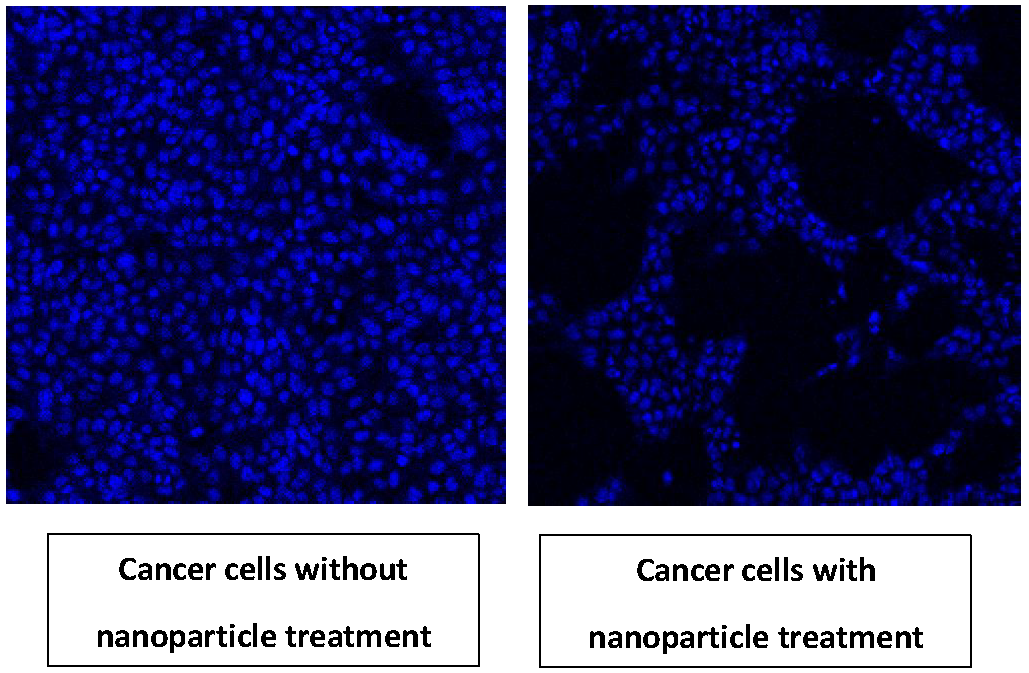
Breast cancer treatment mostly revolved around radiation therapy and surgical interventions, these treatments doesn’t provide satisfactory relief to the patients and carry unmanageable side-effects. Nanomaterials show promising results in treating cancer cells and have many advantages such as high biocompatibility, bioavailability and effective therapeutic capabilities. Interestingly, fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles have been used in many biological and diagnostic applications, but there is no report of use of fluorescent magnetic submicronic polymer nanoparticles (FMSP-nanoparticles) in the treatment of human breast cancer cells. In the present study, we have tested the effect FMSP-nanoparticles on human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). We have tested different concentrations (1.25µg/1mL, 12.5µg/mL and 50µg/1mL) of FMSP-nanoparticles in MCF-7 cells and evaluated the nanoparticles response morphometrically. Our results revealed that FMSP-nanoparticles produced a concentration dependent effect on the cancer cells, dose of 1.25µg/mL produced no significant effect on the cancer cell morphology and cell death, whereas dosages of 12.5µg/mL and 50µg/mL respectively showed significant nuclear augmentation, disintegration, chromatic condensation followed by dose dependent cell death. Our results demonstrate FMSP-nanoparticles have ability to induce cell death in MCF-7 cells and may be considered as a potential anti-cancer agent for breast cancer treatments.